|
Julius Richard Petri
Julius Richard Petri (31 May 185220 December 1921) was a German microbiologist who is generally credited with inventing the device known as the Petri dish, which is named after him, while working as assistant to bacteriologist Robert Koch. Life and career Petri was born in the town of Barmen (now a district of the city of Wuppertal), Germany, on 31 May 1852. He came from a distinguished family of scholars, and was the eldest son of Philipp Ulrich Martin Petri (18171864), a professor in Berlin, and Louise Petri. Petri's grandfather, Viktor Friedrich Leberecht Petri (1782-1857), was also a scholar, being both a director and professor at the Collegium Carolinum in Braunschweig, Germany. Petri first studied medicine at the Kaiser Wilhelm Academy for Military Physicians (18711875) and received his medical degree in 1876. He continued his studies at the Charité Hospital in Berlin where his thesis on the chemistry on protein urine tests earned him his doctorate. He was on active du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barmen
Barmen is a former industrial metropolis of the region of Bergisches Land, Germany, which merged with four other towns in 1929 to form the city of Wuppertal. Barmen, together with the neighbouring town of Elberfeld founded the first electric suspended monorail tramway system, the Schwebebahn ''floating tram''. History Barmen was a pioneering centre for both the early industrial revolution on the European mainland, and for the socialist movement and its theory. It was the location of one of the first concentration camps in Nazi Germany, KZ Wuppertal-Barmen, later better known as Kemna concentration camp. Oberbarmen (Upper Barmen) is the eastern part of Barmen, and Unterbarmen (Lower Barmen) the western part. One of its claims to fame is the fact that Friedrich Engels, co-author of ''The Communist Manifesto'', was born in Barmen. Another of its claims is the fact that Bayer AG was founded there by Friedrich Bayer and master dyer Johann Friedrich Weskott with the express pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori (''Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" (''Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar is a mixture of two components, the linear polysaccharide agarose and a heterogeneous mixture of smaller molecules called agaropectin. It forms the supporting structure in the cell walls of certain species of algae and is released on boiling. These algae are known as agarophytes, belonging to the Rhodophyta (red algae) phylum. The processing of food-grade agar removes the agaropectin, and the commercial product is essentially pure agarose. Agar has been used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture media for microbiological work. Agar can be used as a laxative; an appetite suppressant; a vegan substitute for gelatin; a thickener for soups; in fruit preserves, ice cream, and other desser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book ''The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as cad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
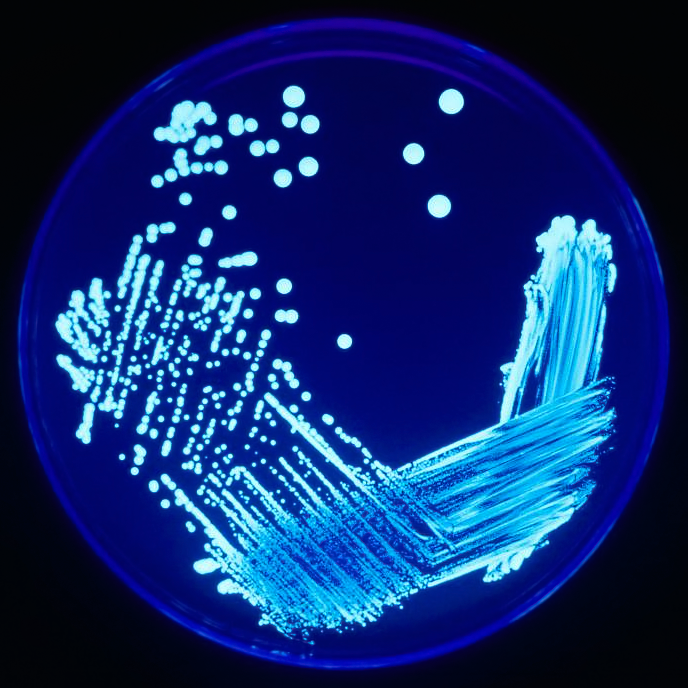
Streaking (microbiology)
In microbiology, streaking is a technique used to isolate a pure strain from a single species of microorganism, often bacteria. Samples can then be taken from the resulting colonies and a microbiological culture can be grown on a new plate so that the organism can be identified, studied, or tested. The modern streak plate method has progressed from the efforts of Robert Koch and other microbiologists to obtain microbiological cultures of bacteria in order to study them. The dilution or isolation by streaking method was first developed by Loeffler and Gaffky in Koch's laboratory, which involves the dilution of bacteria by systematically streaking them over the exterior of the agar in a Petri dish to obtain isolated colonies which will then grow into quantity of cells, or isolated colonies. If the agar surface grows microorganisms which are all genetically same, the culture is then considered as a microbiological culture. Technique Streaking is rapid and ideally a simple process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antisep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular weight) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology, and parasitology. Eukaryotic microorganisms possess membrane-bound organelles and include fungi and protists, whereas prokaryotic organisms—all of which are microorganisms—are conventionally classified as lacking membrane-bound organelles and include Bacteria and Archaea. Microbiologists traditionally relied on culture, staining, and microscopy. However, less than 1% of the microorganisms present in common environments can be cultured in isolation using current means. Microbiologists often rely on molecular biology tools such as DNA sequence based identification, for example the 16S rRNA gene sequence used for bacteria identification. Viruses have been variably classified as organisms, as they have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petri Dishes
A Petri dish (alternatively known as a Petri plate or cell-culture dish) is a shallow transparent lidded dish that biologists use to hold growth medium in which cells can be cultured,R. C. Dubey (2014): ''A Textbook Of Biotechnology For Class-XI'', 4th edition, p. 469. originally, cells of bacteria, fungi and small mosses. The container is named after its inventor, German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri. It is the most common type of culture plate. The Petri dish is one of the most common items in biology laboratories and has entered popular culture. The term is sometimes written in lower case, especially in non-technical literature. What was later called Petri dish was originally developed by German physician Robert Koch in his private laboratory in 1881, as a precursor method. Petri, as assistant to Koch, at Berlin University made the final modifications in 1887 as used today. Penicillin, the first antibiotic, was discovered in 1929 when Alexander Fleming noticed tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)