|
Javan Tiger
The Javan tiger was a '' Panthera tigris sondaica'' population native to the Indonesian island of Java until the mid-1970s. It was hunted to extinction, and its natural habitat converted for agricultural land use and infrastructure. It was one of the three tiger populations in the Sunda Islands. Formerly, it was regarded as a distinct tiger subspecies, which had been assessed as extinct on the IUCN Red List in 2008. In 2017, felid taxonomy was revised and the Javan tiger subordinated to ''P. t. sondaica'' along with the Sumatran tiger and the Bali tiger. Results of mitochondrial DNA analysis of 23 tiger samples from museum collections indicate that tigers colonized the Sunda Islands during the last glacial period 11,000–12,000 years ago. Taxonomy ''Felis tigris sondaicus'' was proposed by Coenraad Jacob Temminck in 1844 as a scientific name for the Javan tiger. In 1929, the British taxonomist Reginald Innes Pocock subordinated the tiger under the genus ''Panthera'' using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujung Kulon
Ujung Kulon National Park is at the westernmost tip of Java, in Banten province of Indonesia. It includes the volcanic island group of Krakatoa in Lampung province, and other islands including Panaitan, as well as smaller offshore islets such as Handeuleum and Peucang in the Sunda Strait. Ujung Kulon means ''Western End'' or ''Point West''. Geography The park encompasses an area of (of which is marine), most of which lies on a peninsula reaching into the Indian Ocean. The explosion of nearby Krakatau in 1883 produced a tsunami (giant wave) that eliminated the villages and crops of the coastal areas on the western peninsula, and covered the entire area in a layer of ash averaging thick. This caused the total evacuation of the peninsula by humans, thereby allowing it to become a repository for much of Java’s flora and fauna, and most of the remaining lowland forest on the island. History It is Indonesia's first proposed national park and was declared a UNESCO World Herit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Innes Pocock
Reginald Innes Pocock F.R.S. (4 March 1863 – 9 August 1947) was a British zoologist. Pocock was born in Clifton, Bristol, the fourth son of Rev. Nicholas Pocock and Edith Prichard. He began showing interest in natural history at St. Edward's School, Oxford. He received tutoring in zoology from Sir Edward Poulton, and was allowed to explore comparative anatomy at the Oxford Museum. He studied biology and geology at University College, Bristol, under Conwy Lloyd Morgan and William Johnson Sollas. In 1885, he became an assistant at the Natural History Museum, and worked in the section of entomology for a year. He was put in charge of the collections of Arachnida and Myriapoda. He was also given the task to arrange the British birds collections, in the course of which he developed a lasting interest in ornithology. The 200 papers he published in his 18 years at the museum soon brought him recognition as an authority on Arachnida and Myriapoda; he described between 300 and 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the ''Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna. The tiger is estimated to have been present in the Indian subcontinent since the Late Pleistocene, for about 12,000 to 16,500 years. Today, it is threatened by poaching, loss and fragmentation of habitat, and was estimated at comprising fewer than 2,500 wild individuals by 2011. None of the ''Tiger Conservation Landscapes'' within its range is considered large enough to support an effective population of more than 250 adult individuals. The Bengal tiger's historical range covered the Indus River valley until the early 19th century, almost all of India, Pakistan, southern Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and southwestern China. Today, it inhabits India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan and southwestern China. India's tiger population was estimated at 2,603–3,346 individuals by 2018. Around 300–5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovid
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species, the family Bovidae consists of 11 (or two) major subfamilies and thirteen major tribes. The family evolved 20 million years ago, in the early Miocene. The bovids show great variation in size and pelage colouration. Excepting some domesticated forms, all male bovids have two or more horns, and in many species, females possess horns, too. The size and shape of the horns vary greatly, but the basic structure is always one or more pairs of simple bony protrusions without branches, often having a spiral, twisted or fluted form, each covered in a permanent sheath of keratin. Most bovids bear 30 to 32 teeth. Most bovids are diurnal. Social activity and feeding usually peak during dawn and dusk. Bovids typically rest before dawn, during midd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer (caribou), white-tailed deer, the roe deer, and the moose. Male deer of all species (except the water deer), as well as female reindeer, grow and shed new antlers each year. In this they differ from permanently horned antelope, which are part of a different family ( Bovidae) within the same order of even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla). The musk deer ( Moschidae) of Asia and chevrotains ( Tragulidae) of tropical African and Asian forests are separate families that are also in the ruminant clade Ruminantia; they are not especially closely related to Cervidae. Deer appear in art from Paleolithic cave paintings onwards, and they have played a role in mythology, religion, and literature throughout history, as well as in hera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (island)
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's most populous island, home to approximately 56% of the Indonesian population. Indonesia's capital city, Jakarta, is on Java's northwestern coast. Many of the best known events in Indonesian history took place on Java. It was the centre of powerful Hindu-Buddhist empires, the Islamic sultanates, and the core of the colonial Dutch East Indies. Java was also the center of the Indonesian struggle for independence during the 1930s and 1940s. Java dominates Indonesia politically, economically and culturally. Four of Indonesia's eight UNESCO world heritage sites are located in Java: Ujung Kulon National Park, Borobudur Temple, Prambanan Temple, and Sangiran Early Man Site. Formed by volcanic eruptions due to geologic subduction of the Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
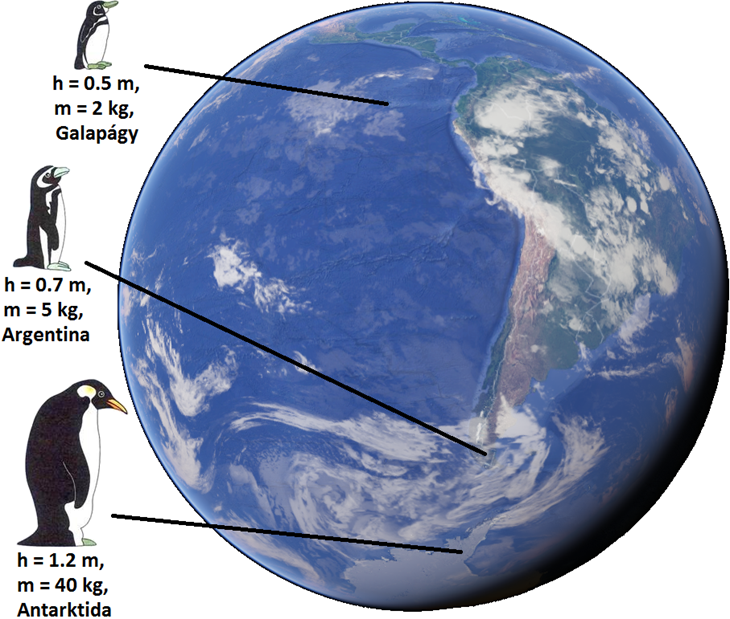
Bergmann’s Rule
Bergmann's rule is an ecogeographical rule that states that within a broadly distributed taxonomic clade, populations and species of larger size are found in colder environments, while populations and species of smaller size are found in warmer regions. Bergmann's rule only describes the overall size of the animals, but does not include body parts like Allen's rule does. Although originally formulated in relation to species within a genus, it has often been recast in relation to populations within a species. It is also often cast in relation to latitude. It is possible that the rule also applies to some plants, such as ''Rapicactus''. The rule is named after nineteenth century German biologist Carl Bergmann, who described the pattern in 1847, although he was not the first to notice it. Bergmann's rule is most often applied to mammals and birds which are endotherms, but some researchers have also found evidence for the rule in studies of ectothermic species, such as the ant ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Bones
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skullcap. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton. In comparative anatomy, neurocranium is sometimes used synonymously with endocranium or chondrocranium. Structure The neurocranium is divided into two portions: * the membranous part, consisting of flat bones, which surround the brain; and * the cartilaginous part, or chondrocranium, which forms bones of the base of the skull. In humans, the neurocranium is usually considered to include the following eight bones: * 1 ethmoid bone * 1 frontal bone * 1 occipital bone * 2 parietal bones * 1 sphenoid bone * 2 temporal bones The ossicles (three on each side) are usually not included as bones of the neurocranium. There may variably also be extra sutural bones present. Below the neuroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnassial
Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified fourth upper premolar and the first lower molar, however this may vary in family. These teeth are also referred to as sectorial teeth. Taxonomy The name carnivoran is applied to a member of the order Carnivora. Carnivorans possess a common arrangement of teeth called carnassials, in which the first lower molar and the last upper premolar possess blade-like enamel crowns that act similar to a pair of shears for cutting meat. This dental arrangement has been modified by adaptation over the past 60 million years for diets composed of meat, for crushing vegetation, or for the loss of the carnassial function altogether as in seals, sea lions, and walruses. Carnassial dentition Carnassial teeth are modified molars (and in the case of carni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Plane
The squamous part of occipital bone is situated above and behind the foramen magnum, and is curved from above downward and from side to side. External surface The external surface is convex and presents midway between the summit of the bone and the foramen magnum a prominence, the external occipital protuberance and inion. Extending lateralward from this on either side are two curved lines, one a little above the other. The upper, often faintly marked, is named the highest nuchal line, and to it the epicranial aponeurosis is attached. The lower is termed the superior nuchal line. That area of the squamous part, which lies above the highest nuchal lines is named the occipital plane ''(planum occipitale)'' and is covered by the '' occipitalis muscle''. That below, termed the nuchal plane, is rough and irregular for the attachment of several muscles. From the external occipital protuberance, an often faintly marked ridge or crest, the median nuchal line, descends to the foram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropenmuseum
The Tropenmuseum ( en, Museum of the Tropics) is an ethnographic museum located in Amsterdam, Netherlands, founded in 1864. One of the largest museums in Amsterdam, the museum accommodates eight permanent exhibitions and an ongoing series of temporary exhibitions, including modern and traditional visual arts and photographic works. The Tropenmuseum is part of the Nationaal Museum van Wereldculturen (Museum of World Cultures), a combination of three ethnographic museums in the Netherlands. History Frederick van Eeden, father of the writer Frederik van Eeden, and secretary of the ''Maatschappij ter bevordering van Nijverheid'' ( en, Society for the Promotion of Industry) established the ''Koloniaal Museum'' ( en, Colonial Museum) in Haarlem in 1864, and opened the museum to the public in 1871. The museum was founded in order to show Dutch overseas possessions, and the inhabitants of these foreign countries, such as Indonesia. In 1871 the institute began research to increase pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Wiesbaden
The Museum Wiesbaden is a two-branch museum of art and natural history in the Hessian capital of Wiesbaden, Germany. It is one of the three Hessian State museums, in addition to the museums in Kassel and Darmstadt. History The foundation of the originally three museums traces back to the citizens of the city and to Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, who stayed in Wiesbaden in 1814/1815 for a rehabilitation measure, and worked hard to establish such a cultural institution. In 1825 he persuaded the Frankfurter private collector to donate his extensive collections of works of art, antiquities and in kind to the Duchy of Nassau in return for the payment of an annuity for life. Under the responsibility of the newly founded associations, but controlled by the ducal government, the citizens of Wiesbaden and the region were able to quickly expand these collections. Together with the pieces of the ("Association for Nassauian Antiquity and Historical Research") founded in 1812, three ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)