|
Jean-Raymond Abrial
Jean-Raymond Abrial (6 November 1938 – 26 May 2025) was a French computer scientist and inventor of the Z and B formal methods. Abrial was a student at the École Polytechnique (class of 1958). Abrial's 1974 paper ''Data Semantics'' laid the foundation for a formal approach to Data Models; although not adopted directly by practitioners, it directly influenced all subsequent models from the Entity-Relationship Model through to RDF. J.-R. Abrial is the father of the Z notation (typically used for formal specification of software), during his time at the Programming Research Group under Prof. Tony Hoare within the Oxford University Computing Laboratory (now Oxford University Department of Computer Science), arriving in 1979 and sharing an office and collaborating with Cliff Jones. He later initiated the B-Method, with better tool-based software development support for refinement from a high-level specification to an executable program, including the Rodin tool. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in France. The palace is owned by the government of France and since 1995 has been managed, under the direction of the Ministry of Culture (France), French Ministry of Culture, by the Public Establishment of the Palace, Museum and National Estate of Versailles. About 15,000,000 people visit the palace, park, or gardens of Versailles every year, making it one of the most popular tourist attractions in the world. Louis XIII built a hunting lodge at Versailles in 1623. His successor, Louis XIV, expanded the château into a palace that went through several expansions in phases from 1661 to 1715. It was a favourite residence for both kings, and in 1682, Louis XIV moved the seat of his court and government to Versailles, making the palace the ''de fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodin Tool
The Rodin tool is a software tool for formal modelling in Event-B. It was developed as part of several collaborative European Union projects, including initially the RODIN project (2004–2007). Overview Event-B is a notation and method developed from the B-Method and is intended to be used with an incremental style of modelling. The idea of incremental modelling has been taken from programming: modern programming languages come with integrated development environment that make it easy to modify and improve programs. The Rodin tool provides such an environment for Event-B. Two characteristics of the Rodin tool are its ease of use and its extensibility. The tool focuses on modelling. It allows the user to modify models and try out variations of a model. The tool is also extensible. This makes it possible to adapt the tool to specific needs, so the tool can be adapted to fit into existing development processes instead of demanding the opposite. There is an associated Event-B wik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
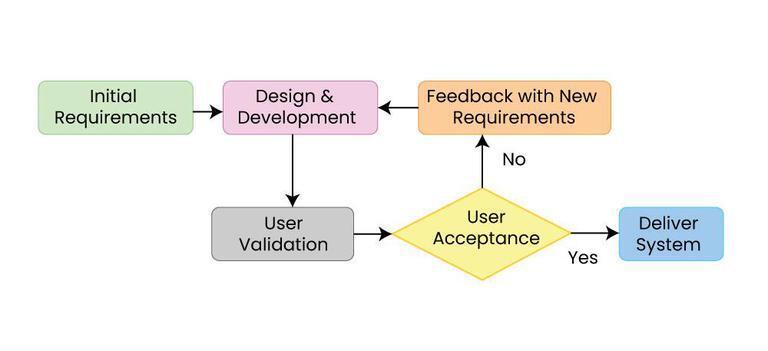
Computer Program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to Execution (computing), execute. It is one component of software, which also includes software documentation, documentation and other intangible components. A ''computer program'' in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to Execution (computing), execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be Translator (computing), translated to machine instructions using a compiler written for the language. (Assembly language programs are translated using an Assembler (computing), assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within an interpreter (computing), interpreter written for the language. If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system Loader (computing), loads it into Random-access memory, memory and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Specification
In computer science, formal specifications are mathematically based techniques whose purpose is to help with the implementation of systems and software. They are used to describe a system, to analyze its behavior, and to aid in its design by verifying key properties of interest through rigorous and effective reasoning tools. These specifications are ''formal'' in the sense that they have a syntax, their semantics fall within one domain, and they are able to be used to infer useful information. Motivation In each passing decade, computer systems have become increasingly more powerful and, as a result, they have become more impactful to society. Because of this, better techniques are needed to assist in the design and implementation of reliable software. Established engineering disciplines use mathematical analysis as the foundation of creating and validating product design. Formal specifications are one such way to achieve this in software engineering reliability as once predicted. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refinement (computing)
Refinement is a generic term of computer science that encompasses various approaches for producing correct computer programs and simplifying existing programs to enable their formal verification. Program refinement In formal methods, program refinement is the verifiable transformation of an ''abstract'' (high-level) formal specification into a ''concrete'' (low-level) executable program. '' Stepwise refinement'' allows this process to be done in stages. Logically, refinement normally involves implication, but there can be additional complications. The progressive just-in-time preparation of the product backlog (requirements list) in agile software development approaches, such as Scrum, is also commonly described as refinement. Data refinement Data refinement is used to convert an abstract data model (in terms of sets for example) into implementable data structures (such as arrays). Operation refinement converts a specification of an operation on a system into an implementabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, writing source code, code, in that it includes conceiving the goal, evaluating feasibility, analyzing software requirements, requirements, software design, design, software testing, testing and software release life cycle, release. The process is part of software engineering which also includes management, organizational management, Software project management, project management, configuration management and other aspects. Software development involves many skills and job specializations including software programmer, programming, software test, testing, Technical writing, documentation, graphic design, user support, marketing, and fundraising. Software development involves many software tools, tools including: compiler, integrated develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCS-FACS
BCS-FACS is the BCS ''Formal Aspects of Computing Science'' Specialist Group. Overview The FACS group, inaugurated on 16 March 1978, organizes meetings for its members and others on formal methods and related computer science topics. There is an associated journal, '' Formal Aspects of Computing'', published by Springer, and a more informal ''FACS FACTS'' newsletter. The group celebrated its 20th anniversary with a meeting at the Royal Society in London in 1998, with presentations by four eminent computer scientists, Mike Gordon, Tony Hoare, Robin Milner and Gordon Plotkin, all Fellows of the Royal Society. From 2002 to 2008 and since 2013 again, the Chair of BCS-FACS has been Jonathan Bowen. Jawed Siddiqi was chair during 2008–2013. In December 2002, BCS-FACS organized a conference on the ''Formal Aspects of Security'' (FASec'02) at Royal Holloway, University of London. In 2004, FACS organized a major event at London South Bank University to celebrate its own 25th anniver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FACS FACTS
BCS-FACS is the British Computer Society, BCS ''Formal Aspects of Computing Science'' Specialist Group. Overview The FACS group, inaugurated on 16 March 1978, organizes meetings for its members and others on formal methods and related computer science topics. There is an associated journal, ''Formal Aspects of Computing'', published by Springer Science+Business Media, Springer, and a more informal ''FACS FACTS'' newsletter. The group celebrated its 20th anniversary with a meeting at the Royal Society in London in 1998, with presentations by four eminent computer scientists, Michael J. C. Gordon, Mike Gordon, Tony Hoare, Robin Milner and Gordon Plotkin, all Fellow of the Royal Society, Fellows of the Royal Society. From 2002 to 2008 and since 2013 again, the Chair of BCS-FACS has been Jonathan Bowen. Jawed Siddiqi was chair during 2008–2013. In December 2002, BCS-FACS organized a conference on the ''Formal Aspects of Security'' (FASec'02) at Royal Holloway, University of London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliff Jones (computer Scientist)
Clifford "Cliff" B. Jones (born 1 June 1944) is a British computer scientist, specializing in research into formal methods. He undertook a late Doctor of Philosophy, DPhil at the Oxford University Computing Laboratory (now the Oxford University Department of Computer Science) under Tony Hoare, awarded in 1981. Jones' thesis proposed an extension to Hoare logic for handling concurrent programs, rely/guarantee. Prior to his DPhil, Jones worked for IBM, between the Hursley and IBM Laboratory Vienna, Vienna Laboratories. In Vienna, Jones worked with Peter Lucas (computer scientist), Peter Lucas, Dines Bjørner and others on the Vienna Development Method (VDM), originally as a method for specifying the formal semantics of programming languages, and subsequently for specifying and verifying programs. Cliff Jones was a professor at the Victoria University of Manchester in the 1980s and early 1990s, worked in industry at Harlequin for a period, and is now a Professor of Computing Scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Department Of Computer Science
The Department of Computer Science is the computer science department of the University of Oxford, England, which is part of the university's Mathematical, Physical and Life Sciences Division. It was founded in 1957 as the Computing Laboratory. By 2014 the staff count was 52 members of academic staff and over 80 research staff. The 2019, 2020 and 2021 Times World University Subject Rankings places Oxford University 1st in the world for Computer Science. Oxford University is also the top university for computer science in the UK and Europe according to Business Insider. The 2020 QS University Subject Rankings places The University of Oxford 5th in the world (with the University of Cambridge placing 6th) for Computer Science. Teaching From its foundation the department taught undergraduates reading for mathematics and engineering degrees, but in 1985 the department's first undergraduate course was established, in 'Mathematics and Computation', followed in 1994 by the 'Computation' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |