|
Java Processor
A Java processor is the implementation of the Java virtual machine (JVM) in hardware. In other words, the Java bytecode that makes up the instruction set of the abstract machine becomes the instruction set of a concrete machine. These were the most popular form of a high-level language computer architecture, and were "an attractive choice for building embedded and real-time systems that are programmed in Java". However, as of 2017, embedded Java is no longer common and no realtime Java chip vendors exist. Implementations There are several research Java processors tested on FPGA, including: * picoJava was the first attempt to build a Java processor, by Sun Microsystems. Its successor picoJava-II was freely available under the Sun Community Source License, and is still available from some archives. * provides hardware support for object-oriented functions * Java Optimized Processor for FPGAs. A PhD thesis iavailable and it has been used in several commercial applications. In 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Virtual Machine
A Java virtual machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. The JVM is detailed by a specification that formally describes what is required in a JVM implementation. Having a specification ensures interoperability of Java programs across different implementations so that program authors using the Java Development Kit (JDK) need not worry about idiosyncrasies of the underlying hardware platform. The JVM reference implementation is developed by the OpenJDK project as open source code and includes a JIT compiler called HotSpot. The commercially supported Java releases available from Oracle are based on the OpenJDK runtime. Eclipse OpenJ9 is another open source JVM for OpenJDK. JVM specification The Java virtual machine is an abstract (virtual) computer defined by a specification. It is a part of the Java runtime environment. The garbage collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Bytecode
Java bytecode is the instruction set of the Java virtual machine (JVM), the language to which Java and other JVM-compatible source code is compiled. Each instruction is represented by a single byte, hence the name bytecode, making it a compact form of data. Due to the nature of bytecode, a Java bytecode program is runnable on any machine with a compatible JVM, without the lengthy process of compiling from source code. Java bytecode is used at runtime either interpreted by a JVM or compiled to machine code via just-in-time (JIT) compilation and run as a native application. As Java bytecode is designed for a cross-platform compatibility and security, a Java bytecode application tends to run consistently across various hardware and software configurations. Relation to Java In general, a Java programmer does not need to understand Java bytecode or even be aware of it. However, as suggested in the IBM developerWorks journal, "Understanding bytecode and what bytecode is li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-level Language Computer Architecture
A high-level language computer architecture (HLLCA) is a computer architecture designed to be targeted by a specific high-level programming language (HLL), rather than the architecture being dictated by hardware considerations. It is accordingly also termed language-directed computer design, coined in and primarily used in the 1960s and 1970s. HLLCAs were popular in the 1960s and 1970s, but largely disappeared in the 1980s. This followed the dramatic failure of the Intel 432 (1981) and the emergence of optimizing compilers and reduced instruction set computer (RISC) architectures and RISC-like complex instruction set computer (CISC) architectures, and the later development of just-in-time compilation (JIT) for HLLs. A detailed survey and critique can be found in . HLLCAs date almost to the beginning of HLLs, in the Burroughs large systems (1961), which were designed for ALGOL 60 (1960), one of the first HLLs. The best known HLLCAs may be the Lisp machines of the 1970s and 1980s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
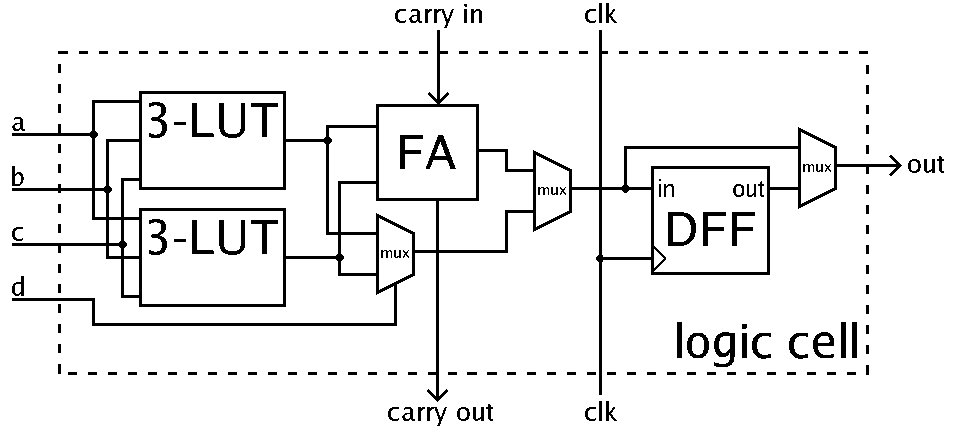
Field-programmable Gate Array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of an array of programmable logic device, programmable logic block, logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit would not be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities. A FPGA configuration is generally written using a hardware descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PicoJava
picoJava is a microprocessor specification dedicated to native execution of Java bytecode without the need for an interpreter or just-in-time compilation. The aim is to speed bytecode execution up by up to 20 times, compared to standard Intel CPU with a Java virtual machine. GNU Compiler Collection added picoJava support in 1999 as machine definition 'pj,'. The open-source version of picoJava has been implemented in an FPGA. See also * Jazelle * MAJC Notes References * McGhan, Harlan; O’Connor, Mike (October 1998). "PicoJava: A Direct Execution Engine For Java Bytecode". ''Computer'', Volume 31, Issue 10: pp. 22–30. * O’Connor, J. Michael; Tremblay, Marc (March/April 1997). "picoJava-I: The Java Virtual Machine in Hardware". ''IEEE Micro'', Volume 17, Issue 2: pp. 45–53. * Hangal, Sudheendra; O'Connor, J. Michael (May/June 1999). "Performance analysis and validation of the picoJava processor." ''IEEE Micro ''IEEE Micro'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, Reduced instruction set computer, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualization, virtualized computing. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California (part of Silicon Valley), on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center. Sun products included computer servers and workstations built on its own Reduced instruction set computer, RISC-based SPARC processor architecture, as well as on x86-based AMD Opteron and Intel Xeon processors. Sun also developed its own computer storage, storage systems and a suite of software products, including the Unix-based SunOS and later Solaris operating system, Solaris operating s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Community Source License
The Sun Community Source License (SCSL) is a community source software licensing model designed by Sun Microsystems that covers the J2SE and J2EE software development kits. Sun introduced the SCSL in 1998 to maintain compatibility within the Java platform and make code available for commercial use. In 2004, Sun began to favor the simpler Java Research License for noncommercial use.{{cite news , first=Martin , last=LaMonica , title=Sun looks to sweeten Java , date=2005-03-16 , url =http://www.zdnetasia.com/sun-looks-to-sweeten-java-39221780.htm , work =ZD Net , access-date = 2010-04-07 The SCSL includes elements similar to an open-source license, but it has significant differences, such as a requirement that code is compatible with Java standards and commercial derivative works are subject to licensing fees. The SCSL is not considered a free software license A free-software license is a notice that grants the recipient of a piece of software extensive rights to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Optimized Processor
Java Optimized Processor (JOP) is a Java processor, an implementation of Java virtual machine (JVM) in hardware. JOP is free hardware under the GNU General Public Licenseversion 3 The intention of JOP is to provide a small hardware JVM for embedded real-time systems. The main feature is the predictability of the execution time of Java bytecodes. JOP is implemented over an FPGA. See also * List of Java virtual machines This article provides non-exhaustive lists of Java SE Java virtual machines (JVMs). It does not include every Java ME vendor. Note that Jakarta EE runs on the standard Java SE JVM but that some vendors specialize in providing a modified JVM optimi ... * SimpCon References External links JOP websiteJOP Github repository * Videoof a talk given at an embedded Java workshop introduces JOP. Java virtual machine {{prog-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of an array of programmable logic device, programmable logic block, logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit would not be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities. A FPGA configuration is generally written using a hardware descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASIC
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficiency video codec. Application-specific standard product chips are intermediate between ASICs and industry standard integrated circuits like the 7400 series or the 4000 series. ASIC chips are typically fabricated using metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, as MOS integrated circuit chips. As feature sizes have shrunk and chip design tools improved over the years, the maximum complexity (and hence functionality) possible in an ASIC has grown from 5,000 logic gates to over 100 million. Modern ASICs often include entire microprocessors, memory blocks including ROM, RAM, EEPROM, flash memory and other large building blocks. Such an ASIC is often termed a SoC ( system-on-chip). Designers of digital ASICs often use a hardware des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcode
In processor design, microcode serves as an intermediary layer situated between the central processing unit (CPU) hardware and the programmer-visible instruction set architecture of a computer. It consists of a set of hardware-level instructions that implement the higher-level machine code instructions or control internal finite-state machine sequencing in many digital processing components. While microcode is utilized in Intel and AMD general-purpose CPUs in contemporary desktops and laptops, it functions only as a fallback path for scenarios that the faster hardwired control unit is unable to manage. Housed in special high-speed memory, microcode translates machine instructions, state machine data, or other input into sequences of detailed circuit-level operations. It separates the machine instructions from the underlying electronics, thereby enabling greater flexibility in designing and altering instructions. Moreover, it facilitates the construction of complex multi-step inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM9E
ARM9 is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by ARM Holdings for microcontroller use. The ARM9 core family consists of ARM9TDMI, ARM940T, ARM9E-S, ARM966E-S, ARM920T, ARM922T, ARM946E-S, ARM9EJ-S, ARM926EJ-S, ARM968E-S, ARM996HS. ARM9 cores were released from 1998 to 2006, and no longer recommended for new IC designs; newer alternatives are ARM Cortex-M cores. Overview With this design generation, ARM moved from a von Neumann architecture (Princeton architecture) to a (modified; meaning split cache) Harvard architecture with separate instruction and data buses (and caches), significantly increasing its potential speed. Most silicon chips integrating these cores will package them as modified Harvard architecture chips, combining the two address buses on the other side of separated CPU caches and tightly coupled memories. There are two subfamilies, implementing different ARM architecture versions. Differences from ARM7 cores Key improvements over ARM7 cores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |