|
Ivittuut Municipality
Ivittuut , (old spelling Ivigtût) was a municipality (from 1951 until 2008), on the coast of Arsuk Fjord in southern Greenland. With an area of just 100 km2 (600 km2 according to other sources), it was the smallest municipality of Greenland, bordering on the former Narsaq municipality in the north, east and south, and on the west by the Labrador Sea. It has been integrated into the new Sermersooq municipality. Due to its small size, the municipality is all ice-free, as it does not extend inward to the ice sheet of Greenland. The town of Ivittuut is abandoned and the only settlement of the municipality is the permanent naval base Kangilinnguit (Grønnedal). The municipality existed ''de jure'' and was about to be absorbed by Narsaq when the 2009 municipal reform took place. Kangilinnguit is the Danish naval headquarters of Greenland, originally established to protect Ivittuut's cryolite mine Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to: Extraction or digging * Miner, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivigtut
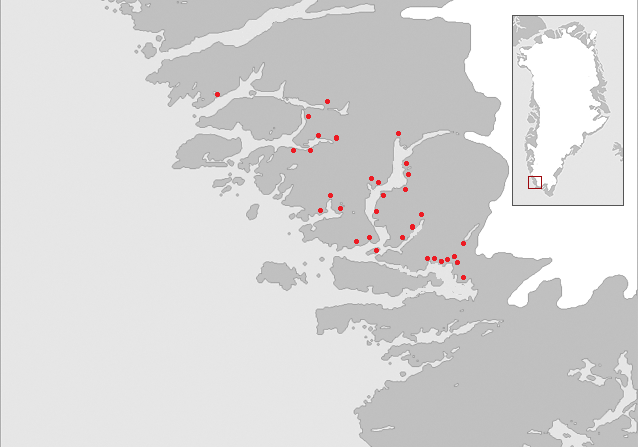
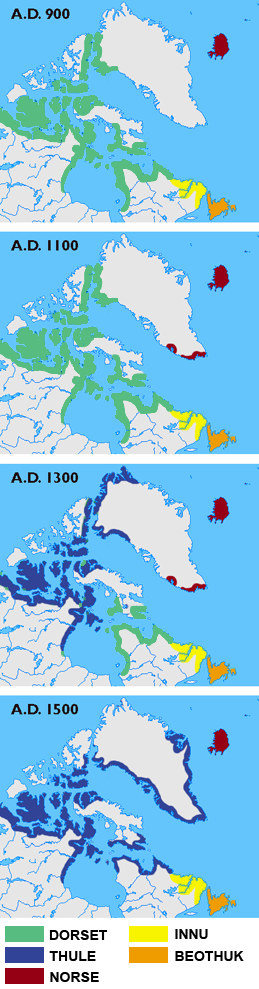
Ivittuut (formerly, Ivigtût) (Kalaallisut: "Grassy Place") is an abandoned mining town near Cape Desolation in southwestern Greenland, in the modern Sermersooq municipality on the ruins of the former Norse Middle Settlement. Ivittuut is one of the few places in the world so far discovered to have naturally occurring cryolite (Na3AlF6, sodium aluminum fluoride), an important agent in modern aluminum extraction. History The area was settled by about twenty farms of Norsemen, a district called the "Middle Settlement" by modern archaeologists from its placement between the larger Western and Eastern Settlements. It is the smallest and least well known of the three, and no written records of its residents survive, for which reasons it is believed to have been established last (and abandoned first) of the three. Investigations show a presence after 985 and with occupation continuing up to at least the 14th century. The town's cryolite deposit was discovered in 1799, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland Ice Sheet
The Greenland ice sheet ( da, Grønlands indlandsis, kl, Sermersuaq) is a vast body of ice covering , roughly near 80% of the surface of Greenland. It is sometimes referred to as an ice cap, or under the term ''inland ice'', or its Danish equivalent, ''indlandsis''. An acronym, GIS, is frequently used in the scientific literature. It is the second largest ice body in the world, after the Antarctic ice sheet. The ice sheet is almost long in a north–south direction, and its greatest width is at a latitude of 77°N, near its northern margin. The average thickness is about and over at its thickest point. In addition to the large ice sheet, smaller ice caps (such as Maniitsoq and Flade Isblink) as well as glaciers, cover between around the periphery. The Greenland ice sheet is adversely affected by climate change. It is more vulnerable to climate change than the Antarctic ice sheet because of its position in the Arctic, where it is subject to the regional amplification o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryolite
Cryolite ( Na3 Al F6, sodium hexafluoroaluminate) is an uncommon mineral identified with the once-large deposit at Ivittuut on the west coast of Greenland, mined commercially until 1987. History Cryolite was first described in 1798 by Danish veterinarian and physician Peder Christian Abildgaard (1740–1801); it was obtained from a deposit of it in Ivigtut (old spelling) and nearby Arsuk Fjord, Southwest Greenland. The name is derived from the Greek language words ''κρύος'' (cryos) = frost, and ''λίθος'' (lithos) = stone. The Pennsylvania Salt Manufacturing Company used large amounts of cryolite to make caustic soda and fluorine compounds, including hydrofluoric acid at its Natrona, Pennsylvania works, and at its integrated chemical plant in Cornwells Heights, Pennsylvania, during the 19th and 20th centuries. It was historically used as an ore of aluminium and later in the electrolytic processing of the aluminium-rich oxide ore bauxite (itself a combination of aluminiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface Naval ship, ships, amphibious warfare, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne naval aviation, aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is Power projection, projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect Sea lane, sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark
) , song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast") , song_type = National and royal anthem , image_map = EU-Denmark.svg , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark , established_title = History of Denmark#Middle ages, Consolidation , established_date = 8th century , established_title2 = Christianization , established_date2 = 965 , established_title3 = , established_date3 = 5 June 1849 , established_title4 = Faroese home rule , established_date4 = 24 March 1948 , established_title5 = European Economic Community, EEC 1973 enlargement of the European Communities, accession , established_date5 = 1 January 1973 , established_title6 = Greenlandic home rule , established_date6 = 1 May 1979 , official_languages = Danish language, Danish , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = German language, GermanGerman is recognised as a protected minority language in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally recognized. Examples Between 1805 and 1914, the ruling dynasty of Egypt were subject to the rulers of the Ottoman Empire, but acted as de facto independent rulers who maintained a polite fiction of Ottoman suzerainty. However, starting from around 1882, the rulers had only de jure rule over Egypt, as it had by then become a British puppet state. Thus, by Ottoman law, Egypt was de jure a province of the Ottoman Empire, but de facto was part of the British Empire. In U.S. law, particularly after ''Brown v. Board of Education'' (1954), the difference between de facto segregation (segregation that existed because of the voluntary associations and neighborhoods) and de jure segregation (segregation that existed because of local laws that m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
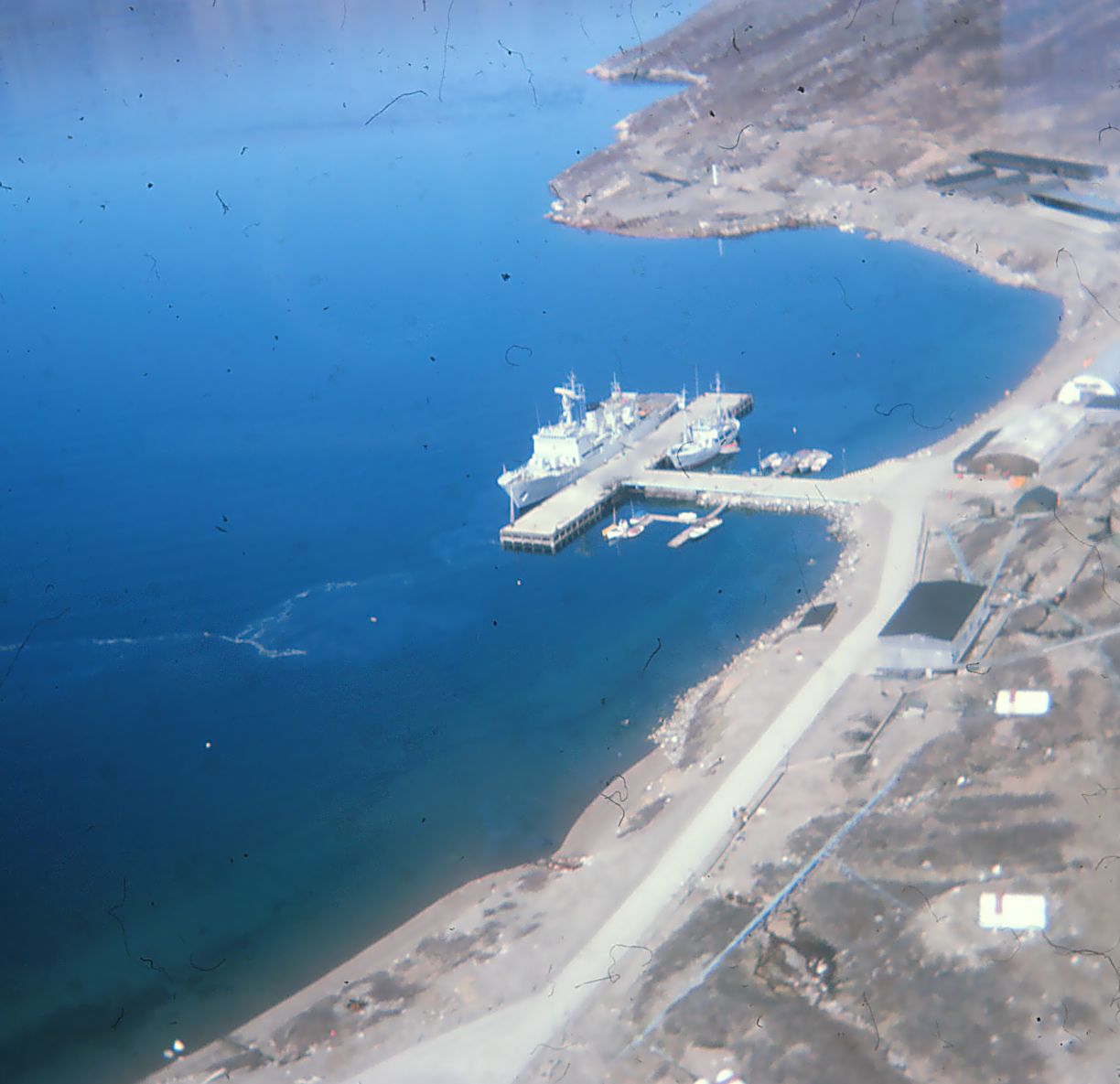
Kangilinnguit
Kangilinnguit or Kangilínguit, formerly Grønnedal , is a settlement and location of a former naval base in Greenland's Sermersooq municipality, located at the mouth of Arsuk Fjord in southwestern Greenland. The settlement had 160 inhabitants in 2010, most of whom are Danish Navy personnel, attached to Island Command Greenland headquarters. For the former U.S. Naval Operating Facility there, see Bluie West Seven. History Kangilinnguit was founded as "Green Valley" by the during the |
Ivittuut
Ivittuut (formerly, Ivigtût) (Kalaallisut: "Grassy Place") is an abandoned mining town near Cape Desolation in southwestern Greenland, in the modern Sermersooq municipality on the ruins of the former Norse Middle Settlement. Ivittuut is one of the few places in the world so far discovered to have naturally occurring cryolite (Na3AlF6, sodium aluminum fluoride), an important agent in modern aluminum extraction. History The area was settled by about twenty farms of Norsemen, a district called the "Middle Settlement" by modern archaeologists from its placement between the larger Western and Eastern Settlements. It is the smallest and least well known of the three, and no written records of its residents survive, for which reasons it is believed to have been established last (and abandoned first) of the three. Investigations show a presence after 985 and with occupation continuing up to at least the 14th century. The town's cryolite deposit was discovered in 1799, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sermersooq
Sermersooq (, da, sted med meget is, lit=place of much ice) is a municipality in Greenland, formed on 1 January 2009 from five earlier, smaller municipalities. Its administrative seat is the city of Nuuk (formerly called Godthåb), the capital of Greenland, and it is the most populous municipality in the country, with 23,123 inhabitants as of January 2020. Creation The municipality consists of former municipalities of eastern and southwestern Greenland, each named after the largest settlement at the time of formation: * Ammassalik Municipality * Ittoqqortoormiit Municipality * Ivittuut Municipality * Nuuk Municipality * Paamiut Municipality Administrative divisions Ammassalik area * Tasiilaq (Ammassalik) * Kuummiit * Kulusuk (Kap Dan) * Tiniteqilaaq * Sermiligaaq * Isortoq Ittoqqortoormiit area * Ittoqqortoormiit (Scoresbysund) * Itterajivit Ivittuut area * Kangilinnguit (Grønnedal) Nuuk area * Nuuk (Godthåb) * Kapisillit * Qeqertarsuatsiaat (Fiskenæsset) Paamiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is the world's largest island. It is one of three constituent countries that form the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark and the Faroe Islands; the citizens of these countries are all citizens of Denmark and the European Union. Greenland's capital is Nuuk. Though a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe (specifically Norway and Denmark, the colonial powers) for more than a millennium, beginning in 986.The Fate of Greenland's Vikings , by Dale Mackenzie Brown, ''Archaeological Institute of America'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labrador Sea
The Labrador Sea (French: ''mer du Labrador'', Danish: ''Labradorhavet'') is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelf, continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, and northeast. It connects to the north with Baffin Bay through the Davis Strait. It is a marginal sea of the Atlantic. The sea formed upon separation of the North American Plate and Greenland Plate that started about 60 million years ago and stopped about 40 million years ago. It contains one of the world's largest turbidity current channel systems, the Northwest Atlantic Mid-Ocean Channel (NAMOC), that runs for thousands of kilometers along the sea bottom toward the Atlantic Ocean. The Labrador Sea is a major source of the North Atlantic Deep Water, a cold water mass that flows at great depth along the western edge of the North Atlantic, spreading out to form the largest identifiable water mass in the World Ocean. History The Labrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narsaq
Narsaq is a town in the Kujalleq municipality in southern Greenland. The name ''Narsaq'' is Kalaallisut for "Plain", referring to the shore of Tunulliarfik Fjord where the town is located. History People have lived in the area for thousands of years, but not continuously. Remains of the Norse settlement can be found in the area. The church ruins of Dyrnæs can be found on the north-western outskirts of the town. The Landnám homestead, ''Landnamsgaarden'', can be found immediately to the west of the town. Dated to the year 1000, the homestead is among the oldest of the Norse ruins in the area. Excavation of the ruins began in 1953 with the discovery of the Narsaq stick, the first Viking Age runic inscription discovered in Greenland. The wider Narsaq area has some of the most striking Norse artefacts and ruins. Erik the Red's Brattahlid is located in present-day Qassiarsuk, and the Gardar bishop seat is in present-day Igaliku. Present day Narsaq was founded as Nordprøven (" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |