|
Judith Campisi
Judith Campisi is an American biochemist and cell biologist. She is a professor of biogerontology at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging. She is also a member of the SENS Research Foundation Advisory Board and an adviser at the Lifeboat Foundation. She is co-editor in chief of the ''Aging Journal,'' together with Mikhail Blagosklonny and David Sinclair, and founder of the pharmaceutical company Unity Biotechnology. She is listed in '' Who's Who in Gerontology''. She is widely known for her research on how senescent cells influence aging and cancer — in particular the Senescence Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP). Career Campisi got her B.A. in Chemistry in 1974 and Ph.D. in Biochemistry in 1979 from the State University of New York at Stony Brook and completed her postdoctoral training at the Harvard Medical School in 1982. She initially joined the Boston University Medical School, and moved onto the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory as a Senior Scientist in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogerontology
Biogerontology is the sub-field of gerontology concerned with the biological aging process, its evolutionary origins, and potential means to intervene in the process. The term "biogerontology" was coined by S. Rattan, and came in regular use with the start of the journaBIOGERONTOLOGYin 2000. It involves interdisciplinary research on the causes, effects, and mechanisms of biological aging. Biogerontologist Leonard Hayflick has said that the natural average lifespan for a human is around 92 years and, if humans do not invent new approaches to treat aging, they will be stuck with this lifespan. James Vaupel has predicted that life expectancy in industrialized countries will reach 100 for children born after the year 2000. Many surveyed biogerontologists have predicted life expectancies of more than three centuries for people born after the year 2100. Other scientists, more controversially, suggest the possibility of unlimited lifespans for those currently living. For example, Aubrey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), commonly referred to as the Berkeley Lab, is a United States Department of Energy National Labs, United States national laboratory that is owned by, and conducts scientific research on behalf of, the United States Department of Energy. Located in the Berkeley Hills, hills of Berkeley, California, the lab overlooks the campus of the University of California, Berkeley, and is managed by the University of California system. History 1931–1941 The laboratory was founded on August 26, 1931, by Ernest Lawrence, as the Radiation Laboratory of the University of California, Berkeley, associated with the Physics Department. It centered physics research around his new instrument, the cyclotron, a type of particle accelerator for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1939. Throughout the 1930s, Lawrence pushed to create larger and larger machines for physics research, courting private philanthropy, philanthropists for funding. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalloproteinase
A metalloproteinase, or metalloprotease, is any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal. An example is ADAM12 which plays a significant role in the fusion of muscle cells during embryo development, in a process known as myogenesis. Most metalloproteases require zinc, but some use cobalt. The metal ion is coordinated to the protein via three ligands. The ligands coordinating the metal ion can vary with histidine, glutamate, aspartate, lysine, and arginine. The fourth coordination position is taken up by a labile water molecule. Treatment with chelating agents such as EDTA leads to complete inactivation. EDTA is a metal chelator that removes zinc, which is essential for activity. They are also inhibited by the chelator orthophenanthroline. Classification There are two subgroups of metalloproteinases: * Exopeptidases, metalloexopeptidases ( EC number: 3.4.17). * Endopeptidases, metalloendopeptidases (3.4.24). Well known metalloendopeptidases include ADAM pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, the person may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after the menopause due to lower levels of estrogen, and after ' andropause' due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a number of diseases or treatments, including alcoholism, anorexia, hyperthyroidism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Initially they may occur only after exercise but can become constant over time. Other symptoms may include joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs; the knee and hip joints; and the joints of the neck and lower back. Joints on one side of the body are often more affected than those on the other. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are the families of protein kinases first discovered for their role in regulating the cell cycle. They are also involved in regulating transcription, mRNA processing, and the differentiation of nerve cells. They are present in all known eukaryotes, and their regulatory function in the cell cycle has been evolutionarily conserved. In fact, yeast cells can proliferate normally when their CDK gene has been replaced with the homologous human gene. CDKs are relatively small proteins, with molecular weights ranging from 34 to 40 kDa, and contain little more than the kinase domain. By definition, a CDK binds a regulatory protein called a cyclin. Without cyclin, CDK has little kinase activity; only the cyclin-CDK complex is an active kinase but its activity can be typically further modulated by phosphorylation and other binding proteins, like p27. CDKs phosphorylate their substrates on serines and threonines, so they are serine-threonine kinases. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
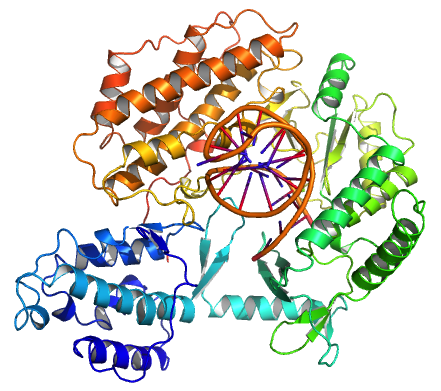
TP53
p53, also known as Tumor protein P53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thought to be, and often spoken of as, a single protein) are crucial in vertebrates, where they prevent cancer formation. As such, p53 has been described as "the guardian of the genome" because of its role in conserving stability by preventing genome mutation. Hence ''TP53'' ''italics'' are used to denote the ''TP53'' gene name and distinguish it from the protein it encodes is classified as a tumor suppressor gene. The name p53 was given in 1979 describing the apparent molecular mass; SDS-PAGE analysis indicates that it is a 53-kilodalton (kDa) protein. However, the actual mass of the full-length p53 protein (p53α) based on the sum of masses of the amino acid residues is only 43.7 kDa. This difference is due to the high number of proline residues in the protein, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.Kimball's Biology Pages. "Oncogenes" Free full text Most normal cells will undergo a programmed form of rapid cell death () when critical functions are altered and malfunctioning. Activated oncogenes can cause those cells designated for apoptosis to survive and proliferate instead. Most oncogenes began as proto-oncogenes: normal genes involved in cell growth and proliferation or inhibition of apoptosis. If, through mutation, normal genes promoting cellular growth are up-regulated (gain-of-function mutation), they will predisp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most eukaryotes. Telomeres protect the end of the chromosome from DNA damage or from fusion with neighbouring chromosomes. The fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' lacks telomerase, but instead uses retrotransposons to maintain telomeres. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase enzyme that carries its own RNA molecule (e.g., with the sequence 3′- CCC AA UCCC-5′ in ''Trypanosoma brucei'') which is used as a template when it elongates telomeres. Telomerase is active in gametes and most cancer cells, but is normally absent from, or at very low levels in, most somatic cells. History The existence of a compensatory mechanism for telomere shortening was first found by Soviet biologist Alexey Olovnikov in 1973, who also suggested the telomere hypothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
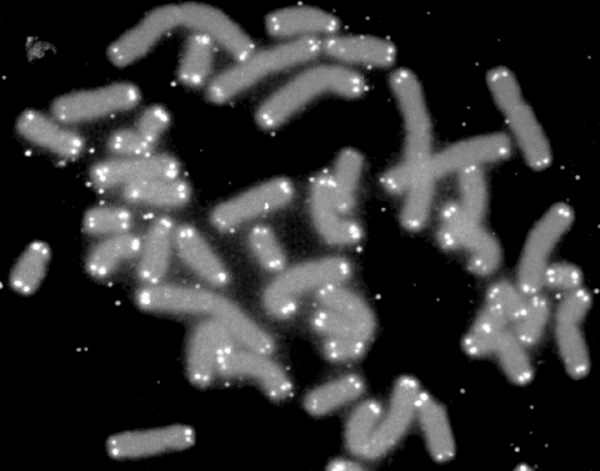
Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery In the early 1970s, Soviet theorist Alexei Olovnikov first recognized that chromosomes could not completely replicate their ends; this is known as the "end replication problem". Building on this, and accommodating Leonard Hayflick's idea of limited somatic cell division, Olovnikov suggested that DNA sequences are lost every time a cell replicates until the loss reaches a critical level, at which point cell division end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)