|
John Henry (toxicologist)
Professor John Anthony Henry (Born: 11 March 1939 at Greenwich, England, died 8 May 2007) was a professor specialising in toxicology in the Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London, at St Mary's Hospital in Paddington. He conducted research on the health effects of cannabis, cocaine and other recreational drugs. Family and childhood Henry was born in Greenwich on 11 March 1939, and was the eldest of four surviving children. His father, Irish Doctor John Aloysius Henry, was a general practitioner, and was the team doctor for Millwall Football Club, which gave the young John a lifelong interest in English Football. Education Henry was educated first at St Joseph's Academy, Blackheath, run by the De Salle brothers. He attended Medical School at King's College London, and joined Opus Dei as a twenty-year-old medical student, there as a "numerary", a celibate member. Throughout the rest of his life, he attended mass daily, and set aside two periods a day for prayer an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwich, England
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross. Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich Meridian (0° longitude) and Greenwich Mean Time. The town became the site of a royal palace, the Palace of Placentia from the 15th century, and was the birthplace of many Tudors, including Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. The palace fell into disrepair during the English Civil War and was demolished to be replaced by the Royal Naval Hospital for Sailors, designed by Sir Christopher Wren and his assistant Nicholas Hawksmoor. These buildings became the Royal Naval College in 1873, and they remained a military education establishment until 1998 when they passed into the hands of the Greenwich Foundation. The historic rooms within these buildings remain open to the public; other buildings are used by University of Greenwich and Trinity Laban Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's College London
King's College London (informally King's or KCL) is a public research university located in London, England. King's was established by royal charter in 1829 under the patronage of King George IV and the Duke of Wellington. In 1836, King's became one of the two founding colleges of the University of London. It is one of the oldest university-level institutions in England. In the late 20th century, King's grew through a series of mergers, including with Queen Elizabeth College and Chelsea College of Science and Technology (in 1985), the Institute of Psychiatry (in 1997), the United Medical and Dental Schools of Guy's and St Thomas' Hospitals and the Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery (in 1998). King's has five campuses: its historic Strand Campus in central London, three other Thames-side campuses (Guy's, St Thomas' and Waterloo) nearby and one in Denmark Hill in south London. It also has a presence in Shrivenham, Oxfordshire, for its professional mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consultant (medicine)
In the United Kingdom, Ireland, and parts of the Commonwealth, consultant is the title of a senior hospital-based physician or surgeon who has completed all of their specialist training and been placed on the specialist register in their chosen speciality. Their role is entirely distinct from that of general practitioners, or GPs. The primary objective of a consultant is to use expert knowledge and skill to diagnose and treat patients while retaining ultimate clinical responsibility for their care. A physician must be on the Specialist Register before they may be employed as a substantive consultant in the National Health Service (NHS). This usually entails holding a Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT) in any of the recognised specialities, but academics with substantial publications and international reputation may be exempted from this requirement, in the expectation that they will practice at a tertiary level. "Locum consultant" appointments of limited duration may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy's Hospital
Guy's Hospital is an NHS hospital in the borough of Southwark in central London. It is part of Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and one of the institutions that comprise the King's Health Partners, an academic health science centre. It is a large teaching hospital and is, with St Thomas' Hospital and King's College Hospital, the location of King's College London GKT School of Medical Education. The hospital's Tower Wing (originally known as Guy's Tower) was, when built in 1974, the tallest hospital building in the world, standing at with 34 floors. The tower was overtaken as the world's tallest healthcare-related building by The Belaire in New York City in 1988. As of June 2019, the Tower Wing, which remains one of the tallest buildings in London, is the world's fifth-tallest hospital building. History The hospital dates from 1721, when it was founded by philanthropist Thomas Guy, who had made a fortune as a printer of Bibles and greatly increased it by speculat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specialist Registrar
A specialist registrar (SpR) is a doctor in the United Kingdom or the Republic of Ireland who is receiving advanced training in a specialist field of medicine in order to become a consultant in that specialty. After graduation from medical school, a specialist registrar will undertake several years of work and training as an intern or pre-registration house officer, and as a senior house officer. It may be required to take diploma examinations in order to enter registrar training. These are administered by the medical royal college or in some cases a separate postgraduate training body responsible for that specialty and are usually termed "memberships". This means membership to the Royal College of their specialty. For example, those wishing to specialise in general medicine must take the examination for Membership of the Royal College of Physicians. Doctors will work in specialist registrar posts for around four to six years, depending on their speciality. They gain experience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercession Of Saints
Intercession of the Saints is a Christian doctrine held by the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. The practice of praying through saints can be found in Christian writings from the 3rd century onward. The 4th-century Apostles' Creed states belief in the communion of Saints, which certain Christian churches interpret as supporting the intercession of saints. However, similar practices are controversial in Judaism, Islam, and Protestantism. Biblical basis Intercession of the living for the living According to the Epistle to the Romans, the living can intercede for the living: "Now I (Paul) beseech you, brethren, for the Lord Jesus Christ's sake, and for the love of the Spirit, that ye strive together with me in your prayers to God for me"Romans 15:30. Mary intercedes at the wedding at Cana and occasions Jesus's first miracle. "On the third day a wedding took place at Cana in Galilee. Jesus’ mother was there, and Jesus and his disciples had also been i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
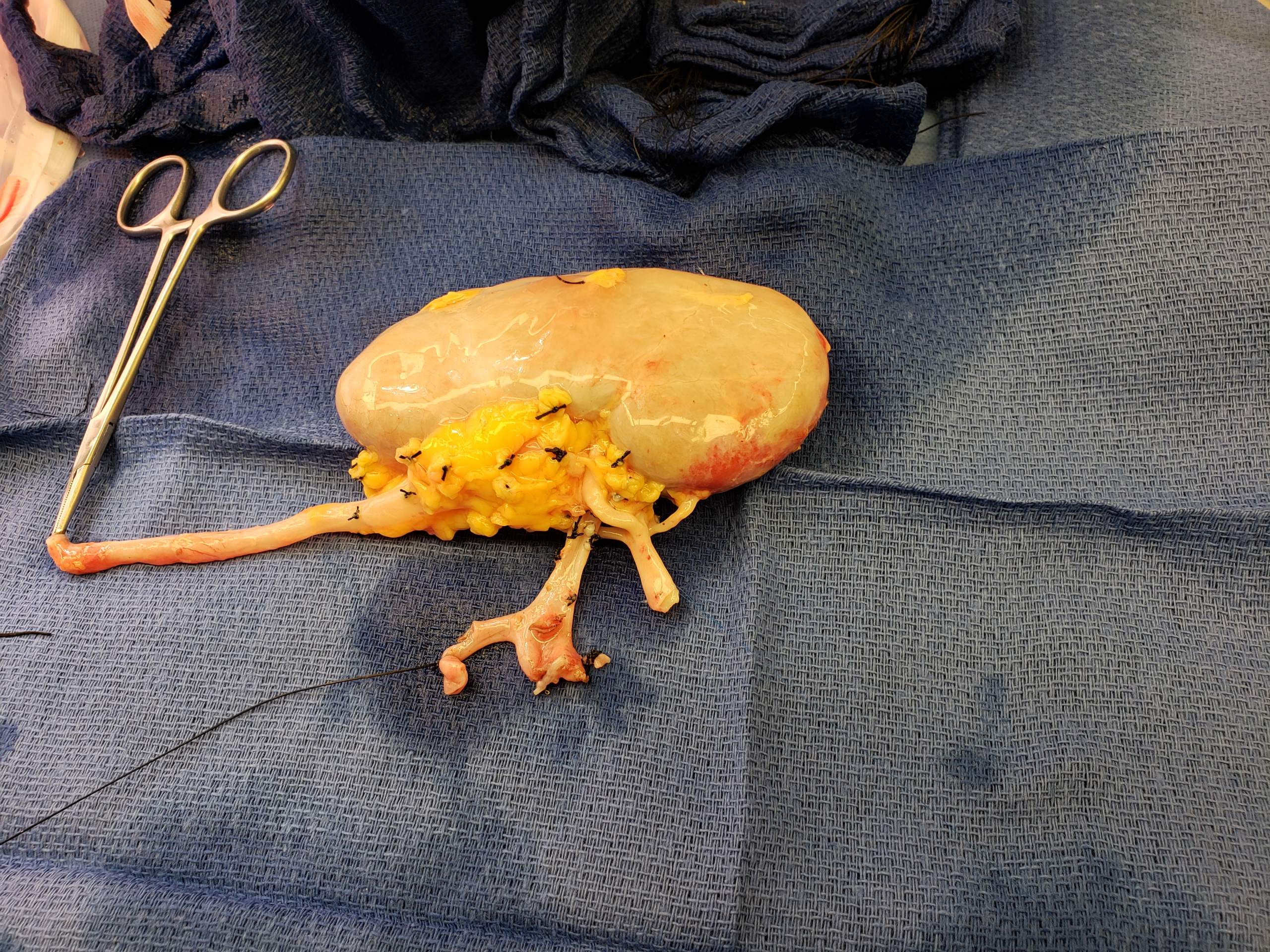
Kidney Transplant
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluation to make sure that they are healthy enough to undergo transplant surgery. If they are deemed a good candidate, they can be placed on a waiting list to receive a kidney from a deceased donor. Once they are placed on the waiting list, they can receive a new kidney very quickly, or they may have to wait many years; in the United States, the average waiting time is three t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hampstead
Hampstead () is an area in London, which lies northwest of Charing Cross, and extends from Watling Street, the A5 road (Roman Watling Street) to Hampstead Heath, a large, hilly expanse of parkland. The area forms the northwest part of the London Borough of Camden, a borough in Inner London which for the purposes of the London Plan is designated as part of Central London. Hampstead is known for its intellectual, liberal, artistic, musical, and literary associations. It has some of the most expensive housing in the London area. Hampstead has more millionaires within its boundaries than any other area of the United Kingdom.Wade, David"Whatever happened to Hampstead Man?" ''The Daily Telegraph'', 8 May 2004 (retrieved 3 March 2016). History Toponymy The name comes from the Old English, Anglo-Saxon words ''ham'' and ''stede'', which means, and is a cognate of, the Modern English "homestead". To 1900 Early records of Hampstead can be found in a grant by King Ethelred the Unread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherhall House
Netherhall House is a catered residential college for men, situated in Hampstead, London, England. It is less than a five-minute walk from Finchley Road tube station. Netherhall House was founded in 1952, in 1966 the 'old wing' was built and opened by the Queen Mother and in 1995 the 'new wing' was opened by Katharine, Duchess of Kent. Overview Netherhall House is a corporate undertaking of Opus Dei,Opus Dei UK. a personal prelature of the . It has a Chaplain who is also a member of the chaplaincy. However, the college is open to students of all faiths a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Dialysis
Kidney dialysis (from Greek , , 'dissolution'; from , , 'through', and , , 'loosening or splitting') is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943. Dialysis may need to be initiated when there is a sudden rapid loss of kidney function, known as acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure), or when a gradual decline in kidney function, chronic kidney disease, reaches stage 5. Stage 5 chronic renal failure is reached when the glomerular filtration rate is 10–15% of normal, creatinine clearance is less than 10 mL per minute and uremia is present. Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not indicated or not possible.Pendse S, Singh A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, high blood potassium, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anemia. Causes of acute kidney failure include low blood pressure, blockage of the urinary tract, certain medications, muscle breakdown, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Causes of chronic kidney failure include diabetes, high blood pressure, nephrotic syndrome, and polycystic kidney disease. Diagnosis of acute failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throat Infection
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a hoarse voice. Symptoms usually last 3–5 days, but can be longer depending on cause. Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media. Pharyngitis is a type of upper respiratory tract infection. Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Strep throat, a bacterial infection, is the cause in about 25% of children and 10% of adults. Uncommon causes include other bacteria such as ''gonococcus'', fungi, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection, such as a cold. Otherwise, a rapid antigen detection test or throat swab is recommended. PCR testing is becoming commonly used as it is as good as taking a throat swab but gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)