|
Jimsar County
Jimsar County is a county in Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. It contains an area of . According to the 2002 census, it has a population of 130,000. Near the town of Jimsar are the ruins of the ancient city of Beiting () or Ting Prefecture (), the headquarters of the Beiting Protectorate during the 8th century. It was later known as Beshbalik () and became one of the capitals of the Uyghur Khaganate and then the Kingdom of Qocho. History The name Beshbalik first appears in history in the description of the events of 713 in the Turkic Kul Tigin inscription. It was one of the largest of five towns in the Uyghur Khaganate. The Tibetans briefly held the city in 790. Established in 1902 as a county, it was known as Fuyuan (孚远) until 1952, when its name was changed to Jimsar. The modern city Jimsar is located at 43°59'N, 89°4'East; It is a location of the Uyghur ancient southern capital Beshbalik or Beshbalyq. "Balıq" means city in Old Turkic language, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of China
Counties ( zh, t=縣, s=县, hp=Xiàn), formally county-level divisions, are found in the third level of the administrative hierarchy in Provinces and Autonomous regions and the second level in municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous counties, county-level cities, banners, autonomous banners and City districts. There are 1,355 counties in Mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of Chinese history. History ''Xian'' have existed since the Warring States period and were set up nationwide by the Qin Dynasty. The number of counties in China proper gradually increased from dynasty to dynasty. As Qin Shi Huang reorganized the counties after his unification, there were about 1,000. Under the Eastern Han Dynasty, the number of counties increased to above 1,000. About 1400 existed when the Sui dynasty abolish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yenisei Kirghiz
The Yenisei Kyrgyz ( otk, 𐰶𐰃𐰺𐰴𐰕:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Qyrqyz bodun), were an ancient Turkic peoples, Turkic people who dwelled along the upper Yenisei River in the southern portion of the Minusinsk Depression from the 3rd century BCE to the 13th century CE. The heart of their homeland was the forested Tannu-Ola mountains, Tannu-Ola mountain range (known in ancient times as the Lao or Kogmen mountains), in modern-day Tuva, just north of Mongolia. The Sayan mountains were also included in their territory at different times. The Yenisei Kyrgyz Khaganate, Kyrgyz Khaganate existed from 550 to 1219 CE; in 840, it took over the leadership of the Uyghur Khaganate, Turkic Khaganate from the Uyghur Khaganate, Uyghurs, expanding the state from the Yenisei territories into Central Asia and the Tarim Basin. History The Yenisei Kyrgyz correlated with :ru:Чаатас, Čaatas culture and may perhaps be correlated to the Tashtyk culture. Their endonym was variously transcribed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jason BeDuhn
Jason David BeDuhn (born 1963) is a historian of religion and culture, currently Professor of Religious Studies at Northern Arizona University. Education BeDuhn holds a B.A. in Religious studies from the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, an M.T.S. in New Testament and Christian Origins from Harvard Divinity School, and a Ph.D. in the Comparative Study of Religions from Indiana University Bloomington. Research Manichaeism and Augustine Much of BeDuhn's published research relates to Manichaeism, particularly its disciplinary and ritual systems, but also its role as a catalyst in religious history, as well as its distinctive interpretation of Christian traditions related to the teachings of Jesus and Paul. BeDuhn considers that the conversion of Augustine from Manichaeism to Nicene Christianity was not a sudden act but a life-long transformation, with the narrative we now have being the product of Augustine's own idealized retrospect. BeDuhn roots Augustine's dissatisfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Yuan
The ''History of Yuan'' (''Yuán Shǐ''), also known as the ''Yuanshi'', is one of the official Chinese historical works known as the ''Twenty-Four Histories'' of China. Commissioned by the court of the Ming dynasty, in accordance to political tradition, the text was composed in 1370 by the official Bureau of History of the Ming dynasty, under direction of Song Lian (1310–1381). The compilation formalized the official history of the preceding Yuan dynasty. Under the guidance of Song Lian, the official dynastic history broke with the old Confucian historiographical tradition, establishing a new historical framework asserting that the influence of history was equal in influence to the great Confucian classics in determining the course of human affairs. Layout and contents The historical work consists of 210 chapters chronicling the history of the Yuan dynasty from the time of Genghis Khan (c. 1162–1227) to the flight of the last Yuan emperor, Toghon Temür ("Emperor Huizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from 1260 to 1294, although after the division of the empire this was a nominal position. He proclaimed the empire's dynastic name "Great Yuan" in 1271, and ruled Yuan China until his death in 1294. Kublai was the second son of Tolui by his chief wife Sorghaghtani Beki, and a grandson of Genghis Khan. He was almost 12 when Genghis Khan died in 1227. He had succeeded his older brother Möngke as Khagan in 1260, but had to defeat his younger brother Ariq Böke in the Toluid Civil War lasting until 1264. This episode marked the beginning of the fragmentation of the empire. Kublai's real power was limited to the Yuan Empire, even though as Khagan he still had influence in the Ilkhanate and, to a significantly lesser degree, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, or Chagatai Ulus ( xng, , translit=Čaɣatay-yin Ulus; mn, Цагаадайн улс, translit=Tsagaadain Uls; chg, , translit=Čağatāy Ulusi; fa, , translit=Xânât-e Joghatây) was a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the late 13th century the khanate extended from the Amu Darya south of the Aral Sea to the Altai Mountains in the border of modern-day Mongolia and China, roughly corresponding to the area once ruled by the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty). Initially, the rulers of the Chagatai Khanate recognized the supremacy of the Great Khan,Dai Matsui – A Mongolian Decree from the Chaghataid Khanate Discovered at Dunhuang. Aspects of Research into Central Asian Buddhism, 2008, pp. 159–178 but by the reign of Kublai Khan, Ghiyas-ud-din Baraq no longer obeyed the emperor's orders. During the mid-14th century, the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asud
The Asud (Mongolian Cyrillic: , IPA: //) were a military group of Alani origin. The Mongol clan Asud is the plural of As, the Arabic name for the Alans. Against the Alans and the Cumans (Kipchaks), the Mongols used divide and conquer tactics by first telling the Cumans to stop allying with the Alans and after the Cumans followed their suggestion the Mongols then attacked the Cumans after defeating the Alans.Halperin, Charles J. 2000. “The Kipchak Connection: The Ilkhans, the Mamluks and Ayn Jalut”. Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London 63 (2). Cambridge University Press: 235. https://www.jstor.org/stable/1559539. Alans were recruited into the Mongol forces with one unit called "Right Alan Guard" which was combined with "recently surrendered" soldiers, Mongols, and Chinese soldiers stationed in the area of the former Kingdom of Qocho and in Besh Balikh the Mongols established a Chinese military colony led by Chinese general Qi Kongzhi (Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
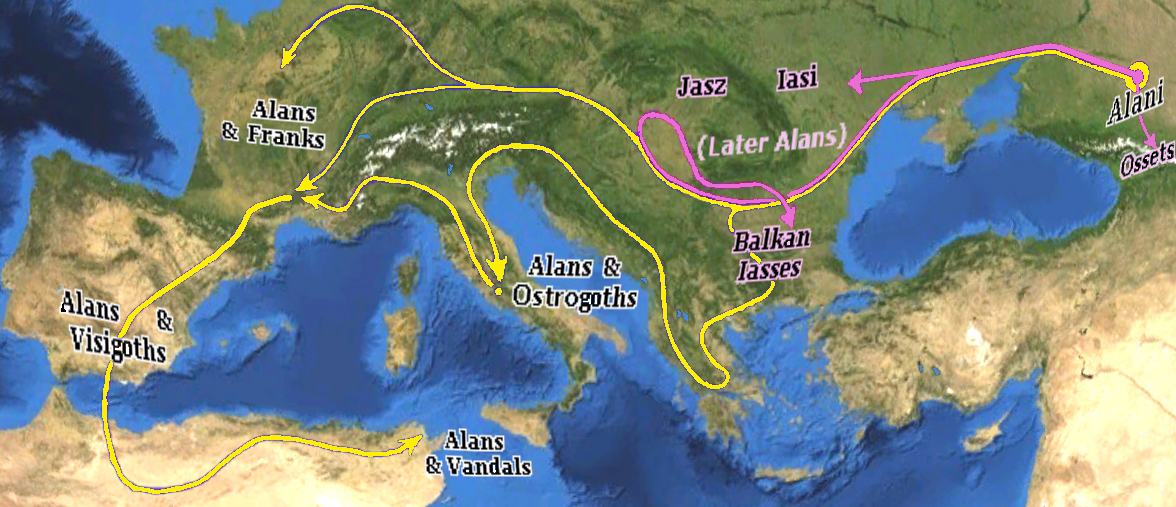
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into parts of the Indian subcontinent, attempted invasions of Southeast Asia and conquered the Iranian Plateau; and westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains. The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomadic tribes in the Mongol homeland under the leadership of Temüjin, known by the more famous title of Genghis Khan (–1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the East with the West, and the Pacific to the Mediterranean, in an enforced ''Pax Mongol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishigten, Khorch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan'' , birth_name = Temüjin , successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan , spouse = , issue = , house = Borjigin , dynasty = Genghisid , regnal name = Genghis Khan () , temple name = Taizu () , posthumous name = Emperor Fatian Qiyun Shengwu () , father = Yesügei , mother = Hoelun , religion = Tengrism , birth_date = , birth_place = Khentii Mountains, Khamag Mongol , death_date = (aged 64–65) , death_place = Xingqing, Western Xia , burial_place = Unknown(presumptively Ikh Khorig, Burkhan Khaldun, Khentii Province) Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death. He came to power by uniting many of the nomadic tribes of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |