|
Wollaston Medal
The Wollaston Medal is a scientific award for geology, the highest award granted by the Geological Society of London. The medal is named after William Hyde Wollaston, and was first awarded in 1831. It was originally made of gold (1831–1845), then palladium, a metal discovered by Wollaston (1846–1860). Next in gold again (1861–1929) and then in palladium again (1930–present). Laureates SourcGeological Society 1831–1850 *1831 William 'Strata' Smith *1835 Gideon Mantell *1836 Louis Agassiz *1837 Proby Thomas Cautley *1837 Hugh Falconer *1838 Richard Owen *1839 Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg *1840 André Hubert Dumont *1841 Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart *1842 Leopold von Buch *1843 Jean-Baptiste Élie de Beaumont *1843 Pierre Armand Dufrenoy *1844 William Conybeare *1845 John Phillips *1846 William Lonsdale *1847 Ami Boué *1848 William Buckland *1849 Joseph Prestwich *1850 William Hopkins 1851–1900 *1851 Adam Sedgwick *1852 William Henry Fitton *1853 Adolphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
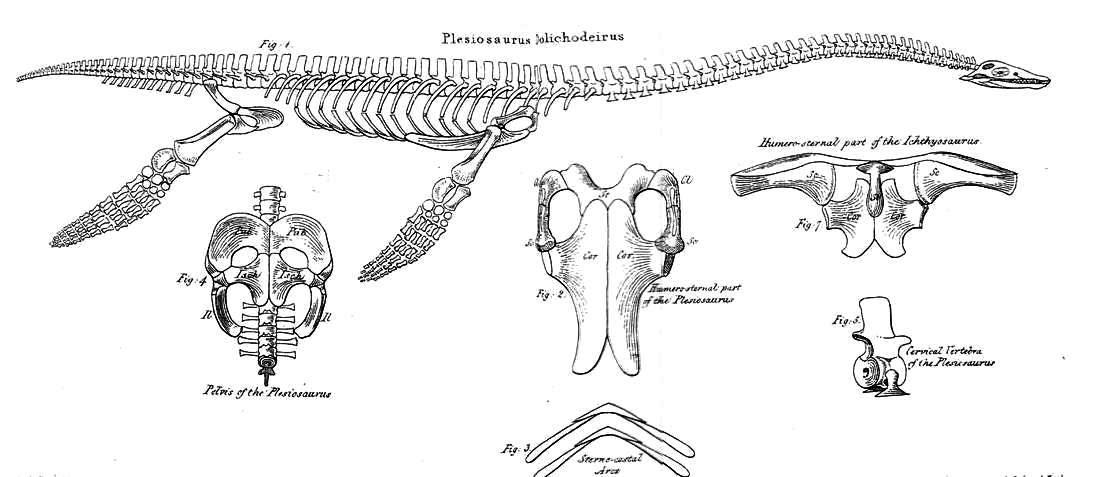
William Conybeare (geologist)
William Daniel Conybeare FRS (7 June 178712 August 1857), dean of Llandaff, was an English geologist, palaeontologist and clergyman. He is probably best known for his ground-breaking work on fossils and excavation in the 1820s, including important papers for the Geological Society of London on ichthyosaur anatomy and the first published scientific description of a plesiosaur. Life and career Childhood and education He was a grandson of John Conybeare, bishop of Bristol (1692–1755), a notable preacher and divine, and son of Dr William Conybeare, rector of St Botolph-without-Bishopsgate. Born in London, he was educated there at Westminster School, then went in 1805 to Christ Church, Oxford, where in 1808 he took his degree of BA, with a first in classics and second in mathematics, and proceeded to MA three years later. Early career Having entered holy orders he became in 1814 curate of Wardington, near Banbury, and he accepted also a lectureship at Brislington near Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Edmond Logan
Sir William Edmond Logan, FRSE FRS FGS (20 April 1798 – 22 June 1875), was a Canadian-born geologist and the founder and first director of the Geological Survey of Canada. Life William Edmond Logan was born into a well-to-do Montreal family in 1798, the third son of William Logan, a baker and owner of real estate, and Janet Edmond, both originally from Scotland. Logan was sent to Edinburgh to receive an education. As was common at the time for young men of means, he learned languages (French, Spanish, some Gaelic and German), music (flute), and became an accomplished artist. In the 1830s, Logan became fascinated with geology while managing a copper-smelting works near Swansea, Wales, on behalf of his uncle, Hart Logan. His self-taught talent for the subject soon brought his geological maps and interpretations to the attention of the most eminent geologists of Great Britain, and it was their later recommendations that clinched Logan's appointment as the founding director of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry De La Beche
Sir Henry Thomas De la Beche KCB, FRS (10 February 179613 April 1855) was an English geologist and palaeontologist, the first director of the Geological Survey of Great Britain, who helped pioneer early geological survey methods. He was the first President of the Palaeontographical Society. Biography De la Beche was born in Welbeck Street, Cavendish Square, London. He was the only son of Thomas De la Beche (1755–1801) and his wife, Elizabeth. The family name was originally Beach, but his father changed it to create a fictional connection with the medieval Barons De la Beche of Aldworth, Berkshire. His father served as a brevet major (later lieutenant-colonel) in the Norfolk Yeomanry, a regiment of fencibles in the British Army, and was a slave owner with an estate in Jamaica. In 1800 the family travelled to the plantation in Jamaica when Thomas inherited the estate and his father died there in the following year. Mother and son returned to England, having been shipwrecke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard John Griffith
Sir Richard John Griffith Bt. FRS FRSE FGS LLD (20 September 1784 – 22 September 1878), was an Irish geologist, mining engineer and chairman of the Board of Works of Ireland, who completed the first complete geological map of Ireland and was the author of the valuation of Ireland; subsequently known as Griffith's Valuation. Biography Griffith was born in Hume Street, Dublin, Ireland on 20 September 1784, the son of Richard Griffith, MP of Millicent House, and Charity Yorke Bramston, daughter of John Bramston of Oundle. His paternal grandmother was the acclaimed actress, essayist and novelist, Elizabeth Griffith. He went to school in Portarlington and later, while attending school in Rathangan, his school was attacked by the rebels during the rebellion of 1798. He also studied in Edinburgh. In 1799 he obtained a commission in the Royal Irish Artillery, but a year later, when the corps was incorporated with that of Great Britain, he retired, and devoted his attention to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard De Verneuil
Philippe Édouard Poulletier de Verneuil (13 February 180529 May 1873) was a French paleontologist. "Le cas d'Édouard de Verneuil (1805-1873) est tout autant révélateur de la façon dont peut naître la passion. Il se préparait à une carrière de magistrat lorsque.." Life He was born in Paris and educated in law, but being of independent means he was free to follow his own inclinations, and having attended lectures on by |
Adolphe D'Archiac
Étienne Jules Adolphe Desmier de Saint-Simon, Vicomte d'Archiac (24 September 180224 December 1868) was a French geologist and paleontologist. Early life He was born at Reims and educated at the Military School of St. Cyr. He served for nine years as a cavalry officer until 1830, when he retired from the service. Prior to this he had published an historical romance (''Zizim, ou les Chevaliers de Rhodes, roman historique du XVe siècle''); but now geology became his primary focus. In his earlier scientific works, which date from 1835, he described the Tertiary and Cretaceous formations of France, Belgium and England, and dealt especially with the distribution of fossils geographically and in sequence. Later on he investigated the Carboniferous, Devonian and Silurian formations. Magnum opus His best work was "''Histoire des progrès de la géologie de 1834 à 1859''", published in eight volumes (1847–1860). In 1853 the Wollaston Medal of the Geological Society of London was aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Fitton
William Henry Fitton (24 January 178013 May 1861) was an Irish physician and amateur geologist. Biography Fitton was born in Dublin and educated at Trinity College in that city. He gained the senior scholarship in 1798, and graduated in the following year. At this time he began to take an interest in geology and to form a collection of fossils. Having adopted the medical profession, he proceeded in 1808 to Edinburgh, where he attended the lectures of Robert Jameson, and thenceforth his interest in natural history and especially in geology steadily increased. He moved to London in 1809, where he studied medicine and chemistry. In 1811 he presented to the Geological Society of London a description of the geological structure of the vicinity of Dublin, with an account of some rare minerals found in Ireland. He took a medical practice at Northampton in 1812, and for some years the duties of his profession engrossed his time. He was admitted M.D. at Cambridge in 1816. In 1820, havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Sedgwick
Adam Sedgwick (; 22 March 1785 – 27 January 1873) was a British geologist and Anglican priest, one of the founders of modern geology. He proposed the Cambrian and Devonian period of the geological timescale. Based on work which he did on Welsh rock strata, he proposed the Cambrian period in 1835, in a joint publication in which Roderick Murchison also proposed the Silurian period. Later in 1840, to resolve what later became known as the Great Devonian Controversy about rocks near the boundary between the Silurian and Carboniferous periods, he and Murchison proposed the Devonian period. Though he had guided the young Charles Darwin in his early study of geology and continued to be on friendly terms, Sedgwick was an opponent of Darwin's theory of evolution by means of natural selection. He strongly opposed the admission of women to the University of Cambridge, in one conversation describing aspiring female students as "nasty forward minxes." Life and career Sedgwick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hopkins
William Hopkins FRS (2 February 179313 October 1866) was an English mathematician and geologist. He is famous as a private tutor of aspiring undergraduate Cambridge mathematicians, earning him the ''sobriquet'' the " senior-wrangler maker." He also made important contributions in asserting a solid, rather than fluid, interior for the Earth and explaining many geological phenomena in terms of his model. However, though his conclusions proved to be correct, his mathematical and physical reasoning were subsequently seen as unsound. Early life Hopkins was born at Kingston-on-Soar, in Nottinghamshire, the only son of William Hopkins, a gentleman farmer. In his youth he learned practical agriculture in Norfolk before his father rented him a small farm at Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk. However, Hopkins was unsuccessful as a farmer and, when his first wife died sometime around 1821, he took the opportunity to mitigate his losses and enter St Peter's College (now Peterhouse) at the Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Prestwich
Sir Joseph Prestwich, FRS (12 March 1812 – 23 June 1896) was a British geologist and businessman, known as an expert on the Tertiary Period and for having confirmed the findings of Boucher de Perthes of ancient flint tools in the Somme valley gravel beds. Biography Born in Clapham, Prestwich was educated in Paris and Reading before entering University College, London where he studied chemistry and natural philosophy. Whilst a student he founded the short-lived Zetetical Society. In 1830 he began working for the family wine business. This job required him to travel throughout the United Kingdom and also abroad to France and Belgium, and during the course of these travels he made many geological observations. He became a Fellow of Geological Society in 1833 and published his first paper there two years later. His 1836 memoir on the ''Geology of Coalbrookdale'', based upon observations made during 1831 and 1832, established his reputation as a geologist. From 1846 his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Buckland
William Buckland DD, FRS (12 March 1784 – 14 August 1856) was an English theologian who became Dean of Westminster. He was also a geologist and palaeontologist. Buckland wrote the first full account of a fossil dinosaur, which he named '' Megalosaurus''. His work proved that Kirkdale Cave in North Yorkshire had been a prehistoric hyena den, for which he was awarded the Copley Medal. It was praised as an example of how scientific analysis could reconstruct distant events. He pioneered the use of fossilised faeces in reconstructing ecosystems, coining the term coprolites. Buckland followed the Gap Theory in interpreting the biblical account of ''Genesis'' as two widely separated episodes of creation. It had emerged as a way to reconcile the scriptural account with discoveries in geology suggesting the earth was very old. Early in his career Buckland believed he had found evidence of the biblical flood, but later saw that the glaciation theory of Louis Agassiz gave a bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |