|
January 2013 Northwest Pacific Bomb Cyclone
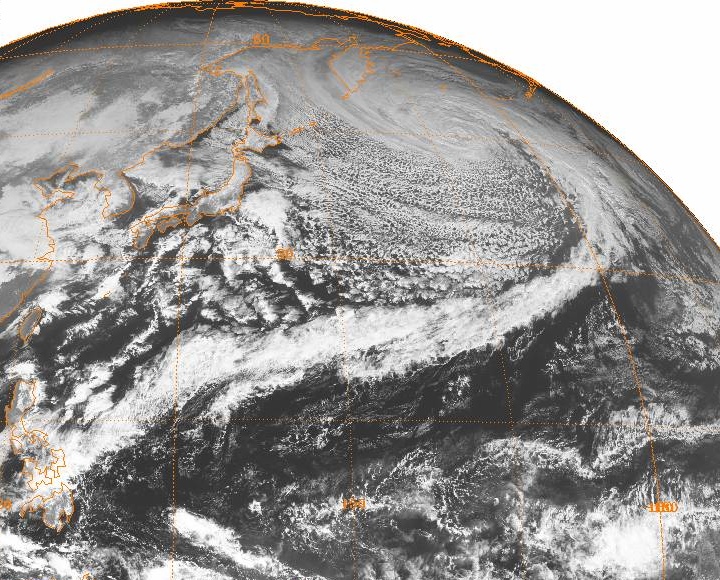
The January 2013 Northwest Pacific cyclone was a powerful extratropical cyclone which caused heavy rainfall and a severe blizzard in Japan in January 2013. Forming northeast of Taiwan on January 13 and absorbing 2013 Pacific typhoon season#Tropical Depression Bising, Tropical Depression Bising soon afterward, the storm quickly intensified in the southern sea off Japan on January 14, and reached its peak intensity east of Japan on January 15, with its central atmospheric pressure decreasing to . The system then weakened, crossed the Kamchatka Peninsula late on January 18, and dissipated east of Hokkaido on January 21. Meteorological history At 0000 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC on January 13, an extratropical cyclone formed northeast of Taiwan, and the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) started to issue storm warnings on the developing low; 18 hours later, the storm southeast of Kyushu absorbed 2013 Pacific typhoon season#Tropical Depression Bising, Tropical Depression Bising whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclone
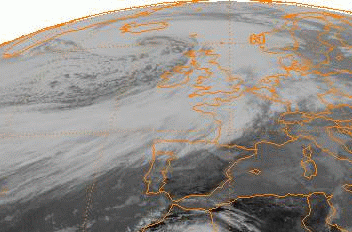
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term " cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Earth between 30° and 60° latitude. They are term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomb (meteorology)
Explosive cyclogenesis (also referred to as a weather bomb, meteorological bomb, explosive development, bomb cyclone, or bombogenesis) is the rapid deepening of an extratropical cyclonic low-pressure area. The change in pressure needed to classify something as explosive cyclogenesis is latitude dependent. For example, at 60° latitude, explosive cyclogenesis occurs if the central pressure decreases by or more in 24 hours. This is a predominantly maritime, winter event, but also occurs in continental settings, This process is the extratropical equivalent of the tropical rapid deepening. Although their cyclogenesis is entirely different from that of tropical cyclones, bomb cyclones can produce winds of , the same order as the first categories of the Saffir–Simpson scale, and yield heavy precipitation. Even though only a minority of the bomb cyclones become so strong, some weaker ones have also caused significant damage. History In the 1940s and 1950s, meteorologists at the Berg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November 2011 Bering Sea Cyclone
The November 2011 Bering Sea cyclone was one of the most powerful extratropical cyclones to affect Alaska on record. On November 8, the National Weather Service (NWS) began issuing severe weather warnings, saying that this was a near-record (or record) storm in the Bering Sea. It rapidly deepened from to in just 24 hours before bottoming out at 943 mbar (hPa; 27.85 inHg), roughly comparable to a Category 3 or 4 hurricane. The storm had been deemed life-threatening by many people. The storm had a forward speed of at least before it had reached Alaska. The storm began affecting Alaska in the late hours of November 8, 2011. The highest gust recorded was on Little Diomede Island. One person was reported missing after being swept into the Bering Sea, and he was later pronounced dead. Meteorological synopsis In early November 2011, an extratropical cyclone developed over the western Pacific Ocean. Gradually intensifying, the system moved rapidly northeastward at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
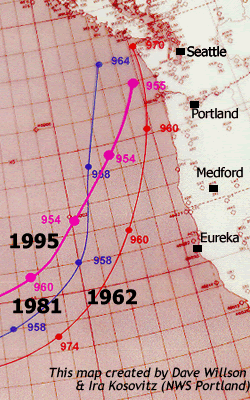
Columbus Day Storm Of 1962
The Columbus Day Storm of 1962 (also known as the Big Blow, and originally, and in Canada as Typhoon Freda) was a Pacific Northwest windstorm that struck the West Coast of Canada and the Pacific Northwest coast of the United States on October 12, 1962. Typhoon Freda was the twenty-eighth tropical depression, the twenty-third tropical storm, and the eighteenth typhoon of the 1962 Pacific typhoon season. Freda originated from a tropical disturbance over the Northwest Pacific on September 28. On October 3, the system strengthened into a tropical storm and was given the name ''Freda'', before becoming a typhoon later that day, while moving northeastward. The storm quickly intensified, reaching its peak as a Category 3-equivalent typhoon on October 5, with maximum 1-minute sustained winds of and a minimum central pressure of . Freda maintained its intensity for another day, before beginning to gradually weaken, later on October 6. On October 9, Freda weakened into a tropical storm, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Gale Of 1880
The Great Gale of 1880 was an intense extratropical cyclone (possibly deeper than 955 millibars (mb) or 28.20") that impacted the Northwest United States on January 9, 1880. Gusts of an estimated 138 miles per hour hit the northwest coast. Buildings, barns, and fences were destroyed. The storm blew a three-masted schooner onto the beach at Coos Bay where it broke in two. Newspaper reports and anecdotes On January 19, 1880, a letter to ''The Daily Oregonian'' from an Astoria, Oregon, Astoria resident reads, From the graphic, and, in some cases, the heart-rending accounts published in the Oregonian descriptive of the disasters resulting from the late severe windstorms in other portions of the state and the neighboring territory, it would appear that our town and county suffered less injury than almost any other. Parts of the lower Columbia River, Columbia seem to have experienced a blizzard, as related from Westport, Oregon, Westport: On the 9th at 2 o-clock P.M., a storm of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coming Of Age Day
is a public holiday in Japan held annually on the second Monday of January. It is held in order to congratulate and encourage all those who have reached or will reach the age of maturity (20 years old) between April 2 of the previous year and April 1 of the current year, and to help them realise that they have become adults. Festivities include held at local and prefectural offices, as well as after-parties among family and friends. History Coming of age ceremonies have been celebrated in Japan since at least 714 CE, during the reign of Empress Genmei when a young prince donned new robes and a hairstyle to mark his passage into adulthood. The holiday was first established in 1948, to be held every year on January 15. In 2000, as a result of the Happy Monday System, Coming of Age Day was changed to the second Monday in January. Japan's low birth rate and shrinking percentage of young people, coupled with disruptions to some ceremonies in recent years (such as an incident in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo Skytree
is a broadcasting and observation tower in Sumida, Tokyo. It became the tallest structure in Japan in 2010Tokyo Sky Tree beats Tokyo Tower, now tallest building in Japan The Mainichi Daily News, 29 March 2010 and reached its full height of in March 2011, making it the tallest tower in the world, displacing the , and the third in the world after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiojiri, Nagano
is a city located in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 67,240 in 27,602 households, and a population density of 230 persons per km². The total area of the city is . Geography Shiojiri is located in central Nagano Prefecture, in the southern end of the Matsumoto Basin. Surrounding municipalities *Nagano Prefecture ** Matsumoto ** Okaya ** Ina ** Tatsuno ** Minamiminowa ** Kiso Town ** Kiso Village ** Asahi Climate The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa''). The average annual temperature in Shiojiri is 11.4 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1161 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 24.6 °C, and lowest in January, at around -1.1 °C. History Shiojiri is located in former Shinano Province, and as its name implies, was traditionally a centre for salt production. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokohama
is the second-largest city in Japan by population and the most populous municipality of Japan. It is the capital city and the most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a 2020 population of 3.8 million. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of Tokyo, in the Kantō region of the main island of Honshu. Yokohama is also the major economic, cultural, and commercial hub of the Greater Tokyo Area along the Keihin region, Keihin Industrial Zone. Yokohama was one of the cities to open for trade with the Western world, West following the 1859 end of the Sakoku, policy of seclusion and has since been known as a cosmopolitan port city, after Kobe opened in 1853. Yokohama is the home of many Japan's firsts in the Meiji (era), Meiji period, including the first foreign trading port and Chinatown (1859), European-style sport venues (1860s), English-language newspaper (1861), confectionery and beer manufacturing (1865), daily newspaper (1870), gas-powered street lamps (1870s), railway station (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blizzard In Shinjuku, Tokyo 2013-01-14
A blizzard is a severe snowstorm characterized by strong sustained winds and low visibility, lasting for a prolonged period of time—typically at least three or four hours. A ground blizzard is a weather condition where snow is not falling but loose snow on the ground is lifted and blown by strong winds. Blizzards can have an immense size and usually stretch to hundreds or thousands of kilometres. Definition and etymology In the United States, the National Weather Service defines a blizzard as a severe snow storm characterized by strong winds causing blowing snow that results in low visibilities. The difference between a blizzard and a snowstorm is the strength of the wind, not the amount of snow. To be a blizzard, a snow storm must have sustained winds or frequent gusts that are greater than or equal to with blowing or drifting snow which reduces visibility to or less and must last for a prolonged period of time—typically three hours or more. Environment Canada defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. It stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the north Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many minor rocks. The Kuril Islands consist of the Greater Kuril Chain and the Lesser Kuril Chain. They cover an area of around , with a population of roughly 20,000. The islands have been under Russian administration since their 1945 invasion as the Soviet Union towards the end of World War II. Japan claims the four southernmost islands, including two of the three largest ( Iturup and Kunashir), as part of its territory, as well as Shikotan and the Habomai islets, which has led to the ongoing Kuril Islands dispute. The disputed islands are k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |