|
Ich Hab In Gottes Herz Und Sinn, BWV 92
(I have given over to God's heart and mind), 92, is a cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach for use in the Lutheran service. He composed the chorale cantata in Leipzig for Septuagesimae and first performed it on 28 January 1725. It is based on the hymn "" by Paul Gerhardt (1647), and is the only chorale cantata Bach based on a hymn by Gerhardt. History and words When Bach composed the cantata, he was in his second year as ''Thomaskantor'' (director of church music) in Leipzig. During his first year, beginning with the first Sunday after Trinity 1723, he had written a cycle of cantatas for the occasions of the liturgical year. In his second year he composed a second annual cycle of cantatas, which was planned to consist exclusively of chorale cantatas, each based on one Lutheran hymn. It included . Bach composed the cantata for Septuagesima, the third Sunday before Lent. The prescribed readings for the Sunday were taken from the First Epistle to the Corinthians, "race for victor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorale Cantata (Bach)
There are 52 chorale cantatas by Johann Sebastian Bach surviving in at least one complete version. Around 40 of these were composed during his second year as Thomaskantor in Leipzig, which started after Trinity Sunday 4 June 1724, and form the backbone of his chorale cantata cycle. The eldest known cantata by Bach, an early version of ''Christ lag in Todes Banden'', BWV 4, presumably written in 1707, was a chorale cantata. The last chorale cantata he wrote in his second year in Leipzig was ''Wie schön leuchtet der Morgenstern'', BWV 1, first performed on Palm Sunday, 25 March 1725. In the ten years after that he wrote at least a dozen further chorale cantatas and other cantatas that were added to his chorale cantata cycle. Lutheran hymns, also known as chorales, have a prominent place in the liturgy of that denomination. A chorale cantata is a church cantata based on a single hymn, both its text and tune. Bach was not the first to compose them, but for his 1724-25 second Leipzi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Cantata (Bach)
Throughout his life as a musician, Johann Sebastian Bach composed cantatas for both secular and sacred use. His church cantatas are cantatas which he composed for use in the Lutheran church, mainly intended for the occasions of the liturgical year. Bach's ''Nekrolog'' mentions five cantata cycles: "Fünf Jahrgänge von Kirchenstücken, auf alle Sonn- und Festtage" (Five year-cycles of pieces for the church, for all Sundays and feast days), which would amount to at least 275 cantatas,Alfred Dörffel. Bach-Gesellschaft Ausgabe Volume 27: '' Thematisches Verzeichniss der Kirchencantaten No. 1–120''. Breitkopf & Härtel, 1878. Introduction, p. VI or over 320 if all cycles would have been ideal cycles.Günther Zedler''Die Kantaten von Johann Sebastian Bach: Eine Einführung in die Werkgattung''.Books on Demand, 2011. p. 24–25/ref> The extant cantatas are around two-thirds of that number, with limited additional information on the ones that went missing or survived as fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recitative
Recitative (, also known by its Italian name "''recitativo''" ()) is a style of delivery (much used in operas, oratorios, and cantatas) in which a singer is allowed to adopt the rhythms and delivery of ordinary speech. Recitative does not repeat lines as formally composed songs do. It resembles sung ordinary speech more than a formal musical composition. Recitative can be distinguished on a continuum from more speech-like to more musically sung, with more sustained melodic lines. The mostly syllabic ''recitativo secco'' ("dry", accompanied only by continuo, typically cello and harpsichord) is at one end of the spectrum, through ''recitativo accompagnato'' (using orchestra), the more melismatic arioso, and finally the full-blown aria or ensemble, where the pulse is entirely governed by the music. Secco recitatives can be more improvisatory and free for the singer, since the accompaniment is so sparse; in contrast, when recitative is accompanied by orchestra, the singer must per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aria
In music, an aria (Italian: ; plural: ''arie'' , or ''arias'' in common usage, diminutive form arietta , plural ariette, or in English simply air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrumental or orchestral accompaniment, normally part of a larger work. The typical context for arias is opera, but vocal arias also feature in oratorios and cantatas, or they can be stand-alone concert arias. The term was originally used to refer to any expressive melody, usually, but not always, performed by a singer. Etymology The Italian term ''aria'', which derives from the Greek ἀήρ and Latin ''aer'' (air), first appeared in relation to music in the 14th century when it simply signified a manner or style of singing or playing. By the end of the 16th century, the term 'aria' refers to an instrumental form (cf. Santino Garsi da Parma lute works, 'Aria del Gran Duca'). By the early 16th century it was in common use as meaning a simple setting of strophic poetry; me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphrase
A paraphrase () is a restatement of the meaning of a text or passage using other words. The term itself is derived via Latin ', . The act of paraphrasing is also called ''paraphrasis''. History Although paraphrases likely abounded in oral traditions, paraphrasing as a specific educational exercise dates back to at least Roman times, when the author Quintilian recommended it for students to develop dexterity in language. In the Middle Ages, this tradition continued, with authors such as Geoffrey of Vinsauf developing schoolroom exercises that included both rhetorical manipulations and paraphrasing as a way of generating poems and speeches. Paraphrasing seems to have dropped off as a specific exercise that students learn, a drop off that largely coincides with the removal of Classical texts from the core of Western education. There is, however, renewed interest in the study of paraphrases, given concerns around plagiarism and original authorship. Analysis A paraphrase typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movement (music)
A movement is a self-contained part of a musical composition or musical form. While individual or selected movements from a composition are sometimes performed separately as stand-alone pieces, a performance of the complete work requires all the movements to be performed in succession. A movement is a section Section, Sectioning or Sectioned may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea * Section (typography), a subdivision, especially of a chapter, in books and documents ** Section sig ..., "a major structural unit perceived as the result of the coincidence of relatively large numbers of structural phenomena". Sources Formal sections in music analysis {{music-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Was Mein Gott Will, Das G'scheh Allzeit
"" (What my God wants should always happen) is a Lutheran hymn in German. The text from c. 1550 is attributed to Albert, Duke of Prussia. The melody, Zahn No. 7568, goes back to a tune by Claudin de Sermisy, written in 1529 for a secular French song. The hymn has belonged to core Lutheran hymnody without interruption and is part of the Protestant hymnal '' Evangelisches Gesangbuch'' as EG 364. It has been set to music throughout centuries, including by Johann Sebastian Bach, who based a chorale cantata on it, ''Was mein Gott will, das g'scheh allzeit'', BWV 111, and used the first stanza as a chorale in the ''St Matthew Passion'' and several cantatas. History The text is attributed to Albert, Duke of Prussia, and is said to have been written in 1547 in three stanzas, with an additional stanza added in a broadsheet publication in Nürnberg c. 1554, and in ''Fünff Schöne Geistliche Lieder'' in Dresden in 1556. The melody was composed by Claudin de Sermisy, published in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanza
In poetry, a stanza (; from Italian language, Italian ''stanza'' , "room") is a group of lines within a poem, usually set off from others by a blank line or Indentation (typesetting), indentation. Stanzas can have regular rhyme scheme, rhyme and Metre (poetry), metrical schemes, but they are not required to have either. There are many different : Stanzaic form, forms of stanzas. Some stanzaic forms are simple, such as four-line quatrains. Other forms are more complex, such as the Spenserian stanza. Fixed verse, Fixed verse poems, such as sestinas, can be defined by the number and form of their stanzas. The stanza has also been known by terms such as ''batch'', ''fit'', and ''stave''. The term ''stanza'' has a similar meaning to ''strophe'', though ''strophe'' sometimes refers to an irregular set of lines, as opposed to regular, rhymed stanzas. Even though the term "stanza" is taken from Italian, in the Italian language the word "strofa" is more commonly used. In music, groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
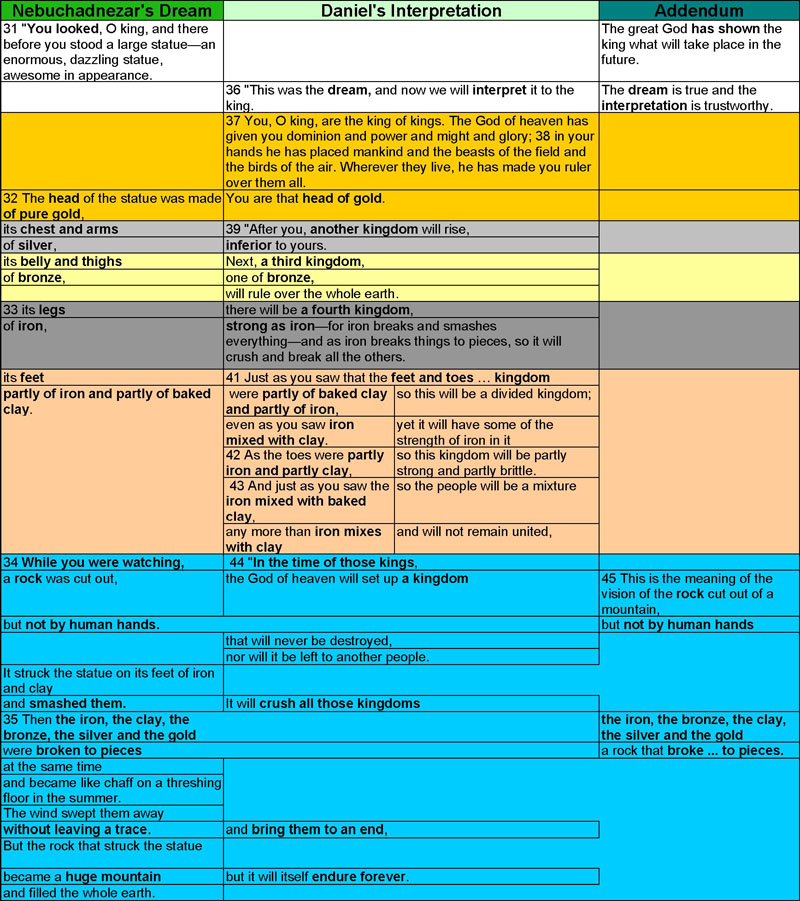
Parable Of The Workers In The Vineyard
__NOTOC__ The Parable of the Workers in the Vineyard (also called the Parable of the Laborers in the Vineyard or the Parable of the Generous Employer) is a parable of Jesus which appears in chapter 20 of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. It is not included in the other canonical gospels. It has been described as a difficult parable to interpret. Text Interpretations The parable has often been interpreted to mean that even those who are converted late in life earn equal rewards along with those converted early, and also that people who convert early in life need not feel jealous of those later converts. An alternative interpretation identifies the early laborers as Jews, some of whom resent the late-comers ( Gentiles) being welcomed as equals in God's Kingdom. Both of these interpretations are discussed in Matthew Henry's 1706 Commentary on the Bible. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew), or simply Matthew. It is most commonly abbreviated as "Matt." is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells how Israel's Messiah, Jesus, comes to his people and forms a community of disciples, of how he taught the people through such events as the Sermon on the Mount and its Beatitudes, and how Israel becomes divided and how Jesus condemns this hostile Israel. This culminates in his departure from the Temple and his execution. At this point many people reject Jesus, and on his resurrection he sends the disciples to the gentiles. Matthew seems to emphasize that the Jewish tradition should not be lost in a church that was increasingly becoming gentile. The gospel reflects the struggles and conflicts between the evangelist's community and the other Jews, particularly with its sharp criticism of the scribes and Pharisees with the position that through their rejection of Christ, the Kingdom of God h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Epistle To The Corinthians
The First Epistle to the Corinthians ( grc, Α΄ ᾽Επιστολὴ πρὸς Κορινθίους) is one of the Pauline epistles, part of the New Testament of the Christian Bible. The epistle is attributed to Paul the Apostle and a co-author, Sosthenes, and is addressed to the Christian church in Corinth. Scholars believe that Sosthenes was the amanuensis who wrote down the text of the letter at Paul's direction. It addresses various issues that had arisen in the Christian community at Corinth, and is composed in a form of Koine Greek. Authorship There is a consensus among historians and theologians that Paul is the author of the First Epistle to the Corinthians (c. AD 53–54). The letter is quoted or mentioned by the earliest of sources, and is included in every ancient canon, including that of Marcion of Sinope. Some scholars point to the epistle's potentially embarrassing references to the existence of sexual immorality in the church as strengthening the case for the aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lent
Lent ( la, Quadragesima, 'Fortieth') is a solemn religious observance in the liturgical calendar commemorating the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke, before beginning his public ministry. Lent is observed in the Anglican, Eastern Orthodox, Lutheran, Methodist, Moravian, Oriental Orthodox, Persian, United Protestant and Roman Catholic traditions. Some Anabaptist, Baptist, Reformed (including certain Continental Reformed, Presbyterian and Congregationalist churches), and nondenominational Christian churches also observe Lent, although many churches in these traditions do not. Which days are enumerated as being part of Lent differs between denominations (see below), although in all of them Lent is described as lasting for a total duration of 40 days. In Lent-observing Western Churches, Lent begins on Ash Wednesday and ends approximately six weeks later; depending on the Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
