Prenatal diagnosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Prenatal testing consists of prenatal screening and prenatal diagnosis, which are aspects of
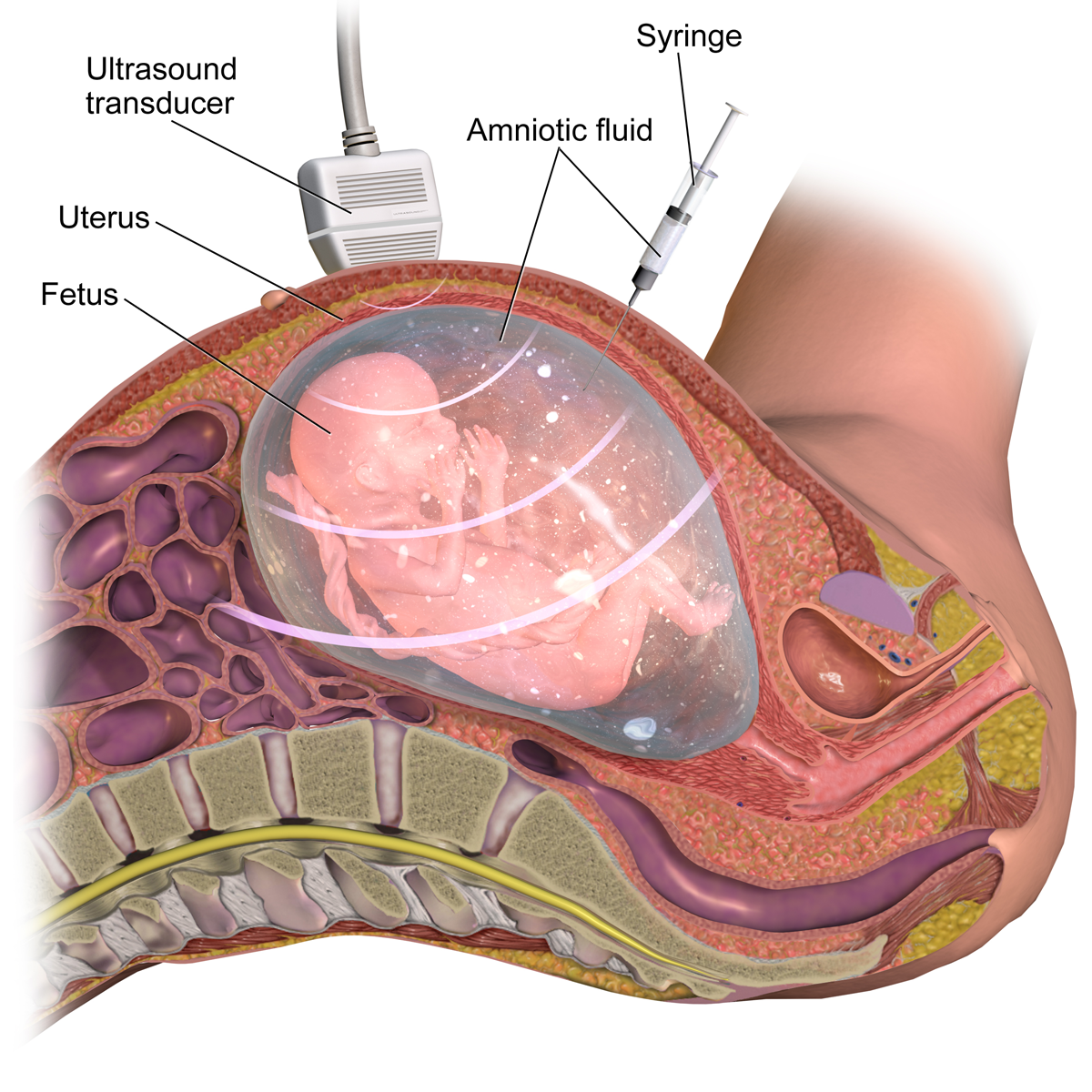 Diagnostic prenatal testing can be performed by
Diagnostic prenatal testing can be performed by
By Alfirevic Z, Mujezinovic F, Sundberg K at The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009 However, transcervical chorionic villus sampling carries a significantly higher risk, compared with a second-trimester amniocentesis, of total pregnancy loss ( Non-invasive techniques include examinations of the woman's womb through
Non-invasive techniques include examinations of the woman's womb through
cdph.ca.gov
Our Bodies Ourselves chapter on Prenatal Testing and Disability Rights
Prenatal Tests and Why Are They Important?
- March Of Dimes {{DEFAULTSORT:Prenatal Diagnosis Obstetrical procedures Midwifery
prenatal care
Prenatal care, also known as antenatal care, is a type of preventive healthcare. It is provided in the form of medical checkups, consisting of recommendations on managing a healthy lifestyle and the provision of medical information such as matern ...
that focus on detecting problems with the pregnancy as early as possible. These may be anatomic and physiologic problems with the health of the zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
, embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
, or fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
, either before gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during preg ...
even starts (as in preimplantation genetic diagnosis
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD or PIGD) is the genetic profiling of embryos prior to implantation (as a form of embryo profiling), and sometimes even of oocytes prior to fertilization. PGD is considered in a similar fashion to prenatal ...
) or as early in gestation as practicable. Screening can detect problems such as neural tube defect
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are a group of birth defects in which an opening in the spine or cranium remains from early in human development. In the third week of pregnancy called gastrulation, specialized cells on the dorsal side of the embryo ...
s, chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
abnormalities, and gene mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s that would lead to genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorde ...
s and birth defect
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities c ...
s, such as spina bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, m ...
, cleft palate
A cleft lip contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose. The opening may be on one side, both sides, or in the middle. A cleft palate occurs when the palate (the roof of the mouth) contains an opening into the nose. The t ...
, Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with child development, physical growth delays, mild to moderate ...
, Tay–Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red b ...
, thalassemia
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can resul ...
, cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. ...
, muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily af ...
, and fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic disorder characterized by mild-to-moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ in males with FXS is under 55, while about two thirds of affected females are intellectually disabled. Physical features may ...
. Some tests are designed to discover problems which primarily affect the health of the mother, such as PAPP-A to detect pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease ...
or glucose tolerance test
The glucose tolerance test (GTT, not to be confused with GGT test) is a medical test in which glucose is given and blood samples taken afterward to determine how quickly it is cleared from the blood. The test is usually used to test for diabetes ...
s to diagnose gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and o ...
. Screening can also detect anatomical defects such as hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary in ...
, anencephaly
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fa ...
, heart defects
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascula ...
, and amniotic band syndrome.
Prenatal screening focuses on finding problems among a large population with affordable and noninvasive methods. Prenatal diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
focuses on pursuing additional detailed information once a particular problem has been found, and can sometimes be more invasive. The most common screening procedures are routine ultrasounds
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies f ...
, blood tests, and blood pressure measurement. Common diagnosis procedures include amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), sometimes called "chorionic ''villous'' sampling" (as "villous" is the adjectival form of the word "villus"), is a form of prenatal diagnosis done to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It ...
. In some cases, the tests are administered to determine if the fetus will be aborted
Aborted is a Belgian death metal band formed in 1995 in Waregem. The group currently consists of vocalist, founder and only constant member Sven de Caluwé, guitarist Ian Jekelis, bassist Stefano Franceschini and drummer Ken Bedene. Although t ...
, though physicians and patients also find it useful to diagnose high-risk pregnancies early so that delivery can be scheduled in a tertiary care hospital where the baby can receive appropriate care.
Prenatal testing in recent years has been moving towards non-invasive methods to determine the fetal risk for genetic disorders. The rapid advancement of modern high-performance molecular technologies along with the discovery of cell-free fetal DNA
Cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is fetal DNA that circulates freely in the maternal blood. Maternal blood is sampled by venipuncture. Analysis of cffDNA is a method of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis frequently ordered for pregnant women of advance ...
(cffDNA) in maternal plasma has led to new methods for the determination of fetal chromosomal aneuploidies. This type of testing is referred to as non-invasive prenatal testing
Prenatal testing consists of prenatal screening and prenatal diagnosis, which are aspects of prenatal care that focus on detecting problems with the pregnancy as early as possible. These may be anatomic and physiologic problems with the health ...
(NIPT). Invasive procedures remain important, though, especially for their diagnostic value in confirming positive non-invasive findings and detecting genetic disorders.
Purpose
There are three purposes of prenatal diagnosis: (1) to enable timely medical or surgical treatment of a condition before or after birth, (2) to give the parents the chance to abort a fetus with the diagnosed condition, and (3) to give parents the chance to prepare psychologically, socially, financially, and medically for a baby with a health problem or disability, or for the likelihood of a stillbirth. Prior information about problems in pregnancy means that healthcare staff as well as parents can better prepare themselves for the delivery of a child with a health problem. For example, Down syndrome is associated with cardiac defects that may need intervention immediately upon birth.Testing guidelines and qualifying risk factors for invasive testing
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists ( ACOG) guidelines currently recommend that anyone who is pregnant, regardless of age, should discuss and be offered non-invasive prenatal genetic screening and diagnostic testing options. Non-invasive prenatal genetic screening is typically performed at the end of the 1st trimester (11–14 weeks) or during the beginning of the second trimester (15–20 weeks) and involves the pregnant woman receiving a blood draw with a needle and a syringe, and an ultrasound of the fetus. Screening tests can then include serum analyte screening orcell-free fetal DNA
Cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is fetal DNA that circulates freely in the maternal blood. Maternal blood is sampled by venipuncture. Analysis of cffDNA is a method of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis frequently ordered for pregnant women of advance ...
, and nuchal translucency ultrasound T respectively. It is important to note that screening tests are not diagnostic, and concerning screening results should be followed up with invasive diagnostic testing for a confirmed diagnosis. Invasive diagnostic prenatal genetic testing can involve chronic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis. The ACOG recommends genetic screening before pregnancy to all pregnant women planning to have a family. After comprehensive counseling and discussion that acknowledges residual risks, it is important to respect the patients' right of choosing to pursue or not pursue any component of genetic testing.
The following are some reasons why a woman might consider her risk of birth defects already to be high enough to warrant skipping screening and going straight for invasive testing.
* Increased risk of fetal aneuploidy based on personal obstetric history or family history affected by aneuploidy
* Increased risk for a known genetic or biochemical disease of the fetus
* Maternal transmissible infectious disease such as rubella or toxoplasma
* Parental request in the context of acute parental anxiety or under exceptional circumstances
By invasiveness
 Diagnostic prenatal testing can be performed by
Diagnostic prenatal testing can be performed by invasive
Invasive may refer to:
*Invasive (medical) procedure
*Invasive species
*Invasive observation, especially in reference to surveillance
*Invasively progressive spread of disease from one organ in the body to another, especially in reference to cancer ...
or non-invasive methods. An invasive method involves probes or needles being inserted into the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
, e.g. amniocentesis, which can be done from about 14 weeks gestation, and usually up to about 20 weeks, and chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), sometimes called "chorionic ''villous'' sampling" (as "villous" is the adjectival form of the word "villus"), is a form of prenatal diagnosis done to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It ...
, which can be done earlier (between 9.5 and 12.5 weeks gestation) but which may be slightly more risky to the fetus. One study comparing transabdominal chorionic villus sampling with second trimester amniocentesis found no significant difference in the total pregnancy loss between the two procedures.Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling for prenatal diagnosis (Review)By Alfirevic Z, Mujezinovic F, Sundberg K at The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009 However, transcervical chorionic villus sampling carries a significantly higher risk, compared with a second-trimester amniocentesis, of total pregnancy loss (
relative risk
The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is the ratio of the probability of an outcome in an exposed group to the probability of an outcome in an unexposed group. Together with risk difference and odds ratio, relative risk measures the association b ...
1.40; 95% confidence interval
In frequentist statistics, a confidence interval (CI) is a range of estimates for an unknown parameter. A confidence interval is computed at a designated ''confidence level''; the 95% confidence level is most common, but other levels, such as ...
1.09 to 1.81) and spontaneous miscarriage (9.4% risk; relative risk 1.50; 95% confidence interval 1.07 to 2.11).
 Non-invasive techniques include examinations of the woman's womb through
Non-invasive techniques include examinations of the woman's womb through ultrasonography
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies f ...
and maternal serum screens (i.e. Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP, α-fetoprotein; also sometimes called alpha-1-fetoprotein, alpha-fetoglobulin, or alpha fetal protein) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AFP'' gene. The ''AFP'' gene is located on the ''q'' arm of chromosome 4 ...
). Blood tests for select trisomies (Down syndrome in the United States, Down and Edwards syndromes in China) based on detecting cell-free placental DNA
Cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is fetal DNA that circulates freely in the maternal blood. Maternal blood is sampled by venipuncture. Analysis of cffDNA is a method of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis frequently ordered for pregnant women of advanced ...
present in maternal blood, also known as non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), have become available. If an elevated risk of chromosomal or genetic abnormality is indicated by a non-invasive screening test, a more invasive technique may be employed to gather more information. In the case of neural tube defects, a detailed ultrasound can non-invasively provide a definitive diagnosis.
One of the major advantages of the non-invasive prenatal testing is that the chance of a false positive result is very low. This accuracy is very important for the pregnant woman, as due to a high sensitivity and specificity of the testing, especially for Down syndrome, the invasive testing could be avoided, which includes the risk of a miscarriage.
By pregnancy stage
Pre-conception
Prior to conception, couples may elect to have genetic testing done to determine the odds of conceiving a child with a known genetic anomaly. The most common in the caucasian population are: *Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. ...
* Fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic disorder characterized by mild-to-moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ in males with FXS is under 55, while about two thirds of affected females are intellectually disabled. Physical features may ...
* Blood disorders such as sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red b ...
* Tay-Sachs disease
* Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common genet ...
Hundreds of additional conditions are known and more discovered on a regular basis. However the economic justification for population-wide testing of all known conditions is not well supported, particularly once the cost of possible false positive results and concomitant follow-up testing are taken into account. There are also ethical concerns related to this or any type of genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
.
One or both partners may be aware of other family members with these diseases. Testing prior to conception may alleviate concern, prepare the couple for the potential short- or long-term consequences of having a child with the disease, direct the couple toward adoption or foster parenting, or prompt for preimplantation genetic testing during ''in vitro'' fertilization. If a genetic disorder is found, professional genetic counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of investigating individuals and families affected by or at risk of genetic disorders to help them understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease; t ...
is usually recommended owing to the host of ethical considerations related to subsequent decisions for the partners and potential impact on their extended families. Most, but not all, of these diseases follow Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later populari ...
patterns. Fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic disorder characterized by mild-to-moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ in males with FXS is under 55, while about two thirds of affected females are intellectually disabled. Physical features may ...
is related to expansion of certain repeated DNA segments and may change generation-to-generation.
First trimester
At early presentation of pregnancy at around 6 weeks, early dating ultrasound scan may be offered to help confirm the gestational age of the embryo and check for a single or twin pregnancy, but such a scan is unable to detect common abnormalities. Details of prenatal screening and testing options may be provided. Around weeks 11–13, nuchal translucency scan (NT) may be offered which can be combined with blood tests for PAPP-A and beta-hCG, two serum markers that correlate with chromosomal abnormalities, in what is called the First Trimester Combined Test. The results of the blood test are then combined with the NT ultrasound measurements, maternal age, and gestational age of the fetus to yield a risk score for Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13. First Trimester Combined Test has a sensitivity (i.e. detection rate for abnormalities) of 82–87% and a false-positive rate of around 5%.Cell-free fetal DNA
Cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is fetal DNA that circulates freely in the maternal blood. Maternal blood is sampled by venipuncture. Analysis of cffDNA is a method of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis frequently ordered for pregnant women of advance ...
is also available during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Second trimester
The anomaly scan is performed between 18 and 22 weeks of gestational age. The International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG) recommends that this ultrasound is performed as a matter of routineprenatal care
Prenatal care, also known as antenatal care, is a type of preventive healthcare. It is provided in the form of medical checkups, consisting of recommendations on managing a healthy lifestyle and the provision of medical information such as matern ...
, to measure the fetus so that growth abnormalities can be recognized quickly later in pregnancy, and to assess for congenital malformations and multiple pregnancies (i.e. twins). The scan can detect anencephaly
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fa ...
, open spina bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, m ...
, cleft lip, diaphragmatic hernia, gastroschisis
Gastroschisis is a birth defect in which the baby's intestines extend outside of the abdomen through a hole next to the belly button. The size of the hole is variable, and other organs including the stomach and liver may also occur outside the ...
, omphalocele
Omphalocele or omphalocoele also called exomphalos, is a rare abdominal wall defect. Beginning at the 6th week of development, rapid elongation of the gut and increased liver size reduces intra abdominal space, which pushes intestinal loops out o ...
, congenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascula ...
, bilateral renal agenesis
Renal agenesis is a medical condition in which one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) fetal kidneys fail to develop.
Unilateral and bilateral renal agenesis in humans, mice and zebra fish has been linked to mutations in the gene GREB1L. It has also ...
, osteochondrodysplasia, Edwards syndrome
Edwards syndrome, also known as trisomy 18, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born small and have heart defects. Other features in ...
, and Patau syndrome.
A second-trimester Quad blood test may be taken (the Triple test is widely considered obsolete but in some states, such as Missouri, where Medicaid
Medicaid in the United States is a federal and state program that helps with healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and ...
only covers the Triple test, that's what the patient typically gets). With ''integrated screening'', both a First Trimester Combined Test and a Triple/Quad test is performed, and a report is only produced after both tests have been analyzed. However patients may not wish to wait between these two sets of tests. With ''sequential screening'', a first report is produced after the first trimester sample has been submitted, and a final report after the second sample. With ''contingent screening'', patients at very high or very low risks will get reports after the first-trimester sample has been submitted. Only patients with ''moderate risk'' (risk score between 1:50 and 1:2000) will be asked to submit a second-trimester sample, after which they will receive a report combining information from both serum samples and the NT measurement. The First Trimester Combined Test and the Triple/Quad test together have a sensitivity of 88–95% with a 5% false-positive rate for Down syndrome, though they can also be analyzed in such a way as to offer a 90% sensitivity with a 2% false-positive rate. Finally, patients who do not receive an NT ultrasound in the 1st trimester may still receive a Serum Integrated test involving measuring PAPP-A serum levels in the 1st trimester and then doing a Quad test in the 2nd trimester. This offers an 85–88% sensitivity and 5% false-positive rate for Down syndrome. Also, a patient may skip the 1st-trimester screening entirely and receive only a 2nd-trimester Quad test, with an 81% sensitivity for Down syndrome and 5% false-positive rate.The California Prenatal Screening Programcdph.ca.gov
Third trimester
Third-trimester prenatal testing generally focuses on maternal wellbeing and reducing fetal morbidity/mortality.Group B streptococcal infection
Group B streptococcal infection, also known as Group B streptococcal disease or just Group B strep, is the infection caused by the bacterium '' Streptococcus agalactiae'' (''S. agalactiae'') (also known as group B streptococcus or GBS). GBS inf ...
(also called Group B strep) may be offered, which is a major cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality. Group B strep is an infection that may be passed to an infant during birth. Vaginal screening for GBS is performed between 34 and 37 weeks of gestational age, so that mothers that are positive for the bacterium can receive treatment before delivery. During the third trimester, some institutions may require evaluations of hemoglobin/hematocrit, syphilis serology, and HIV screening. Also, before delivery, an assessment of fetal position and estimated fetal weight is documented.
Maternal serum screening
First-trimester maternal serum screening can check levels of free β- hCG, PAPP-A, intact or beta hCG, or h-hCG in the woman'sserum
Serum may refer to:
*Serum (blood), plasma from which the clotting proteins have been removed
**Antiserum, blood serum with specific antibodies for passive immunity
* Serous fluid, any clear bodily fluid
* Truth serum, a drug that is likely to mak ...
, and combine these with the measurement of nuchal translucency
A nuchal scan or nuchal translucency (NT) scan/procedure is a sonographic prenatal screening scan (ultrasound) to detect chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus, though altered extracellular matrix composition and limited lymphatic drainage can also ...
(NT). Some institutions also look for the presence of a fetal nasalbone on the ultrasound.
Second-trimester maternal serum screening ( AFP screening, triple screen, quad screen, or penta screen) can check levels of alpha fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP, α-fetoprotein; also sometimes called alpha-1-fetoprotein, alpha-fetoglobulin, or alpha fetal protein) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AFP'' gene. The ''AFP'' gene is located on the ''q'' arm of chromosome 4 ...
, β- hCG, inhibin-A, estriol
Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almos ...
, and h-hCG (hyperglycosolated hCG) in the woman's serum
Serum may refer to:
*Serum (blood), plasma from which the clotting proteins have been removed
**Antiserum, blood serum with specific antibodies for passive immunity
* Serous fluid, any clear bodily fluid
* Truth serum, a drug that is likely to mak ...
.
The triple test measures serum
Serum may refer to:
*Serum (blood), plasma from which the clotting proteins have been removed
**Antiserum, blood serum with specific antibodies for passive immunity
* Serous fluid, any clear bodily fluid
* Truth serum, a drug that is likely to mak ...
levels of AFP, estriol
Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almos ...
, and beta-hCG, with a 70% sensitivity
Sensitivity may refer to:
Science and technology Natural sciences
* Sensitivity (physiology), the ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli
** Sensory processing sensitivity in humans
* Sensitivity and specificity, statisti ...
and 5% false-positive rate. It is complemented in some regions of the United States, as the ''Quad test'' (adding inhibin A to the panel, resulting in an 81% sensitivity and 5% false-positive rate for detecting Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with child development, physical growth delays, mild to moderate ...
when taken at 15–18 weeks of gestational age).
The biomarkers PAPP-A and β- hCG seem to be altered for pregnancies resulting from ICSI, causing a higher false-positive rate. Correction factors have been developed and
should be used when screening for Down's syndrome in singleton pregnancies after ICSI, but in twin pregnancies such correction factors have not been fully elucidated. In vanishing twin pregnancies with a second gestational sac with a dead fetus, first-trimester screening should be based solely on the maternal age and the nuchal translucency scan as biomarkers are altered in these cases.
Advances in prenatal screening
Measurement of fetal proteins in maternal serum is a part of standard prenatal screening for fetal aneuploidy and neural tube defects. Computational predictive model shows that extensive and diverse feto-maternal protein trafficking occurs during pregnancy and can be readily detected non-invasively in maternal whole blood. This computational approach circumvented a major limitation, the abundance of maternal proteins interfering with the detection of fetal proteins, to fetal proteomic analysis of maternal blood. Entering fetal gene transcripts previously identified in maternal whole blood into a computational predictive model helped develop a comprehensive proteomic network of the term neonate. It also shows that the fetal proteins detected in pregnant woman's blood originate from a diverse group of tissues and organs from the developing fetus. Development proteomic networks dominate the functional characterization of the predicted proteins, illustrating the potential clinical application of this technology as a way to monitor normal and abnormal fetal development. The difference inmethylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These t ...
of specific DNA sequences between mother and fetus can be used to identify fetal-specific DNA in the blood circulation of the mother. In a study published in the March 6, 2011, online issue of ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans ar ...
'', using this non-invasive technique a group of investigators from Greece and UK achieved correct diagnosis of 14 trisomy 21 (Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with child development, physical growth delays, mild to moderate ...
) and 26 normal cases. Using massive parallel sequencing, a study testing for trisomy 21 only, successfully detected 209 of 212 cases (98.6%) with 3 false-positives in 1,471 pregnancies (0.2%). With commercially available non-invasive (blood) testing for Down syndrome having become available to patients in the United States and already available in China, in October 2011, the International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis created some guidance. Based on its sensitivity and specificity
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do ...
, it constitutes an advanced screening test and that positive results require confirmation by an invasive test, and that while effective in the diagnosis of Down syndrome, it cannot assess half the abnormalities detected by invasive testing. The test is not recommended for general use until results from broader studies have been reported, but may be useful in high-risk patients in conjunction with genetic counseling.
A study in 2012 found that the maternal plasma cell-free DNA test was also able to detect trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) in 100% of the cases (59/59) at a false-positive rate of 0.28%, and trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) in 91.7% of the cases (11/12) at a false-positive rate of 0.97%. The test interpreted 99.1% of samples (1,971/1,988); among the 17 samples without an interpretation, three were trisomy 18. The study stated that if z-score cutoffs for trisomy 18 and 13 were raised slightly, the overall false-positive rates for the three aneuploidies could be as low as 0.1% (2/1,688) at an overall detection rate of 98.9% (280/283) for common aneuploidies (this includes all three trisomies: Down, Edwards and Patau).
Screening for chromosomal abnormalities
The goal of prenatal genetic testing is to identify pregnancies at high risk of abnormalities, allowing for early intervention, termination or appropriate management and preparation measures.Ultrasound imaging and serum markers as indications for genetic testing
Ultrasound imaging provides the opportunity to conduct a nuchal translucency (NT) scan screening for chromosomal abnormalities such asDown syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with child development, physical growth delays, mild to moderate ...
(trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (trisomy 13). Using the information from the NT scan the mother can be offered an invasive diagnostic test for fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Serum markers are utilized in a similar fashion to identify gestations that should be recommended for further testing. When the NT scan or serum markers arouse suspicion for chromosomal abnormalities the following genetic tests may be conducted on fetal or placental tissue samples: Interphase-fluorescence in situ hybridization
Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by ...
(FISH), quantitative PCR and direct preparation of chromosomes from chorionic villi.
Fetal cell-free DNA
Fetal cell-free DNA testing allows for the detection of apoptotic fetal cells and fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood for the noninvasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy. A meta-analysis that investigated the success rate of using fetal cell-free DNA from maternal blood to screen for aneuploidies found that this technique detected trisomy 13 in 99% of the cases, trisomy 18 in 98% of the cases and trisomy 21 in 99% of the cases. Failed tests using fetal cell-free DNA are more likely to occur in fetuses with trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 but not with trisomy 21. Previous studies found elevated levels of cell-free fetal DNA for trisomy 13 and 21 from maternal serum when compared to women with euploid pregnancies. However, an elevation of cell-free DNA for trisomy 18 was not observed. Circulating fetal nucleated cells comprise only three to six percent of maternal blood plasma DNA, reducing the detection rate of fetal developmental abnormalities. Two alternative approaches have been developed for the detection of fetal aneuploidy. The first involves the measuring of the allelic ratio of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in themRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
coding region in the placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ (anatomy), organ that begins embryonic development, developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation (embryology), implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrien ...
. The next approach is analyzing both maternal and fetal DNA and looking for differences in the DNA methylation patterns.
Digital PCR
Recently, it has been proposed that digitalPCR PCR or pcr may refer to:
Science
* Phosphocreatine, a phosphorylated creatine molecule
* Principal component regression, a statistical technique
Medicine
* Polymerase chain reaction
** COVID-19 testing, often performed using the polymerase chain r ...
analysis can be conducted on fetal cell-free DNA for detection of fetal aneuploidy. Research has shown that digital PCR can be used to differentiate between normal and aneuploid DNA.
A variation of the PCR technique called multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA), targeting DNA, has been successively applied for diagnosing fetal aneuploidy as a chromosome- or gene-specific assay.
Shotgun sequencing
Fetal cell-free DNA has been directly sequenced using shotgun sequencing technology. In one study, DNA was obtained from the blood plasma of eighteen pregnant women. This was followed by mapping the chromosome using the quantification of fragments. This was done using advanced methods in DNA sequencing resulting in the parallel sequencing of the fetal DNA. The amount of sequence tags mapped to each chromosome was counted. If there was a surplus or deficiency in any of the chromosomes, this meant that there was a fetal aneuploid. Using this method of shotgun sequencing, the successful identification of trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edward syndrome), and trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) was possible. This method of noninvasive diagnosis is now starting to be heavily used and researched further.Other techniques
Fetal components in samples from maternal blood plasma can be analyzed by genome-wide techniques not only by total DNA, but also bymethylated DNA
Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP or mDIP) is a large-scale (chromosome- or genome-wide) purification technique in molecular biology that is used to enrich for methylated DNA sequences. It consists of isolating methylated DNA fragments vi ...
immunoprecipitation (with tiling array), microRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. m ...
(such as with Megaplex) and total RNA ( RNA-sequencing).
Patient acceptance
Research was conducted to determine how women felt about noninvasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploid using maternal blood. This study was conducted using surveys. It was reported that eighty-two percent of pregnant women and seventy-nine percent of female medical students view this type of diagnosis in a positive light, agreeing that it is important for prenatal care. Overall, women responded optimistically that this form of diagnosis will be available in the future.Ethical and practical issues
Non-genetic prenatal testing
Parents need to make informed decisions about screening, diagnosis, and any actions to be taken as a result. Many screening tests are inaccurate, so one worrisome test result frequently leads to additional, more invasive tests. If prenatal testing confirms a serious disability, many parents are forced to decide whether to continue the pregnancy or seek an abortion. The "option" of screening becomes an unexpected requirement to decide. ''See'' wrongful abortion. In some genetic conditions, for instancecystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. ...
, an abnormality can only be detected if DNA is obtained from the fetus. Usually an invasive method is needed to do this.
Ultrasound of a fetus, which is considered a screening test, can sometimes miss subtle abnormalities. For example, studies show that a detailed 2nd-trimester ultrasound, also called a level 2 ultrasound, can detect about 97% of neural tube defects such as spina bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, m ...
. Ultrasound results may also show "soft signs," such as an Echogenic intracardiac focus or a Choroid plexus cyst, which are usually normal, but can be associated with an increased risk for chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
abnormalities.
Other screening tests, such as the Quad test, can also have false positives and false negatives. Even when the Quad results are positive (or, to be more precise, when the Quad test yields a score that shows at least a 1 in 270 risk of abnormality), usually the pregnancy is normal, but additional diagnostic tests are offered. In fact, consider that Down syndrome affects about 1:400 pregnancies; if you screened 4000 pregnancies with a Quad test, there would probably be 10 Down syndrome pregnancies of which the Quad test, with its 80% sensitivity, would call 8 of them high-risk. The quad test would also tell 5% (~200) of the 3990 normal women that they are high-risk. Therefore, about 208 women would be told they are high-risk, but when they undergo an invasive test, only 8 (or 4% of the high risk pool) will be confirmed as positive and 200 (96%) will be told that their pregnancies are normal. Since amniocentesis has approximately a 0.5% chance of miscarriage, one of those 200 normal pregnancies might result in a miscarriage because of the invasive procedure. Meanwhile, of the 3792 women told they are low-risk by the Quad test, 2 of them will go on to deliver a baby with Down syndrome. The Quad test is therefore said to have a 4% positive predictive value (PPV) because only 4% of women who are told they are "high-risk" by the screening test actually have an affected fetus. The other 96% of the women who are told they are "high-risk" find out that their pregnancy is normal.
By comparison, in the same 4000 women, a screening test that has a 99% sensitivity and a 0.5% false positive rate would detect all 10 positives while telling 20 normal women that they are positive. Therefore, 30 women would undergo a confirmatory invasive procedure and 10 of them (33%) would be confirmed as positive and 20 would be told that they have a normal pregnancy. Of the 3970 women told by the screen that they are negative, none of the women would have an affected pregnancy. Therefore, such a screen would have a 33% positive predictive value.
The real-world false-positive rate for the Quad test (as well as 1st Trimester Combined, Integrated, etc.) is greater than 5%. 5% was the rate quoted in the large clinical studies that were done by the best researchers and physicians, where all the ultrasounds were done by well-trained sonographers and the gestational age of the fetus was calculated as closely as possible. In the real world, where calculating gestational age may be a less precise art, the formulas that generate a patient's risk score are not as accurate and the false-positive rate can be higher, even 10%.
Because of the low accuracy of conventional screening tests, 5–10% of women, often those who are older, will opt for an invasive test even if they received a low-risk score from the screening. A patient who received a 1:330 risk score, while technically low-risk (since the cutoff for high-risk is commonly quoted as 1:270), might be more likely to still opt for a confirmatory invasive test. On the other hand, a patient who receives a 1:1000 risk score is more likely to feel assuaged that her pregnancy is normal.
Both false positives
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result ...
and false negatives will have a large impact on a couple when they are told the result, or when the child is born. Diagnostic
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engine ...
tests, such as amniocentesis, are considered to be very accurate for the defects they check for, though even these tests are not perfect, with a reported 0.2% error rate (often due to rare abnormalities such as mosaic Down syndrome where only some of the fetal/placental cells carry the genetic abnormality).
A higher maternal serum AFP level indicates a greater risk for anencephaly and open spina bifida. This screening is 80% and 90% sensitive for spina bifida and anencephaly, respectively.
Amniotic fluid acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acety ...
and AFP level are more sensitive and specific
Specific may refer to:
* Specificity (disambiguation)
* Specific, a cure or therapy for a specific illness
Law
* Specific deterrence, focussed on an individual
* Specific finding, intermediate verdict used by a jury in determining the final ...
than AFP in predicting neural tube defects.
Many maternal-fetal specialists do not bother to even do an AFP test on their patients because they do a detail ultrasound on all of them in the 2nd trimester, which has a 97% detection rate for neural tube defects such as anencephaly and open spina bifida. Performing tests to determine possible birth defects is mandatory in all U.S. states. Failure to detect issues early can have dangerous consequences on both the mother and the baby. OBGYN
Obstetrics and Gynaecology (also spelled as Obstetrics and Gynecology; abbreviated as Obs and Gynae, O&G, OB-GYN and OB/GYN) is the medical specialty that encompasses the two subspecialties of obstetrics (covering pregnancy, childbirth, an ...
s may be held culpable. In one case a man who was born with spina bifida was awarded $2 million in settlement, apart from medical expenses, due to the OBGYN's negligence in conducting AFP tests.
No prenatal test can detect ''all'' forms of birth defects and abnormalities.
Prenatal genetic testing
Another important issue is the uncertainty of prenatal genetic testing. Uncertainty on genetic testing results from several reasons: the genetic test is associated with a disease but the prognosis and/or probability is unknown, the genetic test provides information different than the familiar disease they tested for, found genetic variants have unknown significance, and finally, results may not be associated with found fetal abnormalities. Richardson and Ormond thoroughly addressed the issue of uncertainty of genetic testing and explained its implication for bioethics. First, the principle of beneficence is assumed in prenatal testing by decreasing the risk of miscarriage, however, uncertain information derived from genetic testing may harm the parents by provoking anxiety and leading to the termination of a fetus that is probably healthy. Second, the principle of autonomy is undermined given a lack of comprehension resulting from new technologies and changing knowledge in the field of genetics. And third, the principle of justice raised issues regarding equal access to emerging prenatal tests.Availability of treatments
If a genetic disease is detected, there is often no treatment that can help the fetus until it is born. However, in the US, there are prenatal surgeries forspina bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, m ...
fetus. Early diagnosis gives the parents time to research and discuss post-natal treatment and care, or in some cases, abortion. Genetic counselors are usually called upon to help families make informed decisions regarding results of prenatal diagnosis.
Patient education
Researchers have studied how disclosing amniocentesis orchorionic villous sampling
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), sometimes called "chorionic ''villous'' sampling" (as "villous" is the adjectival form of the word "villus"), is a form of prenatal diagnosis done to determine chromosomal abnormalities, chromosomal or genetic dis ...
(CVS) results on a fixed date versus a variable date (i.e. "when available") affects maternal anxiety. Systematic review of the relevant articles found no conclusive evidence to support issuing amniocentesis results as soon as they become available (in comparison to issuing results on a pre-defined fixed date). The researchers concluded that further studies evaluating the effect of different strategies for disclosing CVS results on maternal anxiety are needed.
Concerns from disability rights activists and scholars
Disability rights activists and scholars have suggested a more critical view of prenatal testing and its implications for people with disabilities. They argue that there is pressure to abort fetuses that might be born with disabilities, and that these pressures rely on eugenics interests and ableist stereotypes. This selective abortion relies on the ideas that people with disabilities cannot live desirable lives, that they are "defective," and that they are burdens, while disability scholars argue that "oppression is what's most disabling about disability." Marsha Saxton suggests that women should question whether or not they are relying on real, factual information about people with disabilities or on stereotypes if they decide to abort a fetus with a disability.Societal pressures
Amniocentesis has become the standard of care for prenatal care visits for women who are "at risk" or over a certain age. The wide use of amniocentesis has been defined as consumeristic. and some argue that this can be in conflict with the right to privacy,Botkin JR. Fetal privacy and confidentiality. Hastings Cent Rep. 1995 Sep–Oct;25(5):32–9 Most obstetricians (depending on the country) offer patients the AFP triple test,HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immu ...
test, and ultrasounds routinely. However, almost all women meet with a genetic counselor
Genetic counseling is the process of investigating individuals and families affected by or at risk of genetic disorders to help them understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease; t ...
before deciding whether to have prenatal diagnosis. It is the role of the genetic counselor to accurately inform women of the risks and benefits of prenatal diagnosis. Genetic counselors are trained to be non-directive and to support the patient's decision. Some doctors do advise women to have certain prenatal tests and the patient's partner may also influence the woman's decision.
See also
* Amniocentesis *Amniotic stem cell bank
An amniotic stem cell bank is a facility that stores stem cells derived from amniotic fluid for future use. Stem cell samples in private (or family) banks are stored specifically for use by the individual person from whom such cells have been colle ...
* Amniotic stem cells
* Chorionic villi
* Genetic counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of investigating individuals and families affected by or at risk of genetic disorders to help them understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease; t ...
* Newborn screening
Newborn screening (NBS) is a public health program of screening in infants shortly after birth for conditions that are treatable, but not clinically evident in the newborn period. The goal is to identify infants at risk for these conditions ea ...
Notes and references
External links
Our Bodies Ourselves chapter on Prenatal Testing and Disability Rights
Prenatal Tests and Why Are They Important?
- March Of Dimes {{DEFAULTSORT:Prenatal Diagnosis Obstetrical procedures Midwifery