|
Iyar Dyoman
Iyar ( he, ūÉų┤ūÖūÖųĖū© or , Standard ''╩Š─¬yyar'' Tiberian ''╩Š─¬yy─ür''; from akk, ÆīŚ Æä× itiayari " rosette; blossom") is the eighth month of the civil year (which starts on 1 Tishrei) and the second month of the Jewish religious year (which starts on 1 Nisan) on the Hebrew calendar. The name is Babylonian in origin. It is a month of 29 days. Iyar usually falls in AprilŌĆōMay on the Gregorian calendar. In the Hebrew Bible, before the Babylonian captivity, the month was called Ziv (, ). Ziv is a Hebrew word that means "light" or "glow". Along with all other current, post-biblical Jewish month names, Iyar was adopted during the Babylonian captivity. In the Babylonian calendar its name was AraßĖ½ ─Ćru, which can be interpreted as "month of blossoming". Holidays in Iyar Jewish holidays * 14 Iyar ŌĆō Pesach Sheni * 18 Iyar ŌĆō Lag BaOmer * Fast of Behav ŌĆō see Cheshvan. It is observed on the Monday, Thursday, and Monday after the first Sabbath after Rosh Chodesh Iyar. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lag BaOmer
Lag BaOmer ( he, , ''LaG B─ü╩┐┼Źmer''), also Lag B'Omer or Lag LaOmer, is a Jewish religious holiday celebrated on the 33rd day of the Counting of the Omer, which occurs on the 18th day of the Hebrew month of Iyar. According to some Rishonim, it is the day on which the plague that killed Rabbi Akiva's 24,000 disciples came to an end, and for this reason the mourning period of Sefirat HaOmer concludes on Lag BaOmer in many communities. According to modern kabbalistic tradition, this day is the Celebration of Simeon ben Yochai and/or the anniversary of his death. According to a late medieval tradition, Simeon ben Yochai is buried in Meron, and this association has spawned several well-known customs and practices on Lag BaOmer, including the lighting of bonfires and pilgrimages to Meron. Additionally, in modern-day Israel, the holiday also serves to commemorate the Bar Kokhba Revolt against the Romans. Etymology Lag BaOmer is Hebrew for "33rd ayin the Omer". (The He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Of Behav
The Fast of Behav (ū¬ūóūĀūÖū¬ ūæūö"ūæ) refers to a tradition of Ashkenazic Jews to fast on the Monday, Thursday, and then following Monday after the holidays of Sukkot and Pesach. While today very few people fast, many Ashkenazic communities recite the Selichot for these days. Practically, the fasts are observed in the months of Cheshvan and Iyar, so as not to fast in the happy months of Tishrei and Nisan. Source and practices The Masekhet Soferim (Chapter 21) says that there were "students" who fasted on a Monday, Thursday, and following Monday in the month of Nisan. However, it is clear that this was a private practice which was not publicized. The Tur cites the custom of Ashkenazic and French Jewry to fast in Cheshvan and Iyar. In later generations, this custom spread to some Sephardic communities.Kneset Hagedola492/ref> Some explain that the reason for the fasts is in case one sinned over the long Sukkot or Pesach holidays, and others say that it should be for an atonemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, ūÖų░ū©ūĢų╝ū®ųĖūüū£ųĘūÖų┤ūØ ; ar, ž¦┘ä┘é┘Åž»ž│ ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, ß╝╣╬ĄŽü╬┐ŽģŽā╬▒╬╗╬«╬╝/ß╝Ė╬ĄŽü╬┐ŽāŽī╬╗Žģ╬╝╬▒, HierousalßĖŚm/Hieros├│luma; hy, įĄųĆšĖųéšĮšĪš▓šźš┤, Erusa┼é─ōm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Declaration Of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel ( he, ūöūøū©ū¢ūö ūóū£ ūöū¦ū×ū¬ ū×ūōūÖūĀū¬ ūÖū®ū©ūÉū£), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 ( 5 Iyar 5708) by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization, Chairman of the Jewish Agency for Palestine, and soon to be first Prime Minister of Israel. It declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel, which would come into effect on termination of the British Mandate at midnight that day. The event is celebrated annually in Israel with a national holiday Independence Day on 5 Iyar of every year according to the Hebrew calendar. Background The possibility of a Jewish homeland in Palestine had been a goal of Zionist organizations since the late 19th century. In 1917 British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour stated in a letter to British Jewish community leader Walter, Lord Rothschild that: His Majesty's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fez, Morocco
Fez or Fes (; ar, ┘üž¦ž│, f─üs; zgh, Ō┤╝ŌĄēŌĄŻŌ┤░ŌĄŻ, fizaz; french: F├©s) is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the F├©s-Mekn├©s administrative region. It is the second largest city in Morocco, with a population of 1.11 million according to the 2014 census. Located to the north west of the Atlas Mountains, Fez is linked to several important cities of different regions; it is from Tangier to the northwest, from Casablanca, from Rabat to the west, and from Marrakesh to the southwest. It is surrounded by hills and the old city is centered around the Fez River (''Oued Fes'') flowing from west to east. Fez was founded under Idrisid rule during the 8th-9th centuries CE. It initially consisted of two autonomous and competing settlements. Successive waves of mainly Arab immigrants from Ifriqiya (Tunisia) and al-Andalus (Spain/Portugal) in the early 9th century gave the nascent city its Arab character. After the downfall of the Idrisid dynasty, other emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Conversion
Forced conversion is the adoption of a different religion or the adoption of irreligion under duress. Someone who has been forced to convert to a different religion or irreligion may continue, covertly, to adhere to the beliefs and practices which were originally held, while outwardly behaving as a convert. Crypto-Jews, crypto-Christians, crypto-Muslims and crypto-Pagans are historical examples of the latter. Religion and power In general, anthropologists have shown that the relationship between religion and politics is complex, especially when viewed over the expanse of human history.Firth, Raymond (1981Spiritual Aroma: Religion and Politics ''American Anthropologist'', New Series, Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 582ŌĆō601 While religious leaders and the state generally have different aims, both are concerned with power and order; both use reason and emotion to motivate behavior. Throughout history, leaders of religious and political institutions have cooperated, opposed one another, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138ŌĆō1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, ū©ū×ūæū┤ūØ), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah scholars of the Middle Ages. In his time, he was also a preeminent astronomer and physician, serving as the personal physician of Saladin. Born in C├│rdoba, Almoravid Empire (present-day Spain), on Passover eve, 1138 (or 1135), he worked as a rabbi, physician and philosopher in Morocco and Egypt. He died in Egypt on 12 December 1204, when his body was taken to the lower Galilee and buried in Tiberias. During his lifetime, most Jews greeted Maimonides' writings on Jewish law and ethics with acclaim and gratitude, even as far away as Iraq and Yemen. Yet, while Maimonides rose to become the revered head of the Jewish community in Egypt, his writings also had vociferous critics, particularly in Spain. Nonetheless, he was posthumously ackno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chabad
Chabad, also known as Lubavitch, Habad and Chabad-Lubavitch (), is an Orthodox Jewish Hasidic dynasty. Chabad is one of the world's best-known Hasidic movements, particularly for its outreach activities. It is one of the largest Hasidic groups and Jewish religious organizations in the world. Unlike most Haredi groups, which are self-segregating, Chabad operates mainly in the wider world and caters to secularized Jews. Founded in 1775 by Rabbi Schneur Zalman of Liadi, the name "Chabad" () is an acronym formed from three Hebrew wordsŌĆö (the first three sephirot of the kabbalistic Tree of Life) (): "Wisdom, Understanding, and Knowledge"ŌĆöwhich represent the intellectual and kabbalistic underpinnings of the movement. The name Lubavitch derives from the town in which the now-dominant line of leaders resided from 1813 to 1915. Other, non-Lubavitch scions of Chabad either disappeared or merged into the Lubavitch line. In the 1930s, the sixth Rebbe of Chabad, Rabbi Yosef Yitzcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shmuel Schneersohn
Shmuel Schneersohn (or Rabbi Shmuel of Lubavitch or The Rebbe Maharash) (29 April 1834 ŌĆō 14 September 1882 OS) was an Orthodox rabbi and the fourth Rebbe (spiritual leader) of the Chabad Lubavitch Chasidic movement. Biography Shmuel Schneersohn was born in Lyubavichi, on 2 Iyar 5594 (1834), the seventh son of Menachem Mendel Schneersohn. He faced competition from three of his brothers, primarily from Yehuda Leib Schneersohn who established a dynasty in Kapust upon their father's death. Other brothers also established dynasties in Lyady, Nizhyn, and Ovruch. In 1848, Schneersohn was married to the daughter of his brother, Chaim Shneur Zalman Schneersohn. After several months she died, and he then married Rivkah, a granddaughter of his own grandfather Dovber Schneuri. He had three sons, Zalman Aharon, Shalom Dovber, and Menachem Mendel, as well as one daughter, Devorah Leah. Schneersohn was said to have had chariots on call for the evacuation of books in time of fire. Bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menachem Mendel Of Vitebsk
Menachem Mendel of Vitebsk (1730?ŌĆō1788), also known as Menachem Mendel of Horodok, was an early leader of Hasidic Judaism. Part of the third generation of Hassidic leaders, he was the primary disciple of the Maggid of Mezeritch. From his base in Minsk Menachem Mendel was instrumental in spreading Hasidism throughout Belarus. In the winter of 1772, he - along with Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi (who regarded Rabbi Menachem Mendel as his ''Rebbe'' after the Maggid's passing) - went to the Vilna Gaon with the aim of convincing him to rescind his ban on Hasidism, but the Vilna Gaon would not receive them. After the Maggid's death, Rabbi Menachem Mendel, along with fellow disciple Rabbi Abraham Kalisker ("Kalisker") settled in Horodok. In 1777 the two, along with 300 followers, emigrated to Eretz Israel, settling in Safed, Ottoman Syria. In 1783 they were forced out of Safed, and moved to Tiberias. The synagogue they built there in 1786 still stands among the Ancient synagogues of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
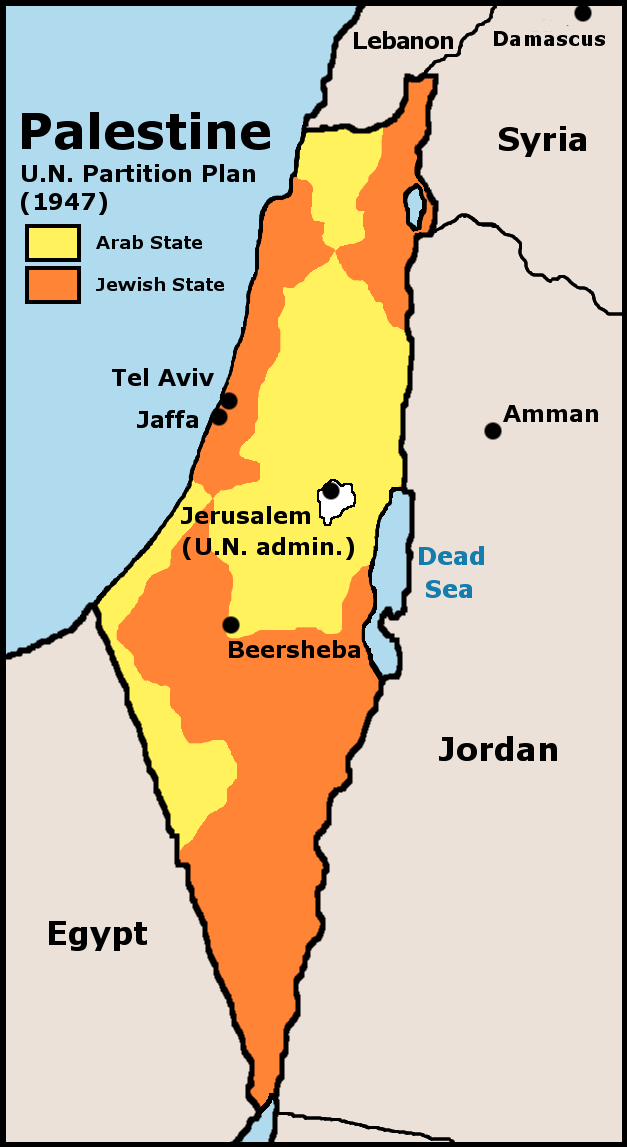
Jerusalem Day
Jerusalem Day ( he, ūÖūĢūØ ūÖū©ūĢū®ū£ūÖūØ, ) is an Public holidays in Israel, Israeli national holiday that commemorates the "reunification" of East Jerusalem (including the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City) with West Jerusalem following the Six-Day War of 1967, which saw Israel occupy East Jerusalem and the West Bank, Israeli annexation of East Jerusalem, effectively annexing the former. It is celebrated annually on 28 Iyar on the Hebrew calendar, and is marked officially throughout Israel with state ceremonies and memorial services. A notable celebrations that marks the holiday is a flag-flying parade known as the Dance of Flags. The Chief Rabbinate of Israel declared Jerusalem Day to be a minor religious holiday, as it marks the regaining for Jews, Jewish people of access to the Western Wall. Historical background Under the 1947 United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, which proposed the establishment of two states in British Mandatory Palestine ŌĆō a Jews, Jewish s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herzl Day
Herzl Day ( he, ūÖūĢūØ ūöū©ū”ū£) is an Israeli national holiday celebrated annually on the tenth of the Hebrew month of Iyar, to commemorate the life and vision of Zionist leader Theodor Herzl. History Herzl Day was created by the Israeli Knesset as part of the Herzl Law. According to the law, passed in June 2004, Herzl Day will be celebrated once a year, on Iyar 10, the birthday of Theodor Herzl. On this day, a state memorial service is held on Mount Herzl in Jerusalem and at IDF camps and schools. Time is devoted to learning about the achievements and Zionist vision of Theodor Herzl and a symposium in memory of Theordor Herzl is held in Jerusalem to discuss world Zionist issues. The Knesset holds a special session to mark Herzl Day. If the Hebrew date, 10 Iyar, falls on Sabbath, Herzl Day is postponed until Sunday. See also *Public holidays in Israel *Culture of Israel *Jewish holidays Jewish holidays, also known as Jewish festivals or ''Yamim Tovim'' ( he, ūÖū×ūÖūØ ū ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |