|
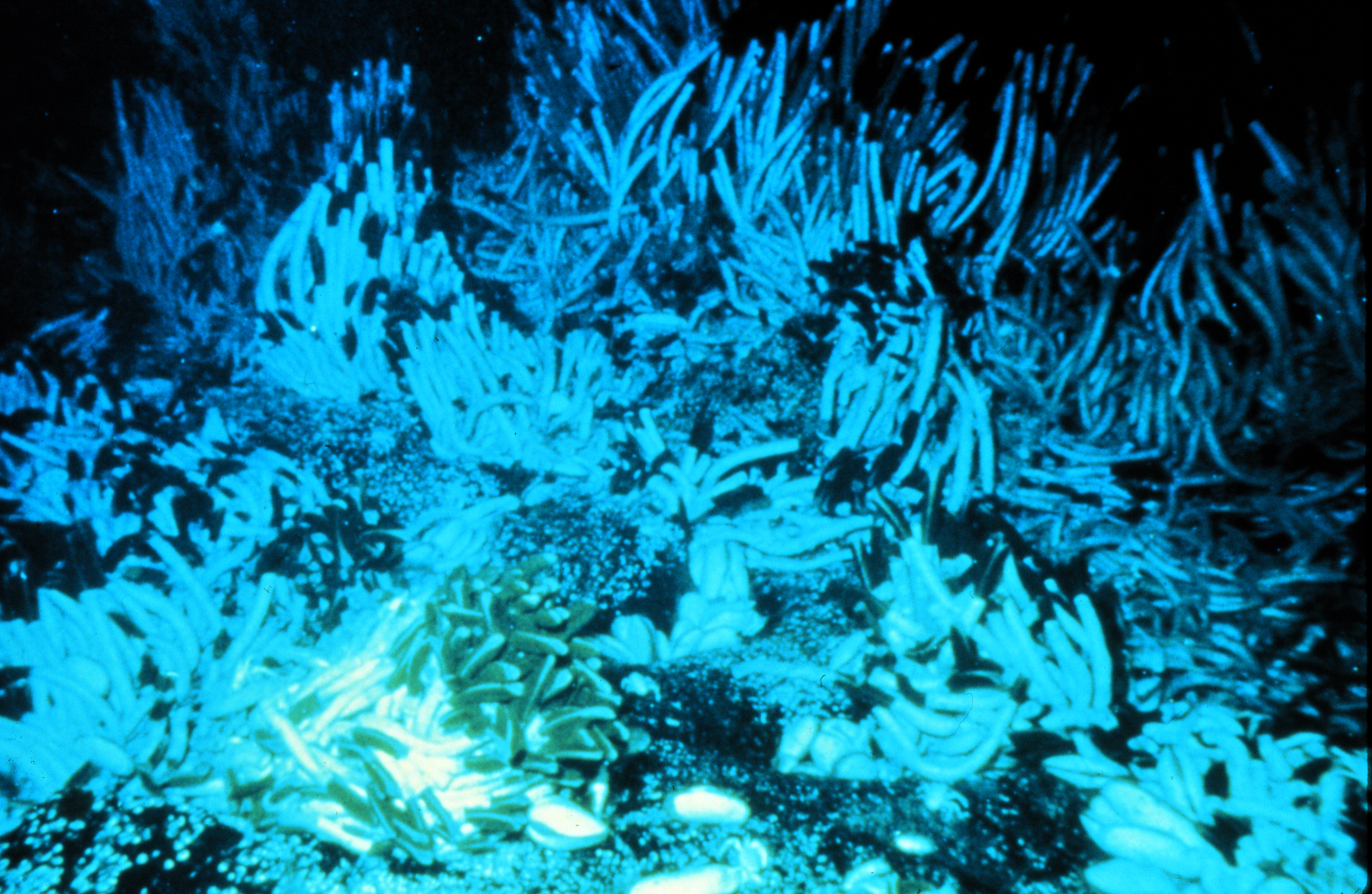
Jack Corliss
John B. ("Jack") Corliss is a scientist who has worked in the fields of geology, oceanography, and the origins of life. Corliss is a University of California, San Diego Alumnus, receiving his PhD from Scripps Institution of Oceanography in the 1960s. As part of his doctoral work under Jerry van Andel, he analyzed samples of basaltic rock from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Chemical traces in these rocks showed evidence of hot water circulation, suggesting the existence of undersea hot springs known as hydrothermal vents. Following the completion of his PhD, Corliss became a researcher at Oregon State University. In 1977, Corliss, Richard von Herzen, and Robert Ballard lead a project using the DSV Alvin submersible to look for the presumed hydrothermal vents near the Galápagos Islands. Corliss, Tjeerd van Andel, and pilot Jack Donnelly were the crew of the Alvin to first discover the vents and the unexpected community of living creatures— giant tube worms, clams, shrimp, etc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
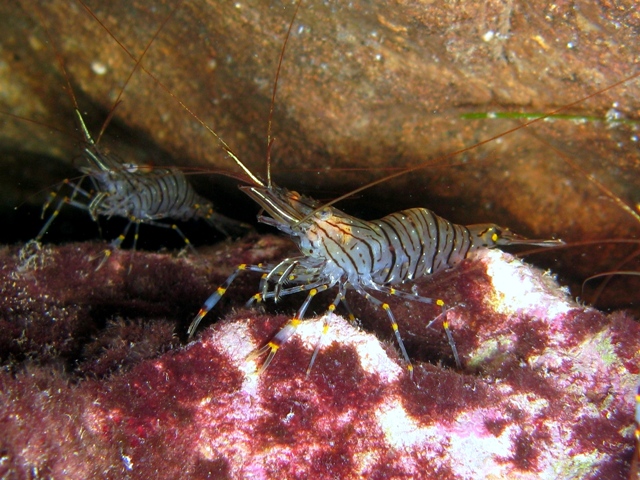
Shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are referred to as "shrimp". More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either group or to only the marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails ( abdomens), long whiskers ( antennae), and slender legs. Any small crustacean which resembles a shrimp tends to be called one. They swim forward by paddling with swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks with the tail driving them backwards very quickly. Crabs and lobsters have strong walking legs, whereas shrimp have thin, fragile legs which they use primarily for perching.Rudloe & Rudloe (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European University
Central European University (CEU) is a private research university accredited in Austria, Hungary, and the United States, with campuses in Vienna and Budapest. The university is known for its highly intensive programs in the social sciences and humanities, low student-faculty ratio, and international student body. A central tenet of the university's mission is the promotion of open societies, as a result of its close association with the Open Society Foundations. CEU is one of eight members comprising the CIVICA Alliance, a group of European higher education institutions in the social sciences, humanities, business management and public policy, such as Sciences Po (France), The London School of Economics and Political Science (UK), Bocconi University (Italy) and the Stockholm School of Economics (Sweden). CEU was founded in 1991 by hedge fund manager, political activist, and billionaire philanthropist George Soros, who provided it with an $880 million endowment, making the uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosphere 2
Biosphere 2 is an American Earth system science research facility located in Oracle, Arizona. Its mission is to serve as a center for research, outreach, teaching, and lifelong learning about Earth, its living systems, and its place in the universe. It is a structure originally built to be an artificial, materially closed ecological system, or vivarium. It remains the largest closed ecological system ever created. Constructed between 1987 and 1991, Biosphere 2 was originally meant to demonstrate the viability of closed ecological systems to support and maintain human life in outer space as a substitute for Earth's biosphere. It was designed to explore the web of interactions within life systems in a structure with different areas based on various biological biomes. In addition to the several biomes and living quarters for people, there was an agricultural area and work space to study the interactions between humans, farming, technology and the rest of nature as a new kind of labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation tends to exist within any given population as a result of genetic mutation and recombination. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection (including sexual selection) and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or more rare within a population. The evolutionary pressures that determine whether a characteristic is common or rare within a population constantly change, resulting in a change in heritable characteristics arising over successive generations. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules. The theory of evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Automata
A cellular automaton (pl. cellular automata, abbrev. CA) is a discrete model of computation studied in automata theory. Cellular automata are also called cellular spaces, tessellation automata, homogeneous structures, cellular structures, tessellation structures, and iterative arrays. Cellular automata have found application in various areas, including physics, theoretical biology and microstructure modeling. A cellular automaton consists of a regular grid of ''cells'', each in one of a finite number of '' states'', such as ''on'' and ''off'' (in contrast to a coupled map lattice). The grid can be in any finite number of dimensions. For each cell, a set of cells called its ''neighborhood'' is defined relative to the specified cell. An initial state (time ''t'' = 0) is selected by assigning a state for each cell. A new ''generation'' is created (advancing ''t'' by 1), according to some fixed ''rule'' (generally, a mathematical function) that determines the new state of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
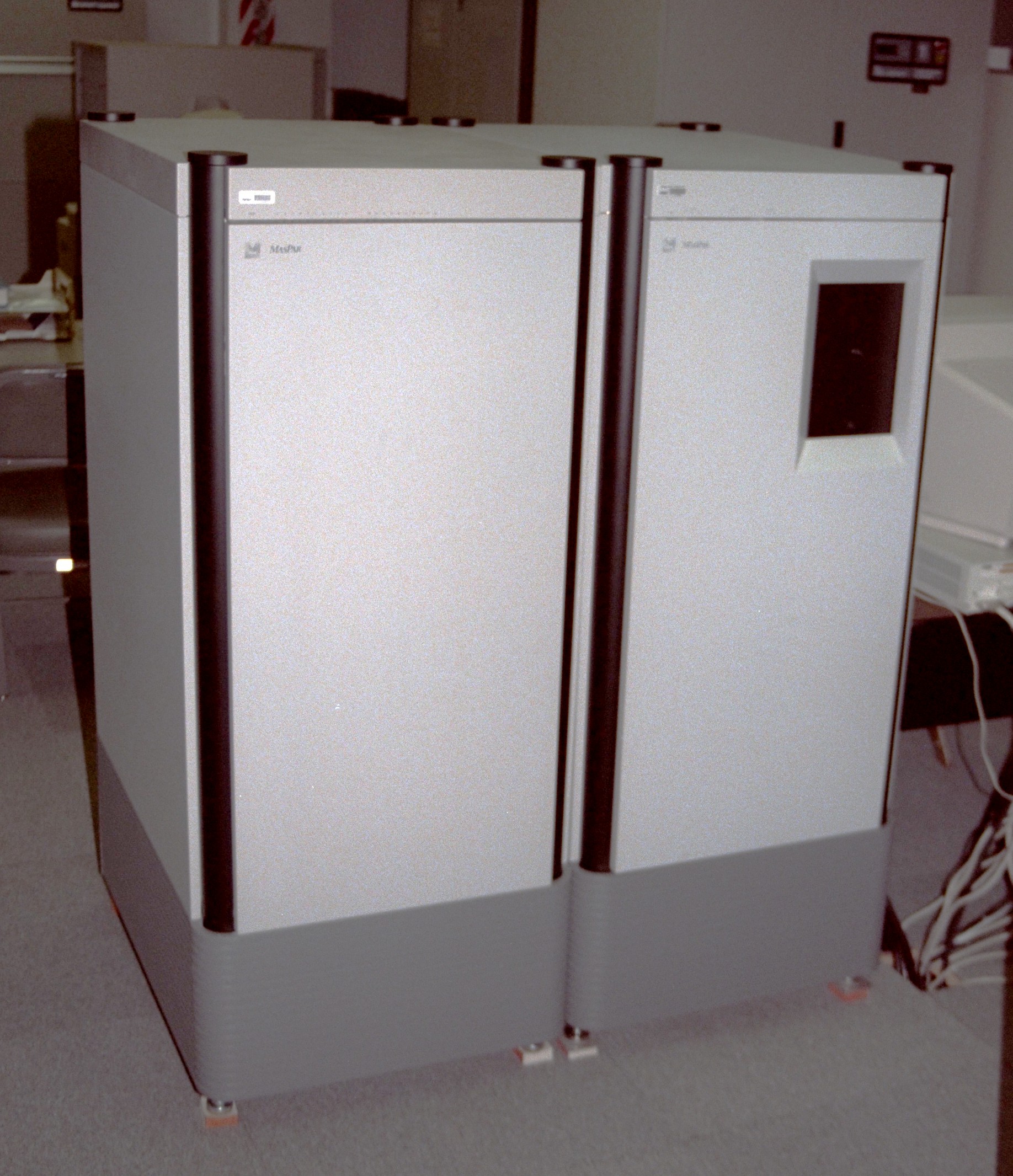
MasPar
MasPar Computer Corporation was a minisupercomputer vendor that was founded in 1987 by Jeff Kalb. The company was based in Sunnyvale, California. History While Kalb was the vice-president of the division of Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) that built integrated circuits, some researchers in that division were building a supercomputer based on the Goodyear MPP (massively parallel processor) supercomputer. The DEC researchers enhanced the architecture by: * making the processor elements to be 4-bit instead of 1-bit John Culver"MasPar: Massively Parallel Computers – 32 cores on a chip" * increasing the connectivity of each processor element to 8 neighbors from 4. * adding a global interconnect for all of the processing elements, which was a triple-redundant switch which was easier to implement than a full crossbar switch. After Digital decided not to commercialize the research project, Kalb decided to start a company to sell this minisupercomputer. In 1990, the first generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodyear MPP
The Goodyear Massively Parallel Processor (MPP) was a massively parallel processing supercomputer built by Goodyear Aerospace for the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. It was designed to deliver enormous computational power at lower cost than other existing supercomputer architectures, by using thousands of simple processing elements, rather than one or a few highly complex CPUs. Development of the MPP began circa 1979; it was delivered in May 1983, and was in general use from 1985 until 1991. It was based on Goodyear's earlier STARAN array processor, a 4x256 1-bit processing element (PE) computer. The MPP was a 128x128 2-dimensional array of 1-bit wide PEs. In actuality 132x128 PEs were configured with a 4x128 configuration added for fault tolerance to substitute for up to 4 rows (or columns) of processors in the presence of problems. The PEs operated in a single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) fashioneach PE performed the same operation simultaneously, on different data elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massively Parallel Processing
Massively parallel is the term for using a large number of computer processors (or separate computers) to simultaneously perform a set of coordinated computations in parallel. GPUs are massively parallel architecture with tens of thousands of threads. One approach is grid computing, where the processing power of many computers in distributed, diverse administrative domains is opportunistically used whenever a computer is available.''Grid computing: experiment management, tool integration, and scientific workflows'' by Radu Prodan, Thomas Fahringer 2007 pages 1–4 An example is BOINC, a volunteer-based, opportunistic grid system, whereby the grid provides power only on a best effort basis.''Parallel and Distributed Computational Intelligence'' by Francisco Fernández de Vega 2010 pages 65–68 Another approach is grouping many processors in close proximity to each other, as in a computer cluster. In such a centralized system the speed and flexibility of the interconnect b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors. It is one of ten major NASA field centers, named in recognition of American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.CENSUS 2000 BLOCK MAP: GODDARD CDP " U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved on September 1, 2018. 1990 Census map of Prince George's County [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corliss Evolution CA
Corliss is both a surname and a given name. People Given name * Corliss Lamont (1902–1995), American philosopher, political activist, and philanthropist * C. C. Moseley (1894–1974), American aviator and aviation businessman * Corliss Palmer (1899–1952), American silent film actress * Corliss P. Stone (1806–1873), mayor of Seattle and businessman * Corliss Waitman (born 1995), Belgian-born American football punter for the Pittsburgh Steelers * Corliss Williamson (born 1973), basketball player Surname * Augustus W. Corliss (1837–1907), American writer, historian and Civil War veteran * George Henry Corliss (1817–1888), inventor of the Corliss steam engine * George W. Corliss (1834–1903), American Civil War recipient of the Medal of Honor * Guy C. H. Corliss (1858–1937), American judge and justice of the Supreme Court of North Dakota * Jack Corliss, scientist and discoverer of undersea hydrothermal vents * Jeb Corliss (born 1976), American skydiver and base jumper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |