|
International Conference On Human–Robot Interaction
The ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) is an annual conference "focusing on human-robot interaction with roots in robotics, psychology, cognitive science, human computer interaction (HCI), human factors, artificial intelligence, organizational behavior, anthropology, and other fields". The conference is a joint undertaking of the Association of Computing Machinery (ACM) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) organizations. See also * ACM *ACM SIGAI *IEEE The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operation ... References External links ACM web siteHCI 2016 conference site {{DEFAULTSORT:International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction Software engineering conferences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membership group, claiming nearly 110,000 student and professional members . Its headquarters are in New York City. The ACM is an umbrella organization for academic and scholarly interests in computer science ( informatics). Its motto is "Advancing Computing as a Science & Profession". History In 1947, a notice was sent to various people: On January 10, 1947, at the Symposium on Large-Scale Digital Calculating Machinery at the Harvard computation Laboratory, Professor Samuel H. Caldwell of Massachusetts Institute of Technology spoke of the need for an association of those interested in computing machinery, and of the need for communication between them. ..After making some inquiries during May and June, we believe there is ample interest to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
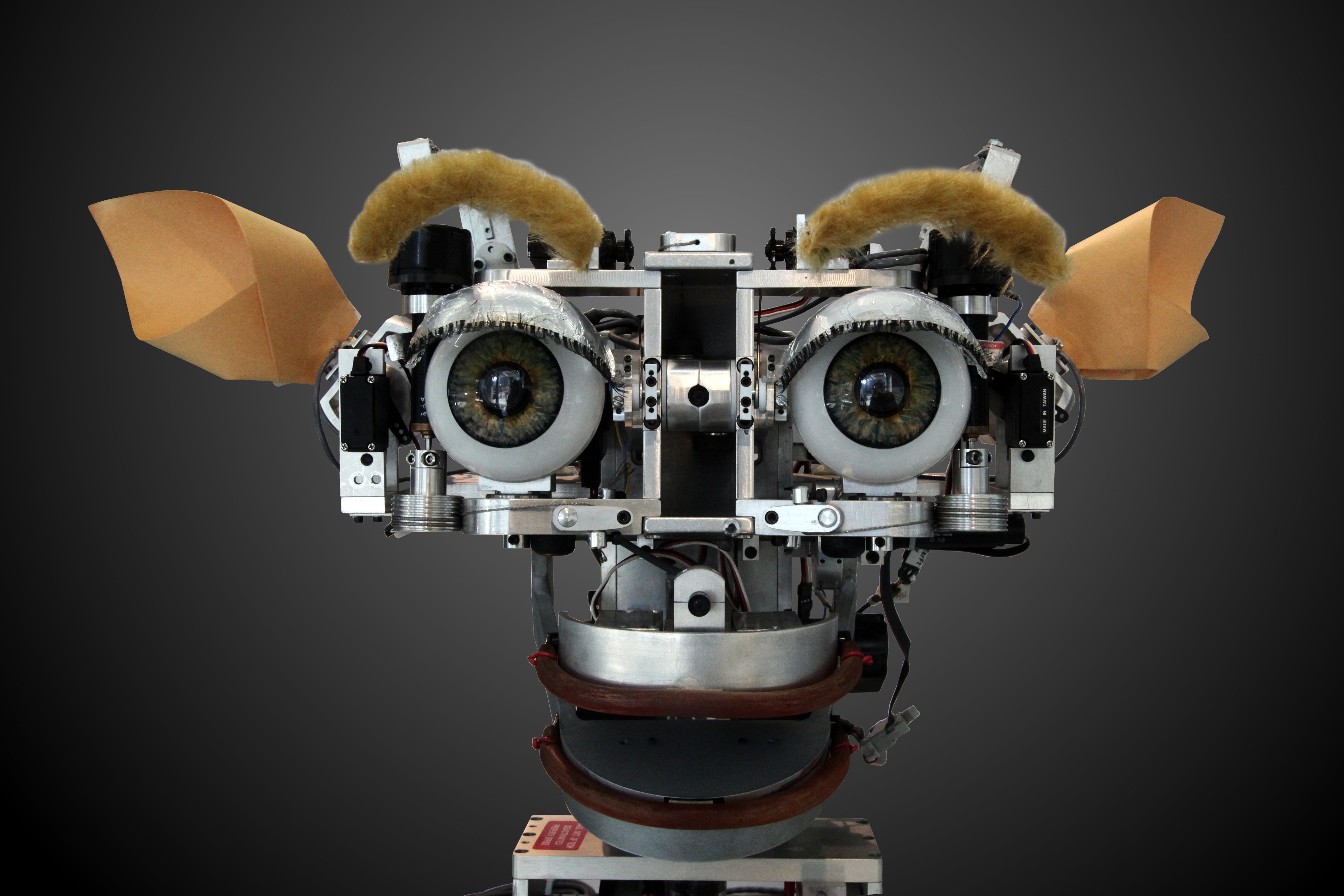
Human–robot Interaction
Human–robot interaction is the study of interactions between humans and robots. It is often referred as HRI by researchers. Human–robot interaction is a multidisciplinary field with contributions from human–computer interaction, artificial intelligence, robotics, natural-language understanding, design, and psychology. Origins Human–robot interaction has been a topic of both science fiction and academic speculation even before any robots existed. Because much of active HRI development depends on natural-language processing, many aspects of HRI are continuations of human communications, a field of research which is much older than robotics. The origin of HRI as a discrete problem was stated by 20th-century author Isaac Asimov in 1941, in his novel ''I, Robot''. He states the Three Laws of Robotics as: # A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm. # A robot must obey the orders by human beings except where such orders would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotics
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrates fields of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, information engineering, mechatronics, electronics, bioengineering, computer engineering, control engineering, software engineering, mathematics, etc. Robotics develops machines that can substitute for humans and replicate human actions. Robots can be used in many situations for many purposes, but today many are used in dangerous environments (including inspection of radioactive materials, bomb detection and deactivation), manufacturing processes, or where humans cannot survive (e.g. in space, underwater, in high heat, and clean up and containment of hazardous materials and radiation). Robots can take any form, but some are made to resemble humans in appearance. This is claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the natural and social sciences. Psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Fernald LD (2008)''Psychology: Six perspectives'' (pp.12–15). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. Ψ (''psi''), the first letter of the Greek word ''psyche'' from which the term psychology is derived (see below), is commonly associated with the science. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as behavioral or cognitive scientists. Some psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human–computer Interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is research in the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and computers. HCI researchers observe the ways humans interact with computers and design technologies that allow humans to interact with computers in novel ways. A device that allows interaction between human being and a computer is known as a "Human-computer Interface (HCI)". As a field of research, human–computer interaction is situated at the intersection of computer science, behavioral sciences, design, media studies, and several other fields of study. The term was popularized by Stuart K. Card, Allen Newell, and Thomas P. Moran in their 1983 book, ''The Psychology of Human–Computer Interaction.'' The first known use was in 1975 by Carlisle. The term is intended to convey that, unlike other tools with specific and limited uses, computers have many uses which often involve an open-ended dialogue between the user and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Factors
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as human factors) is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Four primary goals of human factors learning are to reduce human error, increase productivity, and enhance safety, system availability, and comfort with a specific focus on the interaction between the human and the engineered system. The field is a combination of numerous disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, engineering, biomechanics, industrial design, physiology, anthropometry, interaction design, visual design, user experience, and user interface design. Human factors research employs methods and approaches from these and other knowledge disciplines to study human behavior and generate data relevant to the four primary goals above. In studying and sharing learning on the design of equipment, devices, and processes that fit the human body and its cognitive abilities, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech recognition, computer vision, translation between (natural) languages, as well as other mappings of inputs. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' of Oxford University Press defines artificial intelligence as: the theory and development of computer systems able to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages. AI applications include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google), recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon and Netflix), understanding human speech (such as Siri and Alexa), self-driving cars (e.g., Tesla), automated decision-making and competing at the highest level in strategic game systems (such as chess and Go). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior (OB) or organisational behaviour is the: "study of human behavior in organizational settings, the interface between human behavior and the organization, and the organization itself".Moorhead, G., & Griffin, R. W. (1995). ''Organizational behavior: Managing people and organizations'' (5th edition). Boston. Houghton Mifflin, (p.4) OB research can be categorized in at least three ways: * individuals in organizations (micro-level) * work groups (meso-level) * how organizations behave (macro-level) Chester Barnard recognized that individuals behave differently when acting in their organizational role than when acting separately from the organization. Organizational behavior researchers study the behavior of individuals primarily in their organizational roles. One of the main goals of organizational behavior research is "to revitalize organizational theory and develop a better conceptualization of organizational life". Relation to industrial and organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behavior, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. A portmanteau term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological or physical anthropology studies the biological development of humans. Archaeological anthropology, often termed as 'anthropology of the past', studies human activity through investigation of physical evidence. It is considered a branch of anthropology in North America and Asia, while in Europe archaeology is viewed as a discipline in its own right or grouped under other related disciplines, such as history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''anthropology'' is first attested in reference t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIGAI
ACM SIGAI is the Association for Computing Machinery's Special Interest Group on Artificial Intelligence ( AI), an interdisciplinary group of academic and industrial researchers, practitioners, software developers, end users, and students who work together to promote and support the growth and application of AI principles and techniques throughout computing. SIGAI is one of the oldest special interest groups in the ACM. SIGAI, previously called SIGART, started in 1966, publishing the SIGART Newsletter that later became the SIGART Bulletin and Intelligence Magazine. Conferences SIGAI supports several conferences. * The ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human–Robot Interaction (HRI). * The IEEE/WIC/ ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI). The next conference will be held October 2016 in Omaha, Nebraska. * The IEEE/WIC/ ACM International Joint Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (WI-IAT). * The International Conference on Autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |