|
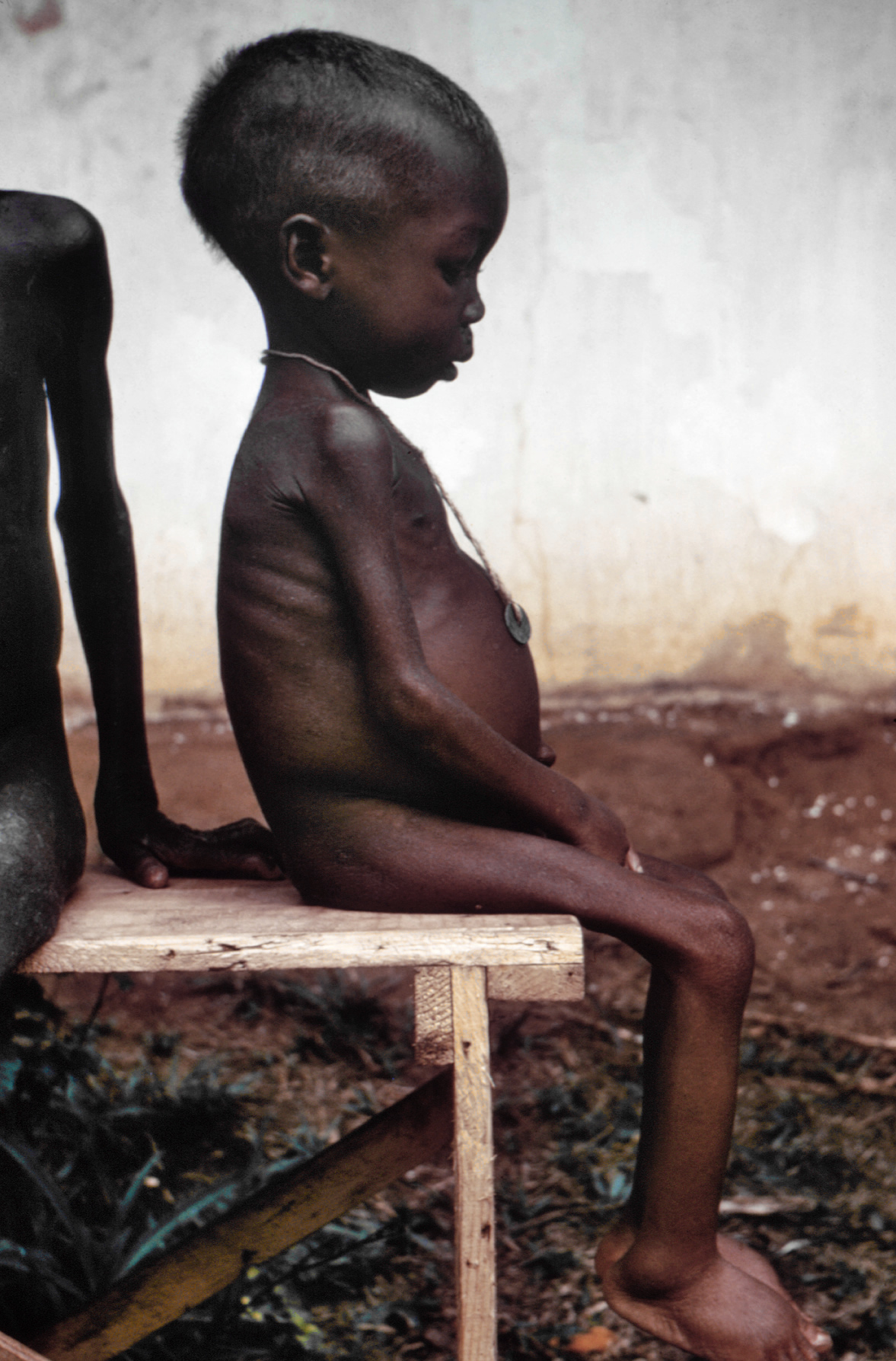
ICRC Hospital Of Novye Atagi
The ICRC Hospital of Novye Atagi is an International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) hospital in Novye Atagi, Chechnya, Russian Federation. It was evacuated in December 1996 when six members of the expatriate team were assassinated during an early morning raid by an unidentified armed group. The decision to create this hospital was made at the end of the First Chechen War in a context of great insecurity. During the battle of Grozny in August 1996, many hospitals had been destroyed. It was completed September 1996. The choice of Novye Atagi A mission of evaluation of the ICRC left Geneva and arrived in the city of Naltchik in Kabardino-Balkaria on August 18. Three possible locations were discussed at this stage: the border between Ingushetia and Chechnya, Grozny, and the villages south of Grozny. The mission left to the field the following day on 19 August. In Ingushetia the local authorities proposed a location to establish the hospital. The mission left then to Chechnya an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novye Atagi
Novye Atagi (russian: Но́вые Атаги́: ce, Жима АтагӀа, ''Ƶima Ataġa'') is a rural locality (a '' selo'') in Shalinsky District of the Chechen Republic, Russia, located south of Grozny Grozny ( rus, Грозный, p=ˈgroznɨj; ce, Соьлжа-ГӀала, translit=Sölƶa-Ġala), also spelled Groznyy, is the capital city of Chechnya, Russia. The city lies on the Sunzha River. According to the 2010 census, it had a po .... Population: Novye Atagi is separated from Starye Atagi by the Argun River. See also * ICRC Hospital of Novye Atagi References External linksThe attack on the ICRC hospital in Novye Atagi {{Authority control [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Red Cross
The Norwegian Red Cross (''Norges Røde Kors'') was founded on 22 September 1865 by prime minister Frederik Stang. In 1895 the Norwegian Red Cross began educating nurses, and in 1907 the Norwegian Ministry of Defence authorized the organization for voluntary medical aid in war. The Norwegian Red Cross was one of the first national organizations in the International Red Cross. The organization now has 150,000 members and provides a variety of humanitarian services, including care for old and the infirm, prisoner visits, outdoor rescue, and international work. Presidents *1865–1880 Frederik Stang *1880–1889 Christian August Selmer *1889–1905 Johan Fredrik Thaulow *1905–1908 Ernst Motzfeldt *1908–1912 Andreas Martin Seip *1912–1913 Christian Wilhelm Engel Bredal Olssøn *1913–1917 Hans Jørgen Darre-Jenssen *1917–1922 Hieronymus Heyerdahl *1922–1930 Torolf Prytz *1930–1940 Jens Meinich *1940–1945 Fridtjof Heyerdahl *1945–1947 Nikolai Nissen Paus *1947� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Red Cross
The Canadian Red Cross Society ()The Canadian Red Cross Society ''Charities Directorate – Government of Canada''. is a humanitarian , and one of 192 national societies. The organization receives funding from both private dona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish language, Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Spain, Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Médecins Sans Frontières
(MSF; pronounced ), also known as Doctors Without Borders, is a humanitarian medical non-governmental organisation (NGO) or charity of French origin known for its projects in conflict zones and in countries affected by endemic diseases. Main areas of work include diabetes, drug-resistant infections, HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C, tropical and neglected diseases, tuberculosis, vaccines and COVID-19. In 2019, the charity was active in 70 countries with over 35,000 personnel; mostly local doctors, nurses and other medical professionals, logistical experts, water and sanitation engineers, and administrators. Private donors provide about 90% of the organisation's funding, while corporate donations provide the rest, giving MSF an annual budget of approximately US$1.63 billion. MSF was founded in 1971, in the aftermath of the Biafran famine of the Nigerian Civil War, by a small group of French doctors and journalists who sought to expand accessibility to medical care across nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merlin (charity)
Medical Emergency Relief International (Merlin) is a former British international non-governmental health charity which sends medical experts to global emergencies. In July 2013, Merlin merged with Save the Children. History Merlin was founded in 1993 by Dr Christopher Besse, Nicholas Mellor and Mark Dalton to create a British charity to send medical teams into disaster zones and then to prevent disease and help develop local health services. Its first mission was to send a convoy to Bosnia carrying £1 million worth of essential food and medicines. Since then Merlin has grown into a specialist charity aimed at responding to natural disasters and humanitarian emergencies, then staying on to rebuild the capacity of local health services. To date, Merlin has worked in over 40 countries and responded to some of the most serious humanitarian emergencies of recent history. These include the Asian tsunami, Darfur and the cyclone in Burma. Merlin has also responded to the 2010 Haiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization For Security And Co-operation In Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, promotion of human rights, freedom of the press, and free and fair elections. It employs around 3,460 people, mostly in its field operations but also in its secretariat in Vienna, Austria, and its institutions. It has its origins in the mid-1975 Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe (CSCE) held in Helsinki, Finland. The OSCE is concerned with early warning, conflict prevention, crisis management, and post-conflict rehabilitation. Most of its 57 participating countries are in Europe, but there are a few members present in Asia and North America. The participating states cover much of the land area of the Northern Hemisphere. It was created during the Cold War era as a forum for discussion between the Western Bloc and Eastern Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Express (France)
''L'Express'' () is a French weekly news magazine headquartered in Paris. The weekly stands at the political centre in the French media landscape, and has a lifestyle supplement, ''L'Express Styles'', and a job supplement, ''Réussir''. History and profile ''L'Express'' was co-founded in 1953 by Jean-Jacques Servan-Schreiber, future president of the Radical Party, and Françoise Giroud, who had earlier edited ''ELLE'' and went on to become France's first minister of women's affairs in 1974 and minister of culture in 1976. When founded during the First Indochina War, it was modelled on the US magazine ''Time'' and the German magazine ''Der Spiegel''. ''L'Express'' is published weekly. The magazine was supportive of the policies of Pierre Mendès-France in Indochina, and in general had a left-of-centre orientation. The magazine opposed the war in Algeria, and especially the use of torture. In March 1958, as a result of an article of Jean-Paul Sartre reviewing the book ''La Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quetta
Quetta (; ur, ; ; ps, کوټه) is the tenth List of cities in Pakistan by population, most populous city in Pakistan with a population of over 1.1 million. It is situated in Geography of Pakistan, south-west of the country close to the Durand line, International border with Afghanistan. It is the capital of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan where it is the largest city. Quetta is at an average elevation of above sea level, making it Pakistan's only high-altitude major city. The city is known as the ''"Fruit Garden of Pakistan"'' due to the numerous fruit orchards in and around it, and the large variety of fruits and dried fruit products produced there. Located in northern Balochistan near the Durand line, Pakistan-Afghanistan border and the road across to Kandahar, Quetta is a trade and communication centre between the two countries. The city is near the Bolan Pass route which was once one of the major gateways from Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Federal District. The republic is the southernmost tip of Russia, sharing land borders with the countries of Azerbaijan and Georgia to the south and southwest, the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia to the west and north, and with Stavropol Krai to the northwest. Makhachkala is the republic's capital and largest city; other major cities are Derbent, Kizlyar, Izberbash, Kaspiysk and Buynaksk. Dagestan covers an area of , with a population of over 3.1 million, consisting of over 30 ethnic groups and 81 nationalities. With 14 official languages, and 12 ethnic groups each constituting more than 1% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khasavyurt
Khasavyurt (russian: Хасавю́рт; av, Хасаюрт; ce, Хаси-Эвл, ''Xasi-Evl''; kum, Хасав-ю́рт, ''Xasav-yurt'') is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia. Population: History It was founded in 1846 and granted town status in 1931. During the Russian Empire, the settlement was the administrative capital of the Khasavyurtovsky Okrug of the Terek Oblast. On August 19, 2012, six police officers were killed and eight people injured at two gun and bomb attacks in the city. The town has thousands of Salafis. In December 2016, the Russian authorities reported the existence of the Khasavyurt Group, allegedly linked to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant – Caucasus Province, Islamic State and a flareup of incidents and skirmishes between the police and local militants in and around the city. Administrative and municipal status Within the subdivisions of Russia#Administrative divisions, framework of admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refectory
A refectory (also frater, frater house, fratery) is a dining room, especially in monasteries, boarding schools and academic institutions. One of the places the term is most often used today is in graduate seminaries. The name derives from the Latin ''reficere'' "to remake or restore," via Late Latin ''refectorium'', which means "a place one goes to be restored" (''cf.'' "restaurant"). Refectories and monastic culture Communal meals are the times when all monks of an institution are together. Diet and eating habits differ somewhat by monastic order, and more widely by schedule. The Benedictine rule is illustrative. The Rule of St Benedict orders two meals. Dinner is provided year-round; supper is also served from late spring to early fall, except for Wednesdays and Fridays. The diet originally consisted of simple fare: two dishes, with fruit as a third course if available. The food was simple, with the meat of mammals forbidden to all but the sick. Moderation in all aspects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |