|
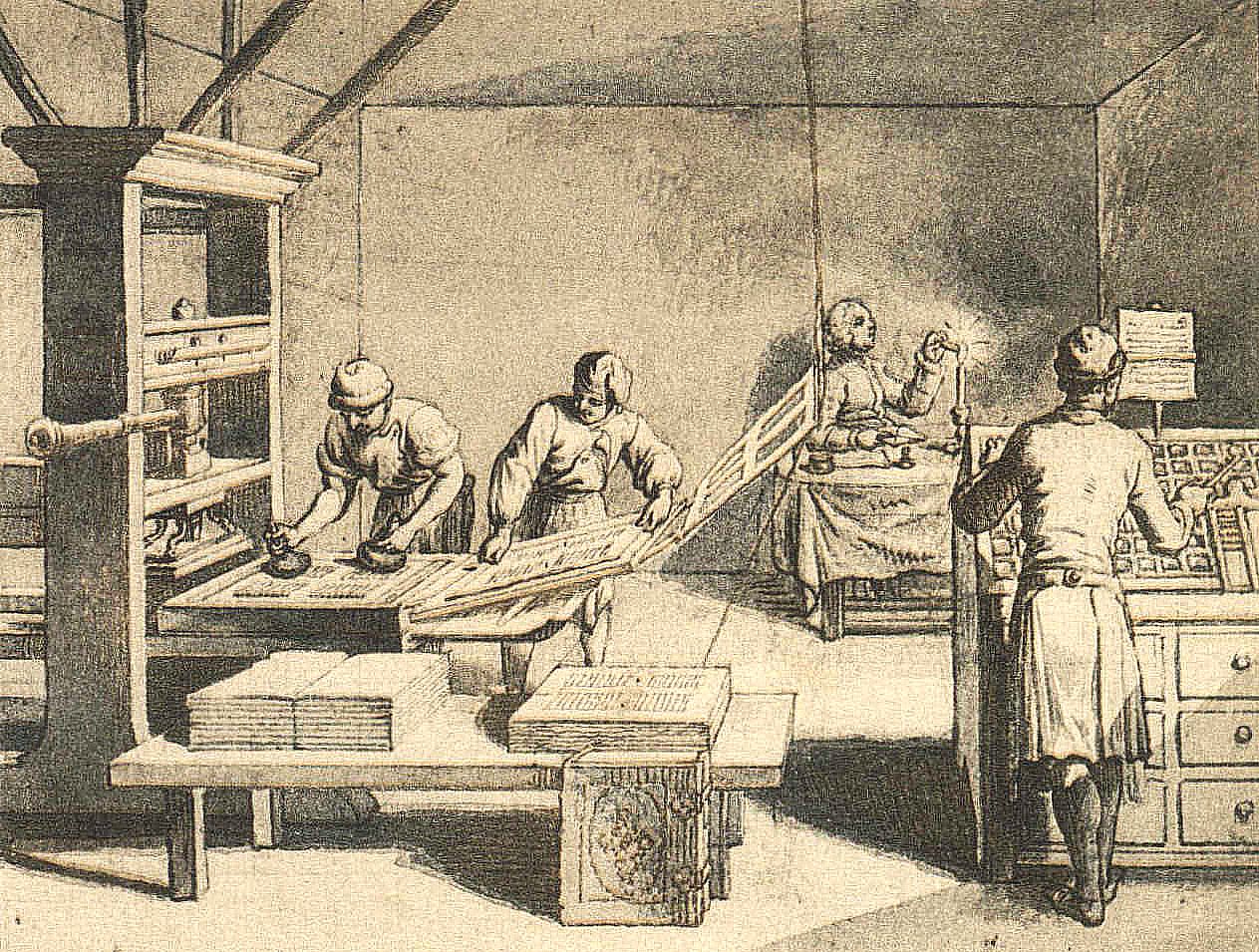
John Carter (printer)
John Carter (July 21, 1745August 19, 1814) was an early American printer, newspaper publisher, and postmaster of Providence, Rhode Island. Carter entered the printing profession as an apprentice of Benjamin Franklin while living in Philadelphia. After he entered into a partnership and ran ''The Providence Gazette'', which he eventually purchased and ran on his own up until the year of his death. During the Gaspee Affair Carter played an active role in reporting the subsequent arrests and other developments in his newspaper, for which he himself was arrested, for libel. During his career as a vigilant printer Carter became one of the leading publishers and printers in the country. Family and early life John Carter was born to a prominent family in Philadelphia. He removed to Providence and after a few years there he married Almey Crawford, on May 14, 1769. Biographical cyclopedia of representative men of Rhode Island, 1881, p. 210 Carter was the son of his father of the same na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since 1854, the city has been coextensive with Philadelphia County, the most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the Delaware Valley, the nation's seventh-largest and one of world's largest metropolitan regions, with 6.245 million residents . The city's population at the 2020 census was 1,603,797, and over 56 million people live within of Philadelphia. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, an English Quaker. The city served as capital of the Pennsylvania Colony during the British colonial era and went on to play a historic and vital role as the central meeting place for the nation's founding fathers whose plans and actions in Philadelphia ultimately inspired the American Revolution and the nation's inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliography Of Early American Publishers And Printers
Bibliography of early American publishers and printers is a selection of books, journals and other publications devoted to these topics covering their careers and other activities before, during and just after the American Revolution. Various works that are not primarily devoted to those topics, but whose content devotes itself to them in significant measure, are sometimes included here also. Works about Benjamin Franklin, a famous printer and publisher, among other things, are too numerous to list in this bibliography, can be found at ''Bibliography of Benjamin Franklin'', and are generally not included here unless they are greatly devoted to Franklin's printing career. Single accounts of printers and publishers that occur in encyclopedia articles are neither included here. Scholarly textbooks A * * * * * * * * * B * Google book * * -2014 publication * * * * * * * * * *Google link * * * * C * * * * – (contains much cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Early American Publishers And Printers
List of early American publishers and printers is a ''stand alone list'' of Wikipedia articles about publishers and printers in colonial and early America, intended as a quick reference, with basic descriptions taken from the ledes of the respective articles. ---- * Jane Aitken 1764–1832Printer, publisher, bookbinder, and bookseller in Philadelphia; Sister of Robert Aitken, who continued his business when he died. Printed and bound dozens of books for the Athenaeum of Philadelphia and about 400 volumes for the American Philosophical Society ---- * Robert Aitken (publisher) 1734–1802Philadelphia printer and the first to publish an English language Bible in the U.S. ---- * Benjamin Franklin Bache 1769–1798Journalist, printer and publisher. Founded the ''Philadelphia Aurora'', a newspaper that supported Jeffersonian philosophy, known for its attacks on Federalist leaders, including George Washington. Known for polarizing the press, promp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation Acts
The Navigation Acts, or more broadly the Acts of Trade and Navigation, were a long series of English laws that developed, promoted, and regulated English ships, shipping, trade, and commerce between other countries and with its own colonies. The laws also regulated England's fisheries and restricted foreigners' participation in its colonial trade. While based on earlier precedents, they were first enacted in 1651 under the Commonwealth. The system was reenacted and broadened with the Restoration by the Act of 1660, and further developed and tightened by the Navigation Acts of 1663, 1673, and 1696. Upon this basis during the 18th century, the Acts were modified by subsequent amendments, changes, and the addition of enforcement mechanisms and staff. Additionally, a major change in the very purpose of the Acts in the 1760s – that of generating a colonial revenue, rather than only regulating the Empire's trade – would help lead to major rebellions, and significant changes in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narragansett Bay
Narragansett Bay is a bay and estuary on the north side of Rhode Island Sound covering , of which is in Rhode Island. The bay forms New England's largest estuary, which functions as an expansive natural harbor and includes a small archipelago. Small parts of the bay extend into Massachusetts. There are more than 30 islands in the bay; the three largest ones are Aquidneck Island, Conanicut Island, and Prudence Island. Bodies of water that are part of Narragansett Bay include the Sakonnet River, Mount Hope Bay, and the southern, tidal part of the Taunton River. The bay opens on Rhode Island Sound and the Atlantic Ocean; Block Island lies less than southwest of its opening. Etymology "Narragansett" is derived from the southern New England Algonquian word meaning "(people) of the small point of land". Geography The watershed of Narragansett Bay has seven river sub-drainage basins, including the Taunton, Pawtuxet, and Blackstone Rivers, and they provide freshwater input at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dudingston
Rear Admiral William Duddingston (1740–1817) was an 18th-century Scottish commander in the Royal Navy, of fame for the Gaspee Affair, ''Gaspee'' Affair, one of the precursors to the American War of Independence. Life He was born in November 1740 in the parish of Kilconquhar in the East Neuk of Fife, the third son of 14 children to James Duddingston (1695-1768) and his wife Margaret Gillespie. The family lived at St Ford (or Sandford) just south-west of Kilconquhar. From 1752 to 1755 he served as a merchant seaman on the Fife coast. He appears as a Royal Navy lieutenant (navy), lieutenant in 1759 but was possibly a midshipman from 1755 to 1759. In September 1768 he was given command of . In March 1772 the ship was ordered to go to Rhode Island to patrol the waters to prevent smuggling of contraband goods in evasion of taxation. In these seizures the crew were awarded a percentage of the value of the goods seized, which was a strong incentive. Seizures were therefore ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), gaining independence from the British Crown and establishing the United States of America as the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of liberal democracy. American colonists objected to being taxed by the Parliament of Great Britain, a body in which they had no direct representation. Before the 1760s, Britain's American colonies had enjoyed a high level of autonomy in their internal affairs, which were locally governed by colonial legislatures. During the 1760s, however, the British Parliament passed a number of acts that were intended to bring the American colonies under more direct rule from the British metropole and increasingly intertwine the economies of the colonies with those of Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |