|
Super Heavy-lift Launch Vehicle
A super heavy-lift launch vehicle can lift to low Earth orbit more than by United States (NASA) classification or by Russian classification. It is the most capable launch vehicle classification by mass to orbit, exceeding that of the heavy-lift launch vehicle classification. Crewed lunar and interplanetary missions are often developed around these launch vehicles' payload capacity. Many early super heavy-lift launch vehicle concepts were made in the 1960s, such as the Sea Dragon. During the Space Race, the Saturn V and N1 were built by the United States and Soviet Union. After the Saturn V's successful Apollo program and the N1's failures, the Soviets' Energia launched twice in the 1980s, once with the Buran spaceplane. The next two decades saw multiple concepts drawn out once again, most notably Shuttle-derived vehicles and Rus-M, but none would be built. In the 2010s, super heavy-lift launch vehicles received interest once again, leading to the launch of the Falcon Heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy-lift Launch Vehicle
A heavy-lift launch vehicle, HLV or HLLV, is an orbital launch vehicle capable of lifting between (by NASA classification) or between (by Russian classification) into low Earth orbit (LEO).50t payloads" , operational heavy-lift launch vehicles include the Ariane 5, the Long March 5, the Proton-M and the Delta IV Heavy. In addition, the Angara A5, the Falcon 9 Full Thrust, and the Falcon Heavy are designed to provide heavy-lift capabilities in at least some configurations but have not yet been proven to carry a 20-tonne payload into LEO. Several other heavy-lift rockets are in development. An HLV is between medium-lift launch vehicles and super heavy-lift launch vehicles. Rated launch vehicles See also * Comparison of orbital launch systems * List of orbital launch systems * Comparison of orbital rocket engines * Comparison of space station cargo vehicles * Medium-lift launch vehicle, capable of lifting between 2,000 and 20,000 kg (4,400 to 44,100 lb) of payloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Spaceflight
Interplanetary spaceflight or interplanetary travel is the crewed or uncrewed travel between stars and planets, usually within a single planetary system. In practice, spaceflights of this type are confined to travel between the planets of the Solar System. Uncrewed space probes have flown to all the observed planets in the Solar System as well as to dwarf planets Pluto and Ceres, and several asteroids. Orbiters and landers return more information than fly-by missions. Crewed flights have landed on the Moon and have been planned, from time to time, for Mars, Venus and Mercury. While many scientists appreciate the knowledge value that uncrewed flights provide, the value of crewed missions is more controversial. Science fiction writers propose a number of benefits, including the mining of asteroids, access to solar power, and room for colonization in the event of an Earth catastrophe. A number of techniques have been developed to make interplanetary flights more economical. Advanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation, and hundreds of experiments. Unable to be re-boosted by the Space Shuttle, which was not ready until 1981, Skylab's orbit eventually decayed, and it disintegrated in the atmosphere on July 11, 1979, scattering debris across the Indian Ocean and Western Australia. Overview Skylab was the only space station operated exclusively by the United States. A permanent station was planned starting in 1988, but funding for this was canceled and replaced with United States participation in an International Space Station in 1993. Skylab had a mass of with a Apollo command and service module (CSM) attached and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and several hundred life sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed spacecraft to operate exclusively in the airless vacuum of space, and remains the only crewed vehicle to land anywhere beyond Earth. Structurally and aerodynamically incapable of flight through Earth's atmosphere, the two-stage lunar module was ferried to lunar orbit attached to the Apollo command and service module (CSM), about twice its mass. Its crew of two flew the complete lunar module from lunar orbit to the Moon's surface. During takeoff, the spent descent stage was used as a launch pad for the ascent stage which then flew back to the command module, after which it was also discarded. Overseen by Grumman, the LM's development was plagued with problems that delayed its first uncrewed flight by about ten months and its first crewed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
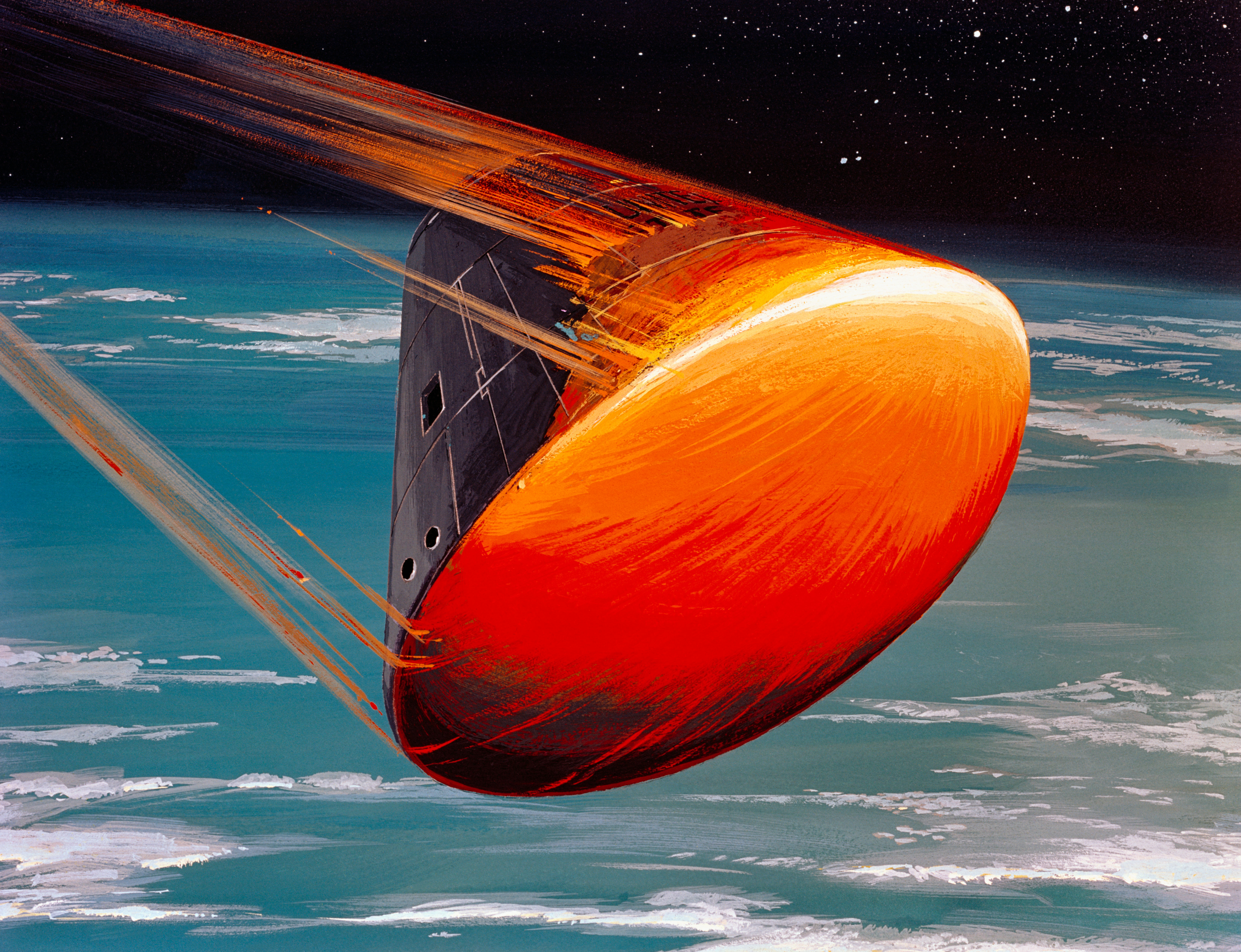
Apollo Service Module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship, which carried a crew of three astronauts and the second Apollo spacecraft, the Apollo Lunar Module, to lunar orbit, and brought the astronauts back to Earth. It consisted of two parts: the conical command module, a cabin that housed the crew and carried equipment needed for atmospheric reentry and splashdown; and the cylindrical service module which provided propulsion, electrical power and storage for various consumables required during a mission. An umbilical connection transferred power and consumables between the two modules. Just before reentry of the command module on the return home, the umbilical connection was severed and the service module was cast off and allowed to burn up in the atmosphere. The CSM was developed and built f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Command Module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship, which carried a crew of three astronauts and the second Apollo spacecraft, the Apollo Lunar Module, to lunar orbit, and brought the astronauts back to Earth. It consisted of two parts: the conical command module, a cabin that housed the crew and carried equipment needed for atmospheric reentry and splashdown; and the cylindrical service module which provided propulsion, electrical power and storage for various consumables required during a mission. An umbilical connection transferred power and consumables between the two modules. Just before reentry of the command module on the return home, the umbilical connection was severed and the service module was cast off and allowed to burn up in the atmosphere. The CSM was developed and built f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Spaceflight
An orbital spaceflight (or orbital flight) is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least one orbit. To do this around the Earth, it must be on a free trajectory which has an altitude at perigee (altitude at closest approach) around ; this is the boundary of space as defined by NASA, the US Air Force and the FAA. To remain in orbit at this altitude requires an orbital speed of ~7.8 km/s. Orbital speed is slower for higher orbits, but attaining them requires greater delta-v. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale has established the Kármán line at an altitude of as a working definition for the boundary between aeronautics and astronautics. This is used because at an altitude of about , as Theodore von Kármán calculated, a vehicle would have to travel faster than orbital velocity to derive sufficient aerodynamic lift from the atmosphere to support itself. Due to atmospheric drag, the lowest altitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Government Of The United States
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a federal district (the city of Washington in the District of Columbia, where most of the federal government is based), five major self-governing territories and several island possessions. The federal government, sometimes simply referred to as Washington, is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial, whose powers are vested by the U.S. Constitution in the Congress, the president and the federal courts, respectively. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of Congress, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court. Naming The full name of the republic is "United States of America". No other name appears in the Constitution, and this i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rus-M
Rus-M (russian: Русь-М) was a proposed launcher design which was intended to become Russia's main launch vehicle for crewed spaceflight after 2018, and an integral part of the Orel spacecraft being developed to replace the Soyuz. Rus-M was being developed by TsSKB-Progress, beginning in 2009. The program was halted in October 2011, restarted in 2012 and finally cancelled in August 2015. History In 2009, Roscomos published the specifications for a Rus-M launch vehicle. Several variants of the Rus-M were later proposed, creating a family of similar launch vehicles. In spring of 2009, TsSKB-Progress won a government contract to develop a new launcher for Russia's human space program. The project was featured in MAKS 2009 Airshow, and preliminary design of the vehicle was expected to be submitted to the Russian space agency Roscosmos by August 2010. Requirements Safety requirements put forward by Roscosmos emphasized that the launcher design is to be extremely reliable; saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)