|
Iranrood
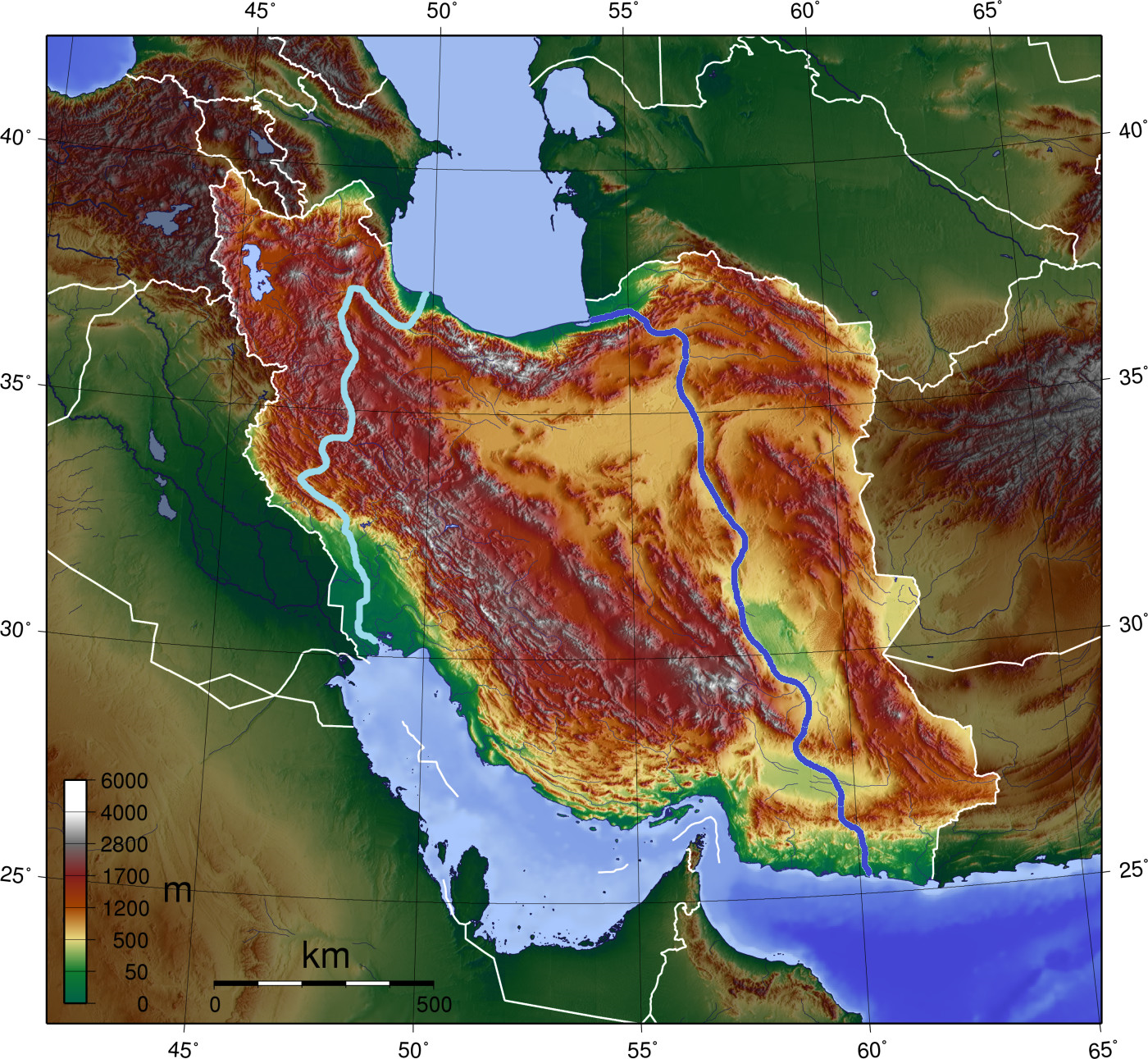
Iranrud (Persian language, Persian: ایرانرود) which means ''Iran River'' in Persian language, Persian, was a plan to build a canal from the Caspian Sea to the Persian Gulf or the Gulf of Oman. The former Soviet Union was eager to realize this project because its only warm water ports led to the Strait of Istanbul and the Dardanelles, which were under the control of Turkey, a NATO country. There were two different proposals for the route of the canal: * directly to the Indian Ocean through Dasht-e Lut, or; * from the Caspian to Lake Urmia and after that to the Persian Gulf. History The idea of linking the two coasts via Iranian territory was first introduced in the 19th century. The first professional study was carried out in the 1960s. First time this plan has been written by Humaan Farzad in 1968. According to his plan some lake must be made between Persian gulf and Oman sea. Three places were suggested: Jazmurian pit and two other places in Dasht-e Lut and Dasht-e Kav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranrood
Iranrud (Persian language, Persian: ایرانرود) which means ''Iran River'' in Persian language, Persian, was a plan to build a canal from the Caspian Sea to the Persian Gulf or the Gulf of Oman. The former Soviet Union was eager to realize this project because its only warm water ports led to the Strait of Istanbul and the Dardanelles, which were under the control of Turkey, a NATO country. There were two different proposals for the route of the canal: * directly to the Indian Ocean through Dasht-e Lut, or; * from the Caspian to Lake Urmia and after that to the Persian Gulf. History The idea of linking the two coasts via Iranian territory was first introduced in the 19th century. The first professional study was carried out in the 1960s. First time this plan has been written by Humaan Farzad in 1968. According to his plan some lake must be made between Persian gulf and Oman sea. Three places were suggested: Jazmurian pit and two other places in Dasht-e Lut and Dasht-e Kav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir-Hossein Mousavi
Mir-Hossein Mousavi Khameneh ( fa, میرحسین موسوی خامنه, Mīr-Hoseyn Mūsavī Khāmené, ; born 2 March 1942) is an Iranian reformist politician, artist and architect who served as the forty-ninth and last Prime Minister of Iran from 1981 to 1989. He was a reformist candidate for the 2009 presidential election and eventually the leader of the opposition in the post-election unrest. Mousavi served as the president of the Iranian Academy of Arts until 2009, when Conservative authorities removed him. In the early years of the revolution, Mousavi was the editor-in-chief of ''Jomhouri-e Eslami'', the official newspaper of the Islamic Republican Party, before being elevated to Minister of Foreign Affairs and eventually the post of Prime Minister. He was the last Prime Minister in Iran prior to the 1989 constitutional changes which removed the post of the prime minister; he then went into semi-retirement for the next 20 years. He remains a member of the Expediency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandar Abas
Bandar Abbas or Bandar-e ‘Abbās ( fa, , , ), is a port city and capital of Hormozgān Province on the southern coast of Iran, on the Persian Gulf. The city occupies a strategic position on the narrow Strait of Hormuz (just across from Musandam Governorate, Oman), and it is the location of the main base of the Iranian Navy. Bandar Abbas is also the capital and largest city of Bandar Abbas County. At the 2016 census, its population was 526,648. Etymology Bandar Abbas has always been a port, and as such its various names have all reflected this function. The most common name over time, Gameroon, traditionally derived from Turkish ''gümrük'', "customhouse" (from Late Greek ''kommerkion'', from Latin ''commercium'', "commerce"), but is now speculated to come from Persian ''kamrūn'', "shrimp" (in Portuguese: ''camarão'', similar to the former Portuguese name). Its current name derives from that of Abbas the Great () paired with ''bandar'' - "port", meaning "Port of Abbas". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dašt-e Kavira
