|
Irtysh (rocket)
Irtysh (), also named Soyuz-5 (), formerly codenamed Fenix in Russian and Sunkar () in Kazakh, is a planned Russian rocket that is being developed by JSC SRC Progress within the "Project Feniks" (). Initially it will replace the capability of Zenit-2 and Proton Medium, and in the future will serve as the base of a super heavy-lift launch vehicle rocket (Yenisei) to match the Energia/ Buran capabilities. , Irtysh is expected to launch from the Baikonur Baiterek, the ex Zenit-2 launch site, in a partnership with the government of Kazakhstan, with a planned debut in late 2023. Project organization The current proposal is led by JSC SRC Progress, with support by Khrunichev and Makeyev, additionally, RSC Energia would handle the launch site, and supply the Blok DM-03, while Roscosmos would finance the development through the Project Fenicks under the 2016–2025 Russian space master plan. KazCosmos would also be a partner since the initial launch pad would be at Baikonur Cosmodro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress State Research And Production Rocket Space Center
The Progress Rocket Space Centre (russian: Ракетно-космический центр «Прогресс»), formerly known as TsSKB-Progress (russian: ЦСКБ-Прогресс), is a Russian joint-stock company under the jurisdiction of Roscosmos State Corporation responsible for space science and aerospace research. It was the developer of the famous Soyuz-FG rocket that was used for crewed space flight, as well as the Soyuz-U that was used for launching uncrewed probes. Overview Progress Centre was the developer and manufacturer of the Soyuz FG series of launch vehicles that were used for human spaceflight launches, and the Soyuz-U series that were used for robotic spacecraft launches. Commercial marketing of these launch vehicles was handled by the company Starsem. TsSKB-Progress' satellite products include the Foton and Foton-M science satellite series, the Yantar military satellites and the Resurs DK Earth resource satellite. The company's main production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blok DM-03
The Blok DM-03 (russian: Блок ДМ-03 meaning ''Block DM-03''), GRAU index ''11S861-03'', is a Russian upper stage used as an optional fourth stage on the Proton-M heavy-lift rocket. Three have been launched, the first in December 2010; the first two launches failed before fourth stage ignition, the first as a result of a problem with the Blok DM's fuel load. Initial versions of the Blok DM-03 are powered by a single RD-58M engine, burning RG-1 and liquid oxygen. The last evolution is powered by the improved RD-58MF, a less powerful but more efficient evolution of the venerable engine. It can carry 25% more propellant than the Blok DM-2, which it replaced as a Proton upper stage for some government launches. However most government launches and all commercial missions use the Briz-M instead. The payloads for the first two Blok DM-03 launches were groups of three Uragan-M satellites for the GLONASS programme, with further missions slated to carry three more Uragan-M sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit
A geosynchronous transfer orbit or geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) is a type of geocentric orbit. Satellites that are destined for geosynchronous (GSO) or geostationary orbit (GEO) are (almost) always put into a GTO as an intermediate step for reaching their final orbit. A GTO is highly elliptic. Its perigee (closest point to Earth) is typically as high as low Earth orbit (LEO), while its apogee (furthest point from Earth) is as high as geostationary (or equally, a geosynchronous) orbit. That makes it a Hohmann transfer orbit between LEO and GSO. Larson, Wiley J. and James R. Wertz, eds. Space Mission Design and Analysis, 2nd Edition. Published jointly by Microcosm, Inc. (Torrance, CA) and Kluwer Academic Publishers (Dordrecht/Boston/London). 1991. While some GEO satellites are launched direct to that orbit, often the launch vehicle lacks the power to put both the rocket and the satellite into that orbit. Instead extra fuel is added to the satellite, the launch vehicle la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Launch Services
International Launch Services, Inc. (ILS) is a joint venture with exclusive rights to the worldwide sale of commercial Angara and Proton rocket launch services. Proton launches take place at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan while Angara is launched from the Plesetsk and Vostochny Cosmodrome in Russia. Ownership ILS was formed in 1995 as a private spaceflight partnership between Lockheed Martin (LM), Khrunichev and Energia. ILS initially co-marketed non-military launches on both the American Atlas and the Russian Proton expendable launch vehicles. With the Atlas V launch of the SES Astra 1KR satellite on 20 April 2006, ILS had made 100 launches, 97 of which were successful. In September 2006, Lockheed-Martin announced its intention to sell its ownership interests in Lockheed Khrunichev Energia International, Inc. (LKEI) and International Launch Services, Inc. (ILS) to Space Transport Inc. Space Transport Inc. was formed specifically for this transaction by Mario Lemme, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KazCosmos
The National Space Agency of the Republic of Kazakhstan ( kk, Қазақстан Республикасы Ұлттық ғарыш агенттiгi, Qazaqstan Respublikasy Ūlttyq ğaryş agenttıgı), also known as KazCosmos, or KazKosmos, is Kazakhstan's national space agency, and was officially established on 27 March 2007. History Cosmonaut corps On 7 January 2000, the Kazakh government decreed it would form a cosmonaut corps. At that time, two Kazakh cosmonauts had already flown, Toktar Aubakirov in 1991, and Talgat Musabayev (1994, 1998; later 2001). Out of 2000 candidates, two were selected, Aidyn Aimbetov and Mukhtar Aymakhanov, in 2002. They were sent to Star City for training from 2003 until 2009, when the world financial crisis indefinitely postponed the spaceflight. In 2009, they returned to work in KazCosmos. They had originally been projected for a spaceflight in 2005 or 2006. Aymakhanov left Kazakhstan in 2012 to become a Russian citizen to pursue a cosmonaut car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roscosmos
The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" (russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос»), commonly known simply as Roscosmos (russian: Роскосмос), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency, which was established on 25 February 1992russian: Российское космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (russian: РКА). and restructured in 1999 and 2004, as the Russian Aviation and Space Agencyrussian: Российское авиационно-космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makeyev Rocket Design Bureau
The JSC Makeyev Design Bureau (russian: ГРЦ Макеева; also known as Makeyev OKB) is a Russian missile design company located in Miass, Russia. Established in December 1947 as SKB-385 in Zlatoust (see Zlatoust Machine-Building Plant), the company was the main designer of submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBM) in Russia. In 1955, the company was moved to Miass. In 1993, the organization was posthumously renamed in honor of Victor Makeyev, who had been the Chief Designer of SKB-385. Its full official name is State Rocket Center «Academician V.P. Makeev Design Bureau». In 1965, SKB-385 was redesignated the Design Bureau of Machine-Building (KBM) under the Ministry of General Machine-Building. Rockets and missiles *R-11 Zemlya *R-13 (missile) *R-17 Elbrus *R-21 (missile) *Shtil' *Volna *R-27 Zyb * R-29 Vysota *R-29RM Shtil *R-29RMU Sineva *R-29RMU2 Layner *R-39 Rif *RS-28 Sarmat *CORONA * ROSSIYANKA References External links Makeyev homepage (English)at the Nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khrunichev State Research And Production Space Center
The Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center (''Государственный космический научно-производственный центр (ГКНПЦ) имени М. В. Хру́ничева'' in Russian) is a Moscow-based manufacturer of spacecraft and space-launch systems, including the Proton and Rokot rockets, and the Russian modules of Mir and the International Space Station. The company's history dates back to 1916, when an automobile factory was established at Fili, western suburb of Moscow. It soon switched production to airplanes and during World War II produced Ilyushin Il-4 and Tupolev Tu-2 bombers. A design bureau, OKB-23, was added to the company in 1951. In 1959, the company started developing intercontinental ballistic missiles, and later spacecraft and space launch vehicles. The company designed and produced all Soviet space stations, including Mir. OKB-23, renamed to ''Salyut Design Bureau'', became an independent company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
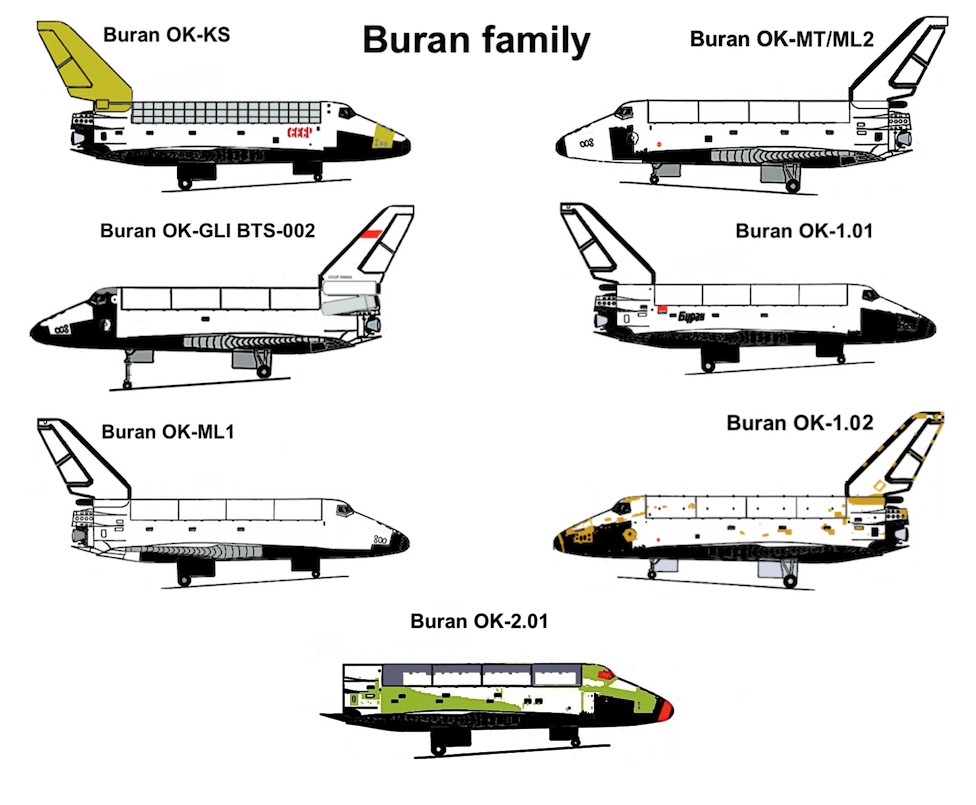
Buran (spacecraft)
''Buran'' (russian: Буран, , meaning "Snowstorm" or "Blizzard"; GRAU index serial number: 11F35 1K, construction number: 1.01) was the first spaceplane to be produced as part of the Soviet/Russian Buran program. Besides describing the first operational Soviet/Russian shuttle orbiter, "Buran" was also the designation for the entire Soviet/Russian spaceplane project and its orbiters, which were known as "Buran-class orbiters". Buran completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988, and was destroyed in the 2002 collapse of its storage hangar. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket, a class of super heavy-lift launch vehicle. It is named after the Asian wind. Construction The construction of the Buran spacecraft began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale orbiter was rolled out. Over 1000 companies all over the Soviet Union were involved in construction and development. The Buran spacecraft was made to be launched on the Soviet Union's super-heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
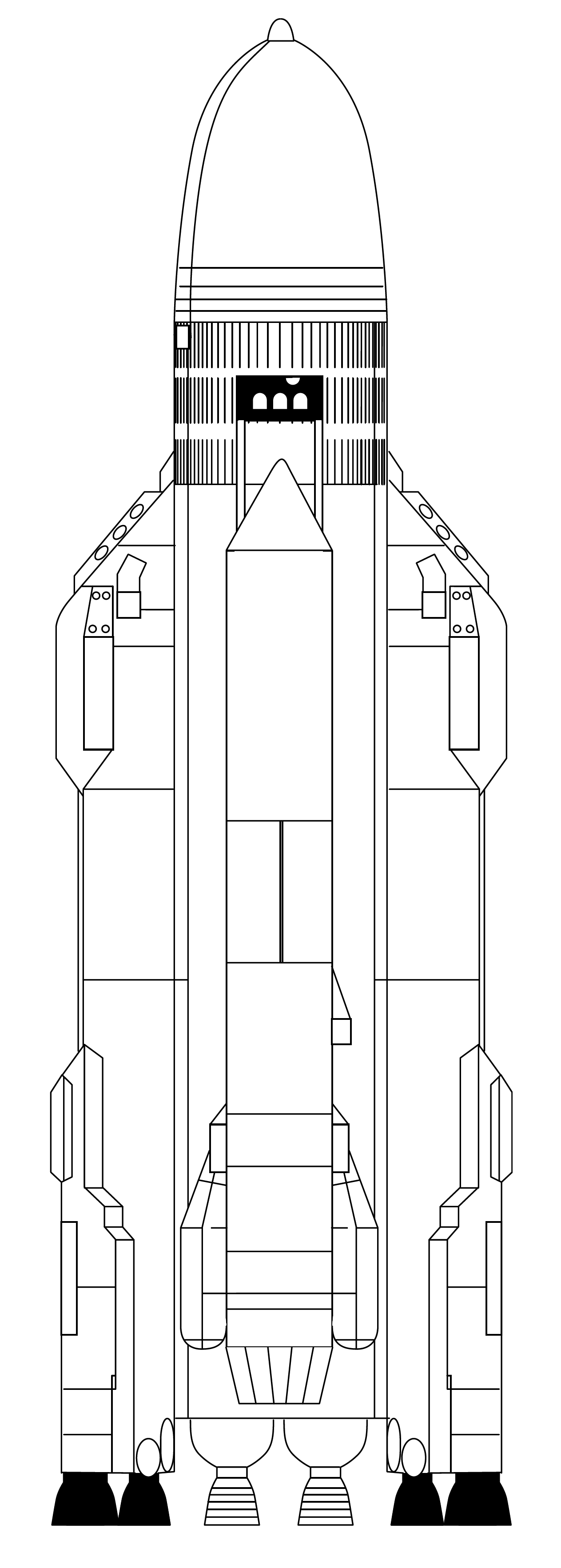
Energia (rocket)
Energia (russian: Энергия, Energiya, Energy; GRAU 11K25) was a 1980s super-heavy lift launch vehicle. It was designed by NPO Energia of the Soviet Union as part of the Buran programme, Buran program for a variety of payloads including the Buran (spacecraft), Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the Khartron NPO "Electropribor". The Energia used four strap-on boosters each powered by a four-chamber RD-170 engine burning kerosene/Liquid oxygen, LOX, and a central core stage with four single-chamber RD-0120 (11D122) engines fueled by liquid hydrogen/LOX. The launch vehicle had two functionally different operational variants: Energia-Polyus, the initial test configuration, in which the Polyus (spacecraft), Polyus system was used as a final stage intended to put the payload into orbit, and Energia-Buran, in which the Buran programme, ''Buran'' orbiter was the payload and the source of the orbit insertion impulse. The launch vehicle had the capacity to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Heavy-lift Launch Vehicle
A super heavy-lift launch vehicle can lift to low Earth orbit more than by United States (NASA) classification or by Russian classification. It is the most capable launch vehicle classification by mass to orbit, exceeding that of the heavy-lift launch vehicle classification. Crewed lunar and interplanetary missions are often developed around these launch vehicles' payload capacity. Many early super heavy-lift launch vehicle concepts were made in the 1960s, such as the Sea Dragon. During the Space Race, the Saturn V and N1 were built by the United States and Soviet Union. After the Saturn V's successful Apollo program and the N1's failures, the Soviets' Energia launched twice in the 1980s, once with the Buran spaceplane. The next two decades saw multiple concepts drawn out once again, most notably Shuttle-derived vehicles and Rus-M, but none would be built. In the 2010s, super heavy-lift launch vehicles received interest once again, leading to the launch of the Falcon Heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix (mythology)
The phoenix is an immortal bird associated with Greek mythology (with analogs in many cultures) that cyclically regenerates or is otherwise born again. Associated with the sun, a phoenix obtains new life by rising from the ashes of its predecessor. Some legends say it dies in a show of flames and combustion, others that it simply dies and decomposes before being born again. In the ''Motif-Index of Folk-Literature'', a tool used by folklore studies, folklorists, the phoenix is classified as motif B32.Thompson. (2001: 581). The origin of the phoenix has been attributed to Ancient Egypt by Herodotus and later 19th-century scholars, but other scholars think the Egyptian texts may have been influenced by classical folklore. Over time the phoenix motif spread and gained a variety of new associations; Herodotus, Lucan, Pliny the Elder, Pope Clement I, Lactantius, Ovid, and Isidore of Seville are among those who have contributed to the retelling and transmission of the phoenix motif. Ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |