|
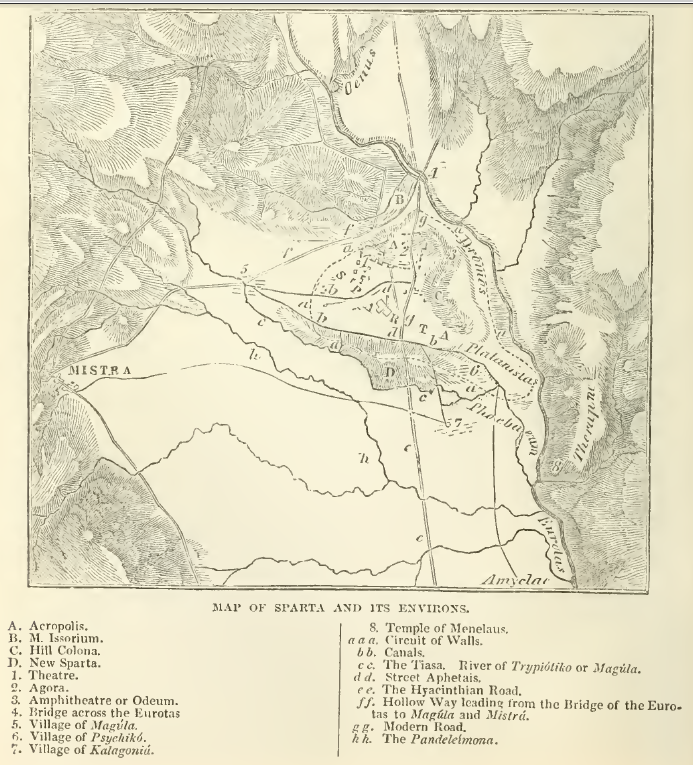
Issorion
The Issorium or Issorion (Ἰσσώριον; Issṓrion), or Mount Issorion, was a hill on the northern city border of Sparta, possibly the heights known today as Klaraki. On it was a sanctuary and temple to the goddess Artemis, in which context the goddess was surnamed ''Artemis Issoria''. (Or, from the nearby Laconian town of Pitane, ''Artemis Pitanata''; or ''Artemis Limnaea''.) During the Theban–Spartan War, circa 370 BC, the Issorium was seized by a group of Spartan mutineers; Agesilaus II Agesilaus II (; ; 445/4 – 360/59 BC) was king of Sparta from 400 to 360 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony that followed the Peloponn ... broke up the conspiracy and had fifteen of the mutineers put to death. References The entry cites Paus. iii.14 §2.25 and §3; Hesych. '; Steph. Byz. '; Plut. '' Ages.'' 32; Polyaen. ii.14. The entry cites Callim. ''Hymn. in Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later times, she was identified with Selene, the Lunar deity, personification of the Moon.Smiths.v. Artemis/ref> She was often said to roam the forests and mountains, attended by her entourage of nymphs. The goddess Diana (mythology), Diana is her Religion in ancient Rome, Roman equivalent. In Greek tradition, Artemis is the daughter of Zeus and Leto, and twin sister of Apollo. In most accounts, the twins are the products of an extramarital liaison. For this, Zeus' wife Hera forbade Leto from giving birth anywhere on solid land. Only the island of Delos gave refuge to Leto, allowing her to give birth to her children. In one account, Artemis is born first and then proceeds to assist Leto in the birth of the second twin, Apollo. Artemis was a kouro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Family Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which speak of Timon in particular in the most affectionate terms. Studies and life Plutarch studied mathematics and philosophy in Athens under Ammonius of Athens, Ammonius from AD 66 to 67. He attended th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Trojan Women
''The Trojan Women'' (, lit. "The Female Trojans") is a tragedy by the Ancient Greece, Greek playwright Euripides, produced in 415 BCE. Also translated as ''The Women of Troy,'' or as its transliterated Greek title ''Troades, The Trojan Women'' presents commentary on the costs of war through the lens of women and children. The four central women of the play are the same that appear in the final book of the ''Iliad,'' lamenting over the corpse of Hector after the Trojan War. ''Hecuba (play), Hecuba'', another tragedy by Euripides, similarly deals with the experiences of women left behind by war and was more popular in antiquity. The tragedy has inspired many modern adaptation across film, literature, and the stage. Historical background Scholar Neil Croally believes that ''The Trojan Women'' was written as a reaction to the Siege of Melos#:~:text=Athens invaded Melos in the,enslaved the women and children., Siege of Melos in 416 BCE during the Peloponnesian War, in which At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euripides
Euripides () was a Greek tragedy, tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him, but the ''Suda'' says it was ninety-two at most. Of these, eighteen or nineteen have survived more or less complete (''Rhesus (play), Rhesus'' is suspect). There are many fragments (some substantial) of most of his other plays. More of his plays have survived intact than those of Aeschylus and Sophocles together, partly because his popularity grew as theirs declinedMoses Hadas, ''Ten Plays by Euripides'', Bantam Classic (2006), Introduction, p. ixhe became, in the Hellenistic Age, a cornerstone of ancient literary education, along with Homer, Demosthenes, and Menander.L.P.E.Parker, ''Euripides: Alcestis'', Oxford University Press (2007), Introduction p. lx Euripides is identified with theatrical innovations that have profoundly influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callimachus
Callimachus (; ; ) was an ancient Greek poet, scholar, and librarian who was active in Alexandria during the 3rd century BC. A representative of Ancient Greek literature of the Hellenistic period, he wrote over 800 literary works, most of which do not survive, in a wide variety of genres. He espoused an aesthetic philosophy, known as Callimacheanism, which exerted a strong influence on the poets of the Roman Empire and, through them, on all subsequent Western canon, Western literature. Born into a prominent family in the Greek city of Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene in modern-day Libya, he was educated in Alexandria, the capital of the Ptolemaic dynasty, Ptolemaic kings of Egypt. After working as a schoolteacher in the city, he came under the patronage of King Ptolemy II Philadelphus and was employed at the Library of Alexandria where he compiled the ''Pinakes'', a comprehensive catalogue of all Greek literature. He is believed to have lived into the reign of Ptolemy III Euergetes. Altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyaenus
Polyaenus or Polyenus ( ; see ae (æ) vs. e; , "much-praised") was a 2nd-century Roman Macedonian author and rhetorician, known best for his ''Stratagems in War'' (), which has been preserved. He was born in Bithynia, Asia Minor. The ''Suda'' calls him a rhetorician, and Polyaenus himself writes that he was accustomed to plead causes before the Roman emperor. Polyaenus dedicated ''Stratagems in War'' to the two emperors Marcus Aurelius () and Lucius Verus (), while they were engaged in the Roman–Parthian War of 161–166, about 163, at which time he was too old to accompany them in their campaigns. Stratagems This work is divided into eight books: the first six contain accounts of the stratagems of the most celebrated Greek generals and rulers, the seventh book contains stratagems of non Greeks and Romans, and the eighth book those of the Romans and of illustrious women. Parts, however, of the sixth and seventh books are lost, so that of the 900 stratagems which Polyaenus de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Lives
* Culture of ancient Greece Culture of ancient Rome Ancient Greek biographical works Ethics literature History books about ancient Rome Cultural depictions of Gaius Marius Cultural depictions of Mark Antony Cultural depictions of Cicero Depictions of Julius Caesar in literature Cultural depictions of Pompey Cultural depictions of Marcus Junius Brutus Cultural depictions of Marcus Licinius Crassus Cultural depictions of Theseus Cultural depictions of Romulus and Remus Cultural depictions of Cato the Younger Cultural depictions of Sulla Cultural depictions of Alexander the Great The ''Parallel Lives'' (, ''Bíoi Parállēloi''; ) is a series of 48 biographies of famous men written in Greek by the Greco-Roman philosopher, historian, and Apollonian priest Plutarch, probably at the beginning of the second century. The lives are arranged in pairs to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings. While any historically valuable similarities are often forced, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesychius Of Alexandria
Hesychius of Alexandria () was a Greek grammarian who, probably in the 5th or 6th century AD, compiled the richest lexicon of unusual and obscure Greek words that has survived, probably by absorbing the works of earlier lexicographers. The work, titled "Alphabetical Collection of All Words" (, ''Synagōgē Pasōn Lexeōn kata Stoicheion''), includes more than 50,000 entries, a copious list of peculiar words, forms and phrases, with an explanation of their meaning, and often with a reference to the author who used them or to the district of Greece where they were current. Hence, the book is of great value to the student of the Ancient Greek dialects and in the restoration of the text of the classical authors generallyparticularly of such writers as Aeschylus and Theocritus, who used many unusual words. Hesychius is important, not only for Greek philology, but also for studying lost languages and obscure dialects of the Balkans in antiquity (such as Albanoid and Thracian) and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephanus Of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephen of Byzantium (; , ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD) was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethnica'' (). Only meagre fragments of the dictionary survive, but the epitome is extant, compiled by one Hermolaus, not otherwise identified. Life Nothing is known about the life of Stephanus, except that he was a Greek grammarian who was active in Constantinople, and lived after the time of Arcadius and Honorius, and before that of Justinian II. Later writers provide no information about him, but they do note that the work was later reduced to an epitome by a certain Hermolaus, who dedicated his epitome to Justinian; whether the first or second emperor of that name is meant is disputed, but it seems probable that Stephanus flourished in Byzantium in the earlier part of the sixth century AD, under Justinian I. The ''Ethnica'' Stephanos' work, originally written in Greek, takes the form of an alphabetical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Description Of Greece
''Description of Greece'' () is the only surviving work by the ancient "geographer" or tourist Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias (c. 110 – c. 180). Pausanias' ''Description of Greece'' comprises ten books, each of them dedicated to some part of mainland Greece. He is essentially describing his own travels, and large parts of Greece are not covered, including the islands. His tour begins in Attica () and continues with Athens, including its suburbs or demes. Then the work goes with Ancient Corinth, Corinthia (), Laconia (), Messenia (ancient region), Messenia (), Ancient Elis, Elis (), Achaea (ancient region), Achaea (), Arcadia (region), Arcadia (), Boeotia (), Phocis (ancient region), Phocis (), and Ozolian Locris (). The work is rather erratic on described topography; its main interest is the cultural geography of ancient Greece, especially its religious sites, in which Pausanias not only mentioned, and occasionally described, architectural and artistic objects, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |