|
John Feeney (filmmaker)
John Feeney (10 August 1922 – 6 December 2006) was a New Zealand-born director, photographer and writer. Early life Feeney was born in NgÄruawÄhia, near Hamilton, on New Zealand's North Island. He became fascinated by photography at a very early age and, at age 8, was given his first camera which, for the rest of his life, he would refer to as his 'magic lantern'. While attending Victoria University in Wellington, he entered the Royal New Zealand Naval Volunteer Reserve to do his compulsory service but, with conscription during WWII, was transferred into the Royal New Zealand Navy. He took part in the D-Day landings of 1944 and, a year later, was discharged with the rank of Lieutenant. He returned to New Zealand, where he took the job of research assistant with New Zealand's War History Branch, which was working on its 38-volume ''Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939â45''. That experience led him to be hired, in 1947, by the National Film Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NgÄruawÄhia
NgÄruawÄhia () is a town in the Waikato region of the North Island of New Zealand. It is located north-west of Hamilton at the confluence of the Waikato and WaipÄ Rivers, adjacent to the Hakarimata Range. NgÄruawÄhia is in the Hamilton Urban Area, the fourth largest urban area in New Zealand. The location was once considered as a potential capital of New Zealand. Demographics NgÄaruawÄhia covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. NgÄruawÄhia had slightly smaller boundaries in the 2018 Census, covering . It had a population of 6,621, an increase of 1,257 people (23.4%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 1,287 people (24.1%) since the 2006 census. There were 1,962 households, comprising 3,234 males and 3,384 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.96 males per female, with 1,914 people (28.9%) aged under 15 years, 1,434 (21.7%) aged 15 to 29, 2,661 (40.2%) aged 30 to 64, and 606 (9.2%) aged 65 or older. Ethniciti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit
Inuit (; iu, áááᦠ'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and Alaska. Inuit languages are part of the EskimoâAleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut. Inuit live throughout most of Northern Canada in the territory of Nunavut, Nunavik in the northern third of Quebec, Nunatsiavut and NunatuKavut in Labrador, and in various parts of the Northwest Territories, particularly around the Arctic Ocean, in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. With the exception of NunatuKavut, these areas are known, primarily by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, as Inuit Nunangat. In Canada, sections 25 and 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982 classify Inuit as a distinctive group of Aboriginal Canadians wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CinemaScope
CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by Spyros P. Skouras, the president of 20th Century Fox, marked the beginning of the modern anamorphic format in both principal 2.55:1, almost twice as wide as the previously common Academy format's 1.37:1 ratio. Although the technology behind the CinemaScope lens system was made obsolete by later developments, primarily advanced by Panavision, CinemaScope's anamorphic format has continued to this day. In film-industry jargon, the shortened form, 'Scope, is still widely used by both filmmakers and projectionists, although today it generally refers to any 2.35:1, 2.39:1, 2.40:1, or 2.55:1 presentation or, sometimes, the use of anamorphic lensing or projection in general. Bausch & Lomb won a 1954 Oscar for its development of the CinemaScope l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharwat Okasha
Tharwat Okasha (Also spelt Sarwat Okasha, ar, ثرÙت عÙاشة; 1921â27 February 2012) was an Egyptian writer, translator and influential minister of culture during the Nasserite era, and is known as the "founder of Egypt's cultural institutions." Biography Tharwat Okasha was an army officer involved in the Free Officers Movement, along with former president Nasser and his comrades, which toppled King Farouk of Egypt from his crown in what is known as the 23 July Revolution of 1952. As a child of an aristocratic family, Okasha received a good education, read books in foreign languages, and learned music very early on in his home. This background made him the most cultured and enlightened officer among his group of army officers. Okasha received his PhD in literature from Sorbonne in the 1960s and worked as visiting scholar at the College De France A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Culture (Egypt)
The Ministry of Culture of Egypt is a Cabinet of Egypt, ministry responsible for maintaining and promoting the culture of Egypt. The current minister is Ines Abdel-Dayem, former chairperson of the Cairo Opera and one of six women in the Egyptian Cabinet. History and structure Until 1958, the ministry of national guidance dealt with the cultural affairs. The ministry was established by President of Egypt, President Gamal Abdel Nasser in 1958 under the name of the ministry of culture and national guidance. The French model was adopted by the establishment. Subsidiaries * Supreme Council of Culture * The General Egyptian Book Authority * National Library and Archives * General Authority for Cultural Palaces * General Authority for Books and National archives ( Dar elkotob ) * Cairo Opera House * General Authority of the National Agency for Urban Harmony * Egyptian Arts Academy * Department of Applied Arts * The Fine Arts Sector * www.cdf.gov.eg/, Cultural Development Fund * The Book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or more strictly, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC, whose heirs ruled most of Nubia for the next 400 years. Nubia was home to several empires, most prominently the Kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in the eighth century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its 25th Dynasty (to be replaced a century later by the native Egyptian 26th Dynasty). From the 3rd century BC to 3rd century AD, northern Nubia would be invaded and annexed to Egypt, ruled by the Greeks and Romans. This territory would be known in the Greco-Roman world as Dodekasc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Ãman DawÅ« is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the List of rivers by length, longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Erit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of The Moon (Africa)
250px, ''Jibhel Kumri'' or Mountains of the Moon as conceived in 1819 Mountains of the Moon (Latin: ''Montes Lunae''; ar, جب٠اÙÙ٠ر, ' or ''Jibbel el Kumri'') is an ancient term referring to a legendary mountain or mountain range in east Africa at the source of the Nile River. Various identifications have been made in modern times, the Rwenzori Mountains of Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo being the most celebrated. Ancient testimony People of the ancient world were long curious about the source of the Nile, especially Ancient Greek geographers. A number of expeditions up the Nile failed to find the source. Eventually, a merchant named Diogenes reported that he had traveled inland from Rhapta in East Africa for twenty-five days and had found the source of the Nile. He reported that it flowed from a group of massive mountains into a series of large lakes. He reported the natives called this range the Mountains of the Moon because of their snowcapped whiten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, áááᦠ, ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' and the ''Nunavut Land Claims Agreement, Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act'', which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the territorial evolution of Canada, first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland was admitted in 1949. Nunavut comprises a major portion of Northern Canada and most of the Arctic Archipelago. Its vast territory makes it the list of the largest country subdivisions by area, fifth-largest country subdivision in the world, as well as North America's second-largest (after Greenland). The capital Iqaluit (formerly Frobisher Bay), on Baffin Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit Circumpolar Council
The Inuit Circumpolar Council (ICC) ( kl, Inuit Issittormiut Siunnersuisooqatigiiffiat), formerly Inuit Circumpolar Conference, is a multinational non-governmental organization (NGO) and Indigenous Peoples' Organization (IPO) representing the 180,000 Inuit, Yupik, and Chukchi peoples (sometimes referred to as Eskimo) people living in Alaska (United States), Canada, Greenland (Kingdom of Denmark), and Chukotka (Russia). ICC was ECOSOC-accredited and was granted special consultative status (category II) at the UN in 1983. The Conference, which first met in June 1977 in Barrow, Alaska (now Utqiaġvik), initially represented Native Peoples from Canada, Alaska and Greenland. In 1980 the charter and by-laws of ICC were adopted. The Conference agreed to replace the term Eskimo with the term Inuit. This has not however met with widespread acceptance by some groups, most pre-eminently the Yupik (see Background section below). The goals of the Conference are to strengthen ties between A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BAFTA Award For Best Short Film
This page lists the winners and nominees for the BAFTA Award for Best British Short Film for each year. The British Academy of Film and Television Arts (BAFTA), is a British organisation that hosts annual awards shows for film, television, children's film and television, and interactive media. Since 1960, selected films have been awarded with the BAFTA award for Best Short Film at an annual ceremony. In the following lists, the titles and names in bold with a dark grey background are the winners and recipients respectively; those not in bold are the nominees. The years given are those in which the films under consideration were released, not the year of the ceremony, which always takes place the following year. Winners and nominees 1950s ; Best Short Film 1960s 1970s ; John Grierson Award (Short Film) ; Best Short Factual Film ; Best Short Fictional Film ; Best Short Film 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s ; Best British Short Film 2020s See also * Academy Award f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenojuak Ashevak
Kenojuak Ashevak, (Inuktitut: á¿ááááªáá áá¯áá, Qinnuajuaq Aasivak), (October 3, 1927 – January 8, 2013) is celebrated as a leading figure of modern Inuit art. Early life and family Kenojuak Ashevak was born in an igloo in an Inuit camp, Ikirasaq, at the southern coast of Baffin Island. Her father, Ushuakjuk, an Inuit hunter and fur trader, and her mother, Silaqqi, named Kenojuak after Silaqqi's deceased father. According to this Inuit naming tradition, the love and respect that had been accorded to her during her lifetime would now pass on to their daughter., Native American Rhymes, Rhodes Educational Publications, 2005. Accessed 8 January 2013. Kenojuak also had a brother and a sister. Kenojuak remembered Ushuakjuk as "a kind and benevolent man." Her father, a respected ''angakkuq'' (shaman), "had more knowledge than average mortals, and he would help all the ." According to Kenojuak, her father believed he could predict weather, predict good hunting se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
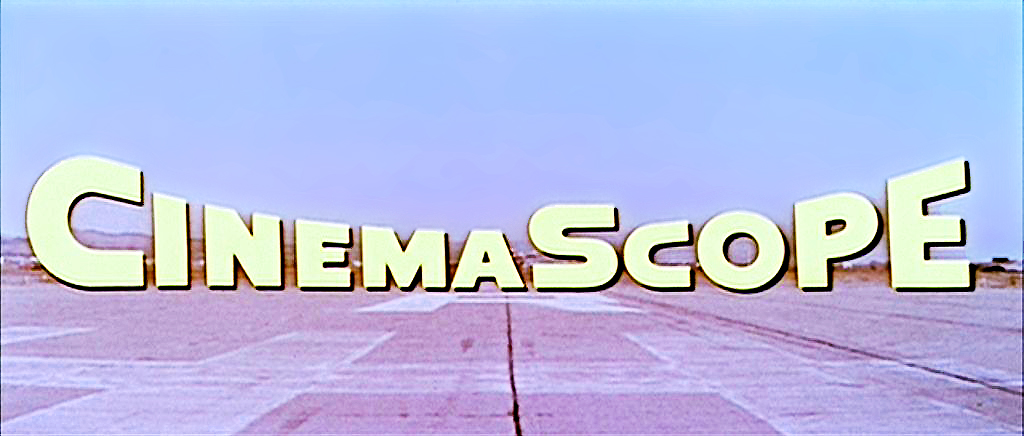




.jpg)