Dasht-e Kavir ( fa, دشت كوير, lit=Low Plains in classical Persian, from ''khwar'' (low), and ''dasht'' (plain, flatland)), also known as Kavir-e Namak () and the Great Salt Desert, is a large desert lying in the middle of the Iranian Plateau. It is about long by wide with a total surface area of about , making it the world's 24th largest desert. The area of this desert stretches from the Alborz mountain range in the north-west to the Dasht-e Lut in the south-east. It is partitioned among the Iranian provinces of Khorasan, Semnan, Tehran, Isfahan and Yazd. Features In the center of the desert lies the Kavir Buzurg (Great Kavir), which is about 320 km long and wide. In the western part of the desert lies the Daryahcheh-e Namak ("salt lake"), . It contains some large salt plates in a mosaic-like shape. It is part of a protected ecological zone, the Kavir National Park. One of the most desolate parts of Dasht-e Kavir is the Rig-e Jenn (‘Dune of the Jinn’). Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dašt-e Lut
The Lut Desert, widely referred to as Dasht-e Lut ( fa, دشت لوت, "Emptiness Plain"), is a large salt desert located in the provinces of Kerman and Sistan and Baluchestan, Iran. It is the world's 33rd-largest desert, and was included on UNESCO's World Heritage List on July 17, 2016. The name is derived from 'Lut' which means bare and empty in Persian and 'dasht' which means plain in Persian. The surface of its sand has been measured at temperatures as high as 70.7 °C (159.3 °F), making it one of the world's driest and hottest places. Description Iran is climatically part of the Afro-Asian belt of deserts, which stretches from Mauritania all the way to Mongolia. The patchy, elongated, light-colored feature in the foreground (parallel to the mountain range) is the northernmost of the Dasht dry lakes that stretch southward . Iran's geography consists of a plateau surrounded by mountains and divided into drainage basins. Dasht-e Lut is one of the largest of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamadan
Hamadan () or Hamedan ( fa, همدان, ''Hamedān'') ( Old Persian: Haŋgmetana, Ecbatana) is the capital city of Hamadan Province of Iran. At the 2019 census, its population was 783,300 in 230,775 families. The majority of people living in Hamadan identify as ethnic Persians. Hamedan is believed to be among the oldest Iranian cities. It is possible that it was occupied by the Assyrians in 1100 BCE; the Ancient Greek historian, Herodotus, states that it was the capital of the Medes, around 700 BCE. Hamedan has a green mountainous area in the foothills of the 3,574-meter Alvand Mountain, in the midwest part of Iran. The city is 1,850 meters Above mean sea level, above sea level. The highly cultural nature of this old city and its historic sites attract tourists during the summer to this city, located approximately southwest of Tehran. The major sights of this city are the Ganj Nameh inscription, the Avicenna monument and the Baba Taher monument. The main language in the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, Kurdish languages, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros Mountains, Zagros and the eastern Taurus Mountains, Taurus mountain ranges. Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey (Turkish Kurdistan, Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq (Iraqi Kurdistan, Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran (Iranian Kurdistan, Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria (Syrian Kurdistan, Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern South Caucasus, Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalism, Kurdish nationalist organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alborz
The Alborz ( fa, البرز) range, also spelled as Alburz, Elburz or Elborz, is a mountain range in northern Iran that stretches from the border of Azerbaijan along the western and entire southern coast of the Caspian Sea and finally runs northeast and merges into the smaller Aladagh Mountains and borders in the northeast on the parallel mountain ridge Kopet Dag in the northern parts of Khorasan. All these mountains are part of the much larger Alpide belt. This mountain range is divided into the Western, Central, and Eastern Alborz Mountains. The Western Alborz Range (usually called the Talysh) runs south-southeastward almost along the western coast of the Caspian Sea. The Central Alborz (the Alborz Mountains in the strictest sense) runs from west to east along the entire southern coast of the Caspian Sea, while the Eastern Alborz Range runs in a northeasterly direction, toward the northern parts of the Khorasan region, southeast of the Caspian Sea. Mount Damavand, the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagros
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgros'' ''کویا زاگرس'') are a long mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. This mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros mountain range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of southeastern Turkey and northeastern Iraq. From this border region, the range continues to the southeast under also the waters of the Persian Gulf. It spans the southern parts of the Armenian highland, the whole length of the western and southwestern Iranian plateau, ending at the Strait of Hormuz. The highest point is Mount Dena, at . Geology The Zagros fold and thrust belt was mainly formed by the collision of two tectonic plates, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khuzestan
Khuzestan Province (also spelled Xuzestan; fa, استان خوزستان ''Ostān-e Xūzestān'') is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. It is in the southwest of the country, bordering Iraq and the Persian Gulf. Its capital is Ahvaz and it covers an area of . Since 2014, it has been part of Iran's Region 4. Historically, one of the most important regions of the Ancient Near East, Khuzestan is what historians refer to as ancient Elam, whose capital was in Susa. The Achaemenid Old Persian term for Elam was ''Hujiyā'' when they conquered it from the Elamites, which is present in the modern name. Khuzestan, meaning "the Land of the Khuz", refers to the original inhabitants of this province, the "Susian" people (Old Persian "Huza" or ''Huja'', as in the inscription at the tomb of Darius the Great at Naqsh-e Rostam). They are the Shushan of the Hebrew sources where they are recorded as "Hauja" or "Huja". In Middle Persian, the term evolves into "Khuz" and "Kuzi". The pre-Islamic Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefid Rud
The Sefid-Rud ( fa, سفیدرود, lit=white river, glk, اسپي بيه, ''Espī bīeh'') (also known as Sepid-Rud) is a river approximately long, rising in the Alborz mountain range of northwestern Iran and flowing generally northeast to enter the Caspian Sea at Rasht. The river is Iran's second longest river after the Karun. Names Other names and transcriptions include Sepīd-Rūd, Sefidrud, Sefidrood, Sepidrood, and Sepidrud. Above Manjil, "Long Red River".Fortescue, L. S. (April 1924) "The Western Elburz and Persian Azerbaijan" ''The Geographical Journal'' 63(4): pp. 301-315, p.310Rawlinson, H. C. (1840) "Notes on a Journey from Tabríz, Through Persian Kurdistán, to the Ruins of Takhti-Soleïmán, and from Thence by Zenján and Ṭárom, to Gílán, in October and November, 1838; With a Memoir on the Site of the Atropatenian Ecbatana" ''Journal of the Royal Geographical Society of London'' 10: pp. 1-64, p. 64 The river is identified with the Amardus ( grc, Ἀμάρδο ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |