|
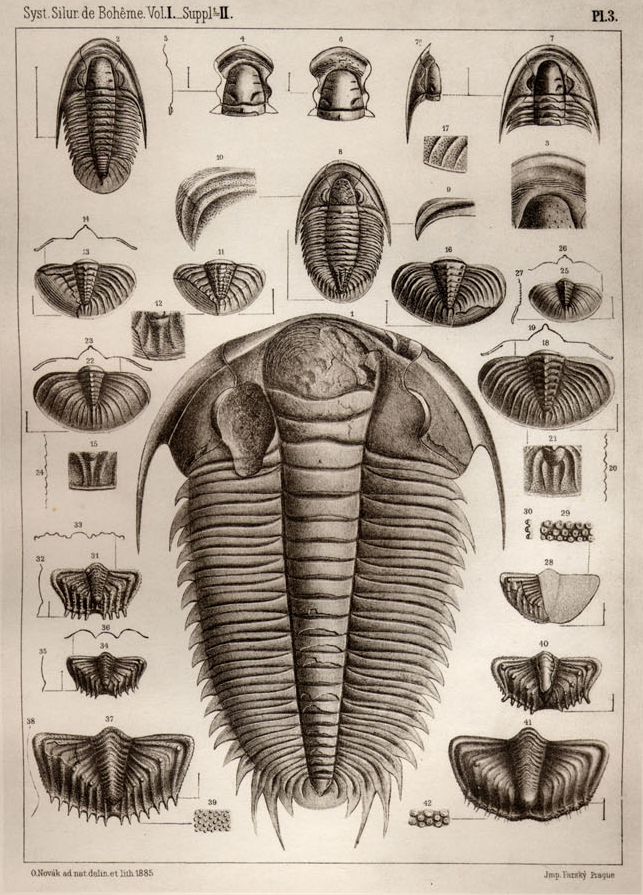
Joachim Barrande
Joachim Barrande (11 August 1799 – 5 October 1883) was a French geologist and palaeontologist. Career Barrande was born at Saugues, Haute Loire, and educated in the École Polytechnique and École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées at Paris. Although he had received the training of an engineer, his first appointment was that of tutor to the duc de Bordeaux (afterwards known as the comte de Chambord), grandson of Charles X, and when the king abdicated in 1830, Barrande accompanied the royal exiles to England and Scotland, and afterwards to Prague. Settling in that city in 1831, he became occupied in engineering works, and his attention was then attracted to the fossils from the Lower Palaeozoic rocks of Bohemia. The publication in 1839 of ''Murchison's Silurian System'' incited Barrande to carry on systematic researches on the equivalent strata in Bohemia. For ten years (1840–1850) he made a detailed study of these rocks, engaging workmen specially to collect fossils, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saugues
Saugues (; oc, Saug) is a commune in the Haute-Loire department in south-central France. Geography The town lies west of Le Puy-en-Velay. History A former stronghold of the Gévaudan, Saugues grew in the 12th century under the authority of the Bishops of Mende and the Lords of Mercœur. A fire in 1788 destroyed most of the town's historical centre. It is in the mountains around and near Saugues that the famous beast of Gévaudan is said to have originated. The Pilgrimage to Compostela Saugues is situated on the Via Podiensis, a variant route of the Way of St. James pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela. Pilgrims arrive in the town from Monistrol-d'Allier, and continue to the next communes of Chanaleilles, La Dômerie du Sauvage and La Chapelle Saint-Roch. Saugues was the traditional meeting point for pilgrims coming from Auvergne, as the path coming from Brioude made them able to avoid Le Puy-en-Velay and instead wind though the Allier river valley through Langeac, Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and community outreach. Considered the first learned society in the United States, it has about 1,000 elected members, and by April 2020 had had only 5,710 members since its creation. Through research grants, published journals, the American Philosophical Society Museum, an extensive library, and regular meetings, the society supports a variety of disciplines in the humanities and the sciences. Philosophical Hall, now a museum, is just east of Independence Hall in Independence National Historical Park; it was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1965. History The Philosophical Society, as it was originally called, was founded in 1743 by Benjamin Franklin, James Alexander, Francis Hopkinson, John Bartram, Philip Syng, Jr. and others a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wollaston Medal
The Wollaston Medal is a scientific award for geology, the highest award granted by the Geological Society of London. The medal is named after William Hyde Wollaston, and was first awarded in 1831. It was originally made of gold (1831–1845), then palladium, a metal discovered by Wollaston (1846–1860). Next in gold again (1861–1929) and then in palladium again (1930–present). Laureates SourcGeological Society 1831–1850 *1831 William 'Strata' Smith *1835 Gideon Mantell *1836 Louis Agassiz *1837 Proby Thomas Cautley *1837 Hugh Falconer *1838 Richard Owen *1839 Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg *1840 André Hubert Dumont *1841 Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart *1842 Leopold von Buch *1843 Jean-Baptiste Élie de Beaumont *1843 Pierre Armand Dufrenoy *1844 William Conybeare *1845 John Phillips *1846 William Lonsdale *1847 Ami Boué *1848 William Buckland *1849 Joseph Prestwich *1850 William Hopkins 1851–1900 *1851 Adam Sedgwick *1852 William Henry Fitton *1853 Adolphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Society Of London
The Geological Society of London, known commonly as the Geological Society, is a learned society based in the United Kingdom. It is the oldest national geological society in the world and the largest in Europe with more than 12,000 Fellows. Fellows are entitled to the postnominal FGS (Fellow of the Geological Society), over 2,000 of whom are Chartered Geologists (CGeol). The Society is a Registered Charity, No. 210161. It is also a member of the Science Council, and is licensed to award Chartered Scientist to qualifying members. The mission of the society is: "Making geologists acquainted with each other, stimulating their zeal, inducing them to adopt one nomenclature, facilitating the communication of new facts and ascertaining what is known in their science and what remains to be discovered". History The Society was founded on 13 November 1807 at the Freemasons' Tavern, Great Queen Street, in the Covent Garden district of London. It was partly the outcome of a previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
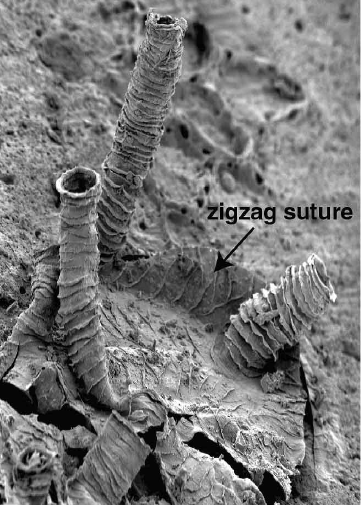
Deiphon
''Deiphon'' is a distinctive genus of Silurian phacopid trilobites of the family Cheiruridae found in Western and Central Europe, and in Central and Eastern United States. The type species, ''D. forbesi'', from England, Bohemia, and Sweden, was discovered and described by the French paleontologist, Joachim Barrande in 1850. Description The glabella was inflated, and globular-shaped, and covered in small wart-like bumps. If it was filled with fat, or oil, the glabellum would have helped to have made the creature positively buoyant. On the other hand, trilobites with large glabellae are often suspected of being predatory, as the volume of glabella would be filled with digestive organs, or used to store captured/swallowed prey. The free cheeks of the cephalon formed a pair of long, curved spines, and the segments of the pleural lobes were separated and elongated to form rib-like struts. These modifications, along with the "V" shaped pygidium give these trilobites a cartoon "fish- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period () and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last extant trilobites finally disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 252 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described. By the time trilobites first appeared in the fossil record, they were already highly diversified and geographically dispersed. Because trilobites had wide diversity and an easily fossilized exoskeleton, they left an extensive fossil record. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusca
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graptolite
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous ( Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch ''Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuselli). Most extinct graptolites belong to two major orders: the bush-like sessile Dendroidea and the planktonic, free-floating Graptoloidea. These orders most likely evolved from encrusting pterobranchs similar to ''Rhabdopleura''. Due to their widespread abundance, plantkonic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became fully terrestrialized. A significant evolutionary milestone d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)