|
Jachin And Boaz
According to the Bible, Boaz ( he, ''Bōʿaz'') and Jachin ( ''Yāḵīn'') were two copper, brass or bronze pillars which stood on the porch of Solomon's Temple, the first Temple in Jerusalem. They are used as symbols in Freemasonry and sometimes in religious architecture. They were probably not support structures but free-standing, based on similar pillars found in other nearby temples. Description In the Bible The pillars were nearly six feet (1.8 metres) thick and 27 feet (8.2 metres) tall. The eight-foot (2.4 metres) high brass chapiters, or capitals, on top of the pillars bore decorations, in brass, of lilies. The original measurement as taken from the Torah was in cubits, which records that the pillars were 18 cubits high and 12 cubits around, and hollow—four fingers thick. (). Nets of checkerwork covered the bowl of each chapiter, decorated with rows of 200 pomegranates, wreathed with seven chains for each chapiter, and topped with lilies (, ). The pillars did not surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Romans during the First Jewish–Roman War as head of Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in 67 AD to Roman forces led by Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish Messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Emperor of Rome. In response, Vespasian decided to keep Josephus as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became Emperor in 69 AD, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the emperor's family name of Flavius.Simon Claude Mimouni, ''Le Judaïsme ancien du VIe siècle avant notre ère au IIIe siècle de notre ère : Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (U
Georgia most commonly refers to: * Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia * Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States Georgia may also refer to: Places Historical states and entities * Related to the country in the Caucasus ** Kingdom of Georgia, a medieval kingdom ** Georgia within the Russian Empire ** Democratic Republic of Georgia, established following the Russian Revolution ** Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, a constituent of the Soviet Union * Related to the US state ** Province of Georgia, one of the thirteen American colonies established by Great Britain in what became the United States ** Georgia in the American Civil War, the State of Georgia within the Confederate States of America. Other places * 359 Georgia, an asteroid * New Georgia, Solomon Islands * South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Canada * Georgia Street, in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada * Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada United K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakin, Georgia
Jakin is a city in Early County, Georgia, Early County, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, United States. Incorporated in 1895, Jakin's population was 155 at the 2010 census. Geography Jakin is located in southern Early County at (31.090574, -84.983179). U.S. Route 84 passes through the southern part of the town, leading southeast to Donalsonville, Georgia, Donalsonville and northwest to Dothan, Alabama. Blakely, Georgia, Blakely, the Early County seat, is to the north via Jakin Road. According to the United States Census Bureau, Jakin has a total area of , all land. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 157 people, 71 households, and 42 families residing in the city. The population density was . There were 86 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the city was 70.70% White (U.S. Census), White, 28.03% African American (U.S. Census), African American, 1.27% from Race (United States Census), other races. Hispanic (U.S. Census), Hispanic or Lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
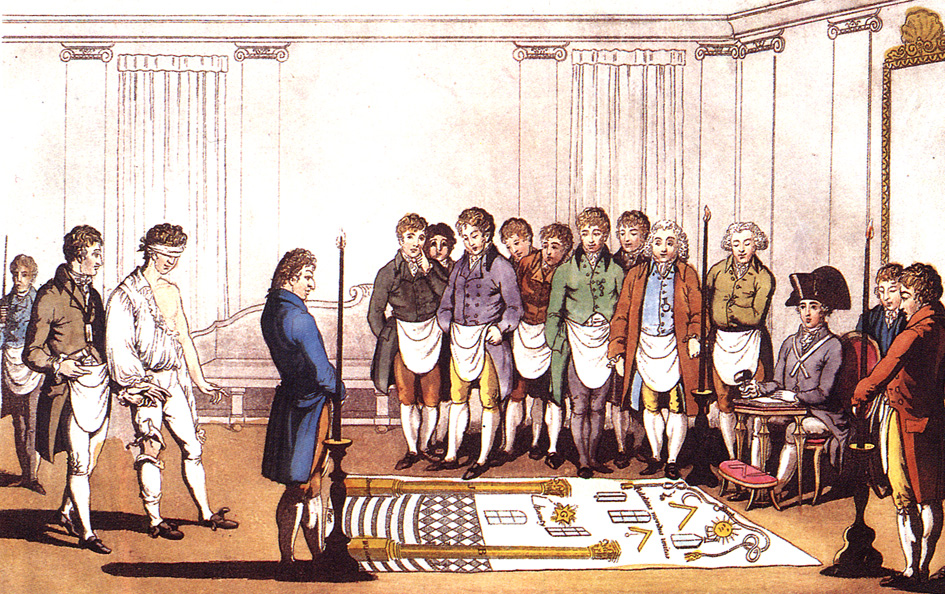
Masonic Ritual And Symbolism
Masonic ritual is the scripted words and actions that are spoken or performed during the degree work in a Masonic lodge. Masonic symbolism is that which is used to illustrate the principles which Freemasonry espouses. Masonic ritual has appeared in a number of contexts within literature including in "The Man Who Would Be King", by Rudyard Kipling, and ''War and Peace'', by Leo Tolstoy. Purpose Freemasonry is described in its own ritual as a "Beautiful and profound system of morality, veiled in allegories and illustrated by symbols". The symbolism of Freemasonry is found throughout the Masonic lodge, and contains many of the working tools of a medieval or renaissance stonemason. The whole system is transmitted to initiates through the medium of Masonic ritual, which consists of lectures and allegorical plays. Common to all of Freemasonry is the three grade system of ''Craft'' or ''Blue Lodge'' freemasonry, whose allegory is centred on the building of the Temple of Solomon, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lund University
, motto = Ad utrumque , mottoeng = Prepared for both , established = , type = Public research university , budget = SEK 9 billion Facts and figures Lund University web site. , head_label = , head = Erik Renström , academic_staff = 4,780 (2022) (academic staff, researchers and employed research students) , administrative_staff = 2,890 (2022) , students = 46 000 (29 000 full-time e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalby Church
Dalby Church ( sv, Dalby kyrka), sometimes also called the Church of the Holy Cross in Dalby (''Helgakorskyrkan i Dalby'') is a church in Dalby, Lund Municipality in the Swedish province of Scania. It is one of the oldest churches in Sweden. When it was built Dalby was part of Denmark, and the church was commissioned by King Sweyn II of Denmark. It was constructed during the second half of the 11th century. For six years, it served as the seat of a bishop, before the diocese was merged with the Diocese of Lund nearby. The church was built with inspiration from Hildesheim Cathedral, and masons from Hildesheim appear to have worked on its construction site. Archaeological excavations have revealed the remains of buildings west of the church, which some researchers have interpreted as the remains of a royal palace connected to the church, or possibly some kind of ecclesiastical compound. The church was enlarged during the 12th century, and a community of canons serving it eventually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Würzburg Cathedral
Würzburg Cathedral (german: Würzburger Dom) is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany, dedicated to Saint Kilian. It is the seat of the Bishop of Würzburg and has served as the burial place for the Prince-Bishops of Würzburg for hundreds of years. With an overall length of 103 metres, it is the fourth largest Romanesque church building in Germany, and a masterpiece of German architecture from the Salian period. Notable later additions include work by Tilman Riemenschneider and Balthasar Neumann. The cathedral was heavily damaged by British bombs in March 1945 but rebuilt post-World War II. History The present cathedral was built from 1040 onwards by Bishop Bruno of Würzburgis. It likely was the third church on the site: the previous two, built in about 787 and 855, were respectively destroyed and severely damaged by fire. After Bruno's accidental death in 1045, his successor Adalbero completed the building in 1075. Due to several rebuildings, notabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscania
Tuscania is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Viterbo, Lazio Region, Italy. Until the late 19th century the town was known as Toscanella. History Antiquity According to the legend, Tuscania was founded by Aeneas' son, Ascanius, where he had found twelve dog pups (whence the Etruscan name ''Tus''-''Cana'', ''cana'' being similar to Latin ''canis'' for "dog"). Another legend attributes the foundation to one Tusco, son of Hercules and Araxes. Evidence of human presence in the area dates from the Neolithic age, but probably the city proper was founded in the 7th century BC when the acropolis on St. Peter's Hill was surrounded by a line of walls. Villages existed in the vicinity. In the following years its strategic position gave Tuscania a leading role in the Etruscan world. After the defeat of the coastal cities by the Greeks (4th century BC), Tuscania also became a maritime trade centre through the port of ''Regas'' (next to today's Montalto di Castro). There is no re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Maria Maggiore, Tuscania
Santa Maria Maggiore is an ancient Romanesque basilica church located at the foot of ''Colle di San Pietro'' (St Peter Hill) in Tuscania, Province of Viterbo, Region of Lazio, Italy. Atop the hill is the Basilica of San Pietro. History A church named ''Santa Maria Maggiore'' is first documented here in a Papal bull from the year 852 from Pope Leo IV to the Bishop of Tuscania. Records of a consecration date to 1206. The church has been reconstructed many times over the centuries. The facade has three distinctive and finely decorated medieval portals. The central one is flanked by two spiral-fluted marble columns nestled on two "lion" bases, and topped by an animal figure. These enclose four thinner columns receding backward, each with their individual capital, generally Corinthian in appearance but some contain human figures. In the pilasters flanking the door stand two figures of the Apostles Peter and Paul, partly rebuilt after an act of vandalism. In the lunette are rectangu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RWS Tarot 02 High Priestess
The three-letter abbreviation RWS may stand for: Businesses and organizations *Ravens Wood School, Keston, London Borough of Bromley, England *Royal Watercolour Society, an English institution of painters working in watercolours *Running with Scissors (company), a video game developer *RWS Group, Europe's largest patent translation and localisation services provider Sports *RWS Bruxelles, a Belgian football club *RWS Motorsport, an auto racing team based in Anger, Bavaria, Germany Weapons * 6.5 X 68 RWS, a cartridge produced by Rheinisch-Westfälische Sprengstoffwerke for the Mauser 98 bolt-action rifle *Remote weapon station, a weapon mounting used on some armored military vehicles Other uses *Audi R8 RWS, the rear wheel series of Audi R8 sports car * ISO 639:rws or Musi, a Malayan language * RESTful web service, appears in Whois-RWS, a type of Internet number lookup service *Resorts World Sentosa, an integrated resort in Singapore *Romano–Ward syndrome Romano–Ward syndrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopaedia Judaica
The ''Encyclopaedia Judaica'' is a 22-volume English-language encyclopedia of the Jewish people, Judaism, and Israel. It covers diverse areas of the Jewish world and civilization, including Jewish history of all eras, culture, holidays, language, scripture, and religious teachings. As of 2010, it had been published in two editions accompanied by a few revisions. The English-language ''Judaica'' was also published on CD-ROM. The CD-ROM version has been enhanced by at least 100,000 hyperlinks and several other features, including videos, slide shows, maps, music and Hebrew pronunciations. While the CD-ROM version is still available, the publisher has discontinued it. The encyclopedia was written by Israeli, American and European professional subject specialists. History Preceding attempts Between 1901 and 1906 ''The Jewish Encyclopedia'' had been published in 12 volumes. It was followed by the ''Jüdisches Lexikon I–II'' (1927–28, in German), ''Encyclopaedia Judaica I–II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)