|
Jean Laforgue
Jean Laforgue (11 January 1782, Marciac – 6 November 1852, Dresden) was a French scholar living in Dresden, mainly known for having edited and censored the first edition (known as ''Édition Laforgue'') of Giacomo Casanovas memoirs, Histoire de ma vie. Biography Jean Laforgue was born in Marciac, in the Gers department in southwestern France, on 11 January 1782. From 1822 to 1827, he was a French language teacher in Dresden Ritter-Akademie (Dresden knight academy). In 1825, he was given the task of preparing the first French edition of Casanova's memoirs by the publisher Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus. His translation is heavily criticized today not only for having made a lot of changes to the original manuscript, but also for its dull literary style. In approximately 1831, Laforgue gave back the manuscript to Brockhaus, without four chapters whose fate remains unknown as of today. After 1831, he resumed giving French lessons at the Dresden Ritter-Akademie. Laforgue rewritings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
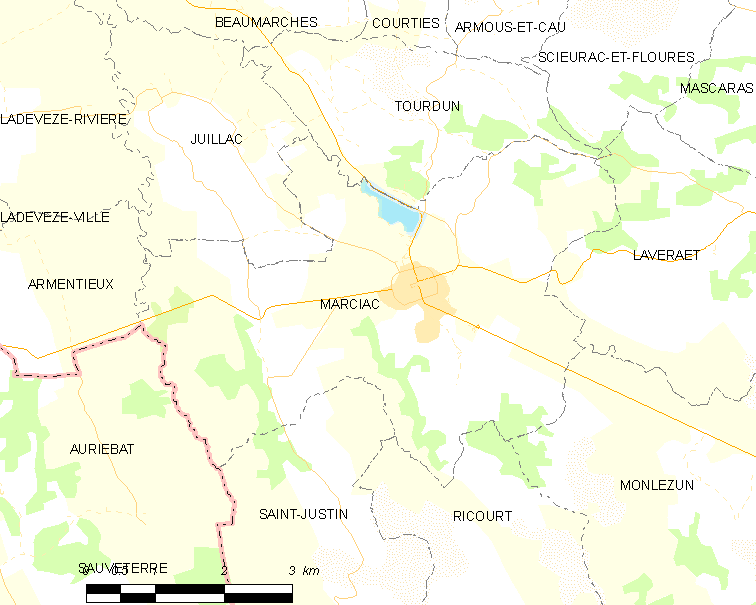
Marciac
Marciac (, , ) is a commune in the Gers department, Occitania, southwestern France. It is known for its annual international festival Jazz in Marciac, which runs for a fortnight every summer. Geography History The name of this Bastide was received by the King of France's representative, seneschal Guichard de Marciac. The abbot of the monastery of La Case Dieu and the count of Pardiac had invited Guichard de Marciac with the hope he would ensure a safe place for Marciac's citizens and guarantee the prosperity of the city for years to come. In 2008, during the financial crisis of 2007–2008, a team from Marciac won the 'best baguette' category in the French-hosted (but United States-sponsored) baking world cup, the Coupe du Monde de la Boulangerie. Population Festivals A great emphasis is placed on jazz in the town, which is taught as a regular subject in local schools. The town itself is known for its annual Jazz in Marciac festival, held for a fortnight in August ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation. Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and most of these systems have undergone substantial standardization, thus exhibiting less dialect variation than the spoken language. These processes can fossilize pronunciation patterns that are no longer routinely observed in speech (e.g., "would" and "should"); they can also reflect deliberate efforts to introduce variability for the sake of national identity, as seen in Noah Webster's efforts to introduce easily noticeable differences between American and British spelling (e.g., "honor" and "honour"). Some nations (e.g. France and Spain) have established language academies in an attempt to regulate orthography officially. For most languages (including English) however, there are no such authorities and a sense of 'correct' orthography evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1782 Births
Year 178 ( CLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Rufus (or, less frequently, year 931 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 178 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Bruttia Crispina marries Commodus, and receives the title of '' Augusta''. * Emperor Marcus Aurelius and his son Commodus arrive at Carnuntum in Pannonia, and travel to the Danube to fight against the Marcomanni. Asia * Last (7th) year of ''Xiping'' era and start of ''Guanghe'' era of the Chinese Han Dynasty. * In India, the decline of the Kushan Empire begins. The Sassanides take over Central Asia. Religion * The Montanist heresy is condemned for the first time. Births * Lü Meng, Chinese general (d. 220) * P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Lacassin
Francis Lacassin (; 18 November 1931 – 12 August 2008) ''lefigaro.fr'' d'après AFP, 14 août 2008 was a French journalist, editor, writer, screenplay writer and essayist. Biography Lacassin started to work for the 's magazine '' Bizarre'' in 1964. He was writing about fantastic and detective literature in '' Magazine Littéraire'', worked for ' ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnier Frères
Garnier () is a mass market cosmetics brand of French cosmetics company L'Oréal. It produces hair care and skin care products. Launch ''Laboratoires Garnier'' was founded in France in 1904 by Alfred Amour Garnier. The company's first product was a patented as the first hair lotion derived from natural plant ingredients. The company then introduced sun-care products in 1936, followed by permanent home hair color in 1960. Expansion and products Over the decades Garnier expanded from hair color and hair care Hair care is an overall term for hygiene and cosmetology involving the hair which grows from the human scalp, and to a lesser extent facial, pubic and other body hair. Hair care routines differ according to an individual's culture and the physic ... into skincare since acquisition in 1970. References {{L'Oreal Brands Shampoo brands L'Oréal brands French brands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like ''liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assembly, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to * the French word for "ancient, old" ** Société des anciens textes français * the French for "former, senior" ** Virelai ancien ** Ancien Régime ** Ancien Régime in France {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus
Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus (4 May 1772 – 20 August 1823) was a German encyclopedia publisher and editor, famed for publishing the '' Conversations-Lexikon'', which is now published as the Brockhaus encyclopedia. Biography Brockhaus was educated at the gymnasium of his native Dortmund, and from 1788 to 1793 served an apprenticeship in a mercantile house at Düsseldorf. He then devoted two years at the University of Leipzig to the study of modern languages and literature, after which he set up in Dortmund an emporium for English goods. In 1801, he transferred this business to Arnheim, and in the following year to Amsterdam. In 1805, having given up his first line of trade, Brockhaus began business as a publisher. Two journals projected by him were not allowed by the government to survive for any length of time, and in 1810 the complications in the affairs of Holland induced him to return homewards. In 1811 he settled at Altenburg. About three years previously he had purc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg and Cologne), and the third most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Radeberg and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. Many boroughs west of the Elbe lie in the foreland of the Ore Mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight Academy
Knight academies were first established in Western European states in the late 16th century. They prepared aristocratic youth for state and military service. It added to the hitherto rudimentary education of the aristocratic youth natural science, statesmanship and languages. Later many converted to humanistic high schools. History Institutions exclusively for the education of nobles emerged only in the second half of the 16th century. They had their origin in Southern and Western Europe and were then also established in the Holy Roman Empire. At first sons of nobles went to French academies during their Grand Tour. The first German institution modeled on the French ones was the Collegium illustre of Tübingen, founded in 1594. In 1598, another knight academy was founded in Kassel. In the course of the 17th century, many more facilities were founded, such as the ''Kriegs- und Ritterschule'' of Siegen. After the Thirty Years' War, two new academies in Lüneburg (1655) and Wolfen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French ( Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the ''Organisation internationale de la Francophonie'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |