|
Joseph Daniel Schulman
Joseph Daniel Schulman (born 1941) is an American physician, medical researcher, and biomedical entrepreneur in the fields of genetic diseases and human reproduction. Life Schulman was born in 1941 in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from Harvard Medical School in 1966 and trained in pediatrics, genetics, and obstetrics and gynecology at Massachusetts General Hospital, the National Institutes of Health, and Cornell-New York Hospital Medical Center. Schulman worked at Cambridge University with Drs. Robert Geoffrey Edwards and Patrick Steptoe, contributing to the development of the first methods for successful human in-vitro fertilization (IVF). He is recognized as a pioneer and authority in the fields of fetal medicine, prenatal genetics, and IVF. Career In 1974, Schulman joined the staff of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development where he headed the Section on Human Biochemical Genetics. He founded and was first Director of the Interinstitute Program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, behind New York County (Manhattan). Brooklyn is also New York City's most populous borough,2010 Gazetteer for New York State . Retrieved September 18, 2016. with 2,736,074 residents in 2020. Named after the Dutch village of Breukelen, Brooklyn is located on the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics & IVF Institute
The Genetics & IVF Institute (GIVF) is an international provider of infertility and genetics services and products, and also engages in biomedical research in these fields. The Institute was founded in 1984 by Dr. Joseph D. Schulman and associates. GIVF headquarters are in Fairfax, VA, US, and its facilities include locations in Pennsylvania, Minnesota, California, and Texas in the United States, as well as in China, Mexico, and several other countries. Genetics & IVF Institute has been responsible for numerous key innovations to help couples have healthy babies and to improve the reproductive health of women. These include: First U.S. medical center to introduce non-surgical ultrasound guided egg retrieval (transvaginal oocyte retrieval) for IVF; achieved America's first frozen embryo twin birth; first American team to publicly report pregnancies using ICSI ( intracytoplasmic sperm injection); first to offer clinical laboratory testing for certain mutations in the BRCA1 and B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sperm
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromosomes, that normally develops into an embryo.) Sperm cells contribute approximately half of the nuclear genetic information to the diploid offspring (excluding, in most cases, mitochondrial DNA). In mammals, the sex of the offspring is determined by the sperm cell: a spermatozoon bearing an X chromosome will lead to a female (XX) offspring, while one bearing a Y chromosome will lead to a male (XY) offspring. Sperm cells were first observed in Antonie van Leeuwenhoek's laboratory in 1677. Mammalian spermatozoon structure, function, and size Humans The human sperm cell is the reproductive cell in males and will only survive in warm environments; once it leaves the male body the sperm's survival likelihood is reduced and it may die, thereby dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huntington Disease
Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is a neurodegenerative disease that is mostly inherited. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental abilities. A general lack of coordination and an unsteady gait often follow. It is also a basal ganglia disease causing a hyperkinetic movement disorder known as chorea. As the disease advances, uncoordinated, involuntary body movements of chorea become more apparent. Physical abilities gradually worsen until coordinated movement becomes difficult and the person is unable to talk. Mental abilities generally decline into dementia. The specific symptoms vary somewhat between people. Symptoms usually begin between 30 and 50 years of age but can start at any age. The disease may develop earlier in each successive generation. About eight percent of cases start before the age of 20 years, and are known as ''juvenile HD'', which typically present with the slow movement symptoms of Parkinson's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or through biochemical analysis to measure specific protein output. In a medical setting, genetic testing can be used to diagnose or rule out suspected genetic disorders, predict risks for specific conditions, or gain information that can be used to customize medical treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup. Genetic testing can also be used to determine biological relatives, such as a child's biological parentage (genetic mother and father) through DNA paternity testing, or be used to broadly predict an individual's ancestry. Genetic testing of plants and animals can be used for similar reasons as in humans (e.g. to assess relatedness/ancestry or predict/diagnose genetic disorders), to gain information used for selective breeding, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include sinus infections, poor growth, fatty stool, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms. Cystic fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. It is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies of the gene for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein. Those with a single working copy are carriers and otherwise mostly healthy. CFTR is involved in the production of sweat, digestive fluids, and mucus. When the CFTR is not functional, secretions which are usually thin instead become thick. The condition is diagnosed by a sweat test and genetic testing. Screening of infants at bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
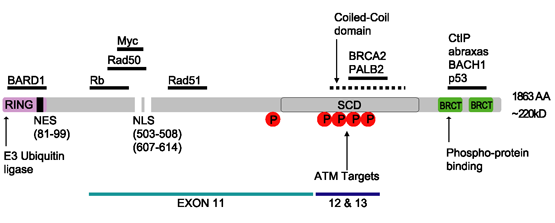
BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are a human gene and its protein product, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associated) are maintained by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. One alternative symbol, FANCD1, recognizes its association with the FANC protein complex. Orthologs, styled ''Brca2'' and Brca2, are common in other vertebrate species. May 2021 ''BRCA2'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (specifically, a caretaker gene), found in all humans; its protein, also called by the synonym breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein, is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA2'' and ''BRCA1'' are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double strand bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA1'' and '' BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a normal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenatal Diagnosis
Prenatal testing consists of prenatal screening and prenatal diagnosis, which are aspects of prenatal care that focus on detecting problems with the pregnancy as early as possible. These may be anatomic and physiologic problems with the health of the zygote, embryo, or fetus, either before gestation even starts (as in preimplantation genetic diagnosis) or as early in gestation as practicable. Screening can detect problems such as neural tube defects, chromosome abnormalities, and gene mutations that would lead to genetic disorders and birth defects, such as spina bifida, cleft palate, Down syndrome, Tay–Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and fragile X syndrome. Some tests are designed to discover problems which primarily affect the health of the mother, such as PAPP-A to detect pre-eclampsia or glucose tolerance tests to diagnose gestational diabetes. Screening can also detect anatomical defects such as hydrocephalus, anencephal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
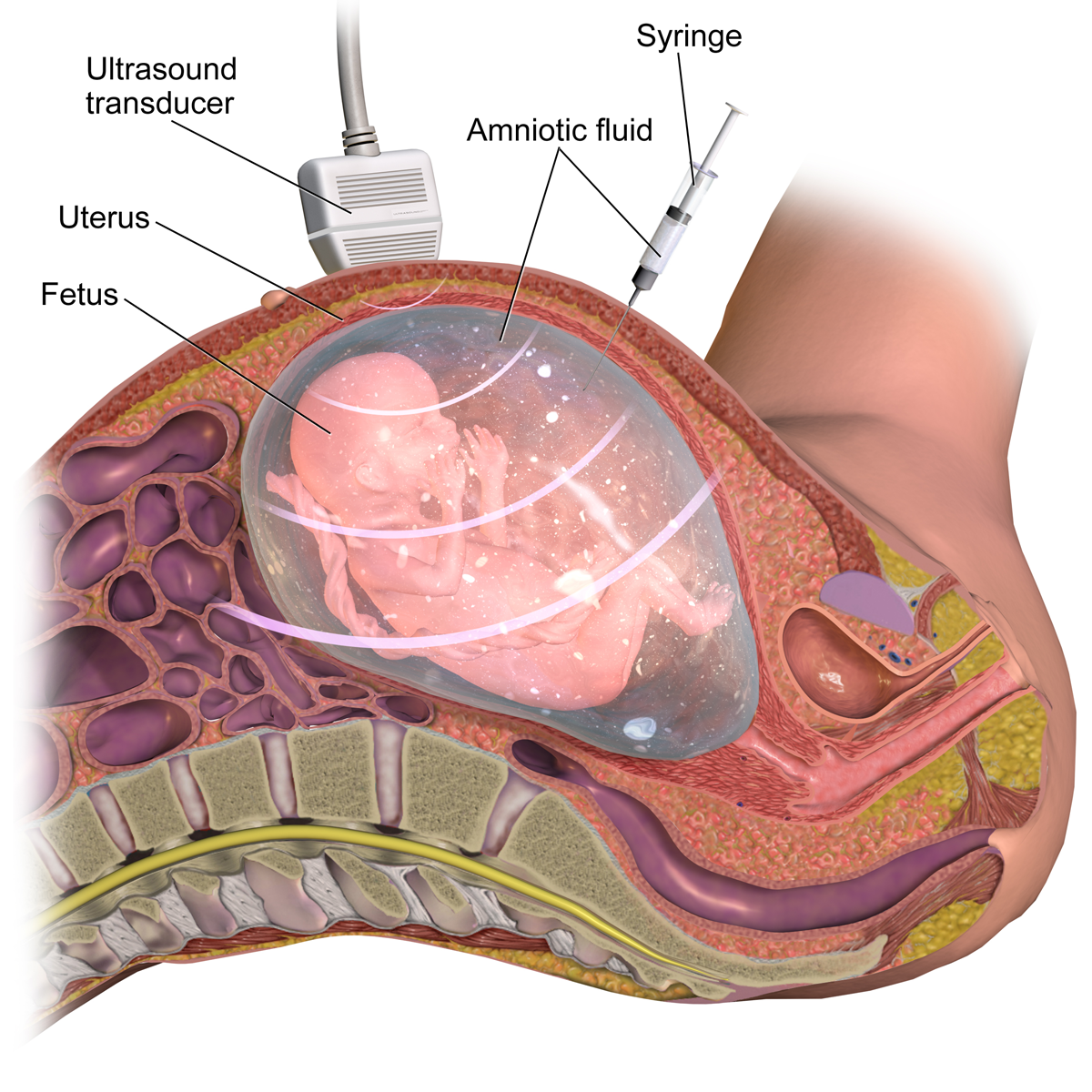
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is necessary to conclusively diagnose the majority of genetic disorders, with amniocentesis being the gold-standard procedure after 15 weeks' gestation. In this procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the abdomen of the pregnant woman. The needle punctures the amnion, which is the membrane that surrounds the developing fetus. The fluid within the amnion is called amniotic fluid, and because this fluid surrounds the developing fetus, it contains fetal cells. The amniotic fluid is sampled and analyzed via methods such as karyotyping and DNA analysis technology for genetic abnormalities. An amniocentesis is typically performed in the second trimester between the 15th and 20th week of gestation. Women who choose to have this test are prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorionic Villus Sampling
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), sometimes called "chorionic ''villous'' sampling" (as "villous" is the adjectival form of the word "villus"), is a form of prenatal diagnosis done to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It entails sampling of the chorionic villus (placental tissue) and testing it for chromosomal abnormalities, usually with FISH or PCR. CVS usually takes place at 10–12 weeks' gestation, earlier than amniocentesis or percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling. It is the preferred technique before 15 weeks. CVS was performed for the first time in Milan by Italian biologist Giuseppe Simoni, scientific director of Biocell Center, in 1983. Use as early as eight weeks in special circumstances has been described. It can be performed in a transcervical or transabdominal manner. Although this procedure is mostly associated with testing for Down syndrome, overall, CVS can detect more than 200 disorders. Indications Poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)