|
Intransitive Case
In grammar, the intransitive case (abbreviated ), also denominated passive case or patient case, is a grammatical case used in some languages to mark the argument of an intransitive verb, but not used with transitive verbs. It is generally seen in languages that display tripartite nominal morphologies; it contrasts with the nominative and absolutive cases employed in other languages' morphosyntax to mark the argument of intransitive clauses. As a distinct intransitive case has zero marking in all languages known to have one, and is the citation form of the noun, it is frequently called absolutive, a word used for an unmarked citation-form argument in various case systems. See also *Transitive case *Nominative case *Absolutive case In grammar, the absolutive case (abbreviated ) is the case of nouns in ergativeŌĆōabsolutive languages that would generally be the subjects of intransitive verbs or the objects of transitive verbs in the translational equivalents of nominativeŌĆ ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domains such as phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, often complemented by phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are currently two different approaches to the study of grammar: traditional grammar and Grammar#Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency, Fluent speakers of a variety (linguistics), language variety or ''lect'' have effectively internalized these constraints, the vast majority of which ŌĆō at least in the case of one's First language, native language(s) ŌĆō are language acquisition, acquired not by conscious study or language teaching, instruction but by hearing other speakers. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glossing Abbreviations
This article lists common abbreviations for grammatical terms that are used in linguistic interlinear glossing of oral languages in English. The list provides conventional glosses as established by standard inventories of glossing abbreviations such as the Leipzig Glossing rules, the most widely known standard. These will generally be the glosses used on Wikipedia. Synonymous glosses are listed as alternatives for reference purposes. In a few cases, long and short standard forms are listed, intended for texts where that gloss is rare or common. Conventions * Grammatical abbreviations are generally written in full or small caps to visually distinguish them from the translations of lexical words. For instance, capital or small-cap (frequently abbreviated to ) glosses a grammatical past-tense morpheme, while lower-case 'past' would be a literal translation of a word with that meaning. Similarly, (small) cap might be a locative suffix used in nominal inflections, prototypically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers ( determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals), which corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English language, English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative case, nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver and the accusative case, accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative case, nominative and accusative case, accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English language, English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the Nominative case, nominative, Accusative case, accusative and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
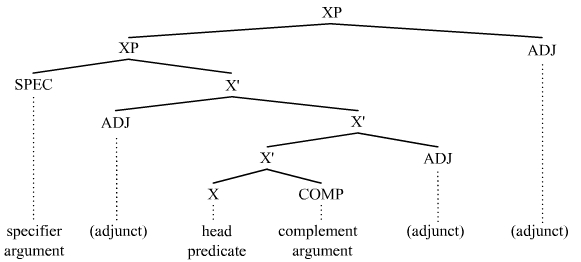
Argument (linguistics)
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the '' complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is generally believed to exist in all languages. Dependency grammars sometimes call ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intransitive Verb
In grammar, an intransitive verb is a verb whose context does not entail a direct object. That lack of transitivity distinguishes intransitive verbs from transitive verbs, which entail one or more objects. Additionally, intransitive verbs are typically considered within a class apart from modal verbs and defective verbs. Examples In the following sentences, verbs are used without a direct object: *"Rivers flow." *"I sneezed." *"My dog ran." *"Water evaporates when it's hot." *"You've grown since I last saw you!" *"I wonder how old I will be when I die." The following sentences contain transitive verbs (they entail one or more objects): *"We watched ''a movie'' last night." *"She's making ''promises''." *"When I said that, my sister smacked ''me''." *"Santa gave ''me'' ''a present''." *"He continuously clicked ''his pen'' and it was incredibly annoying to me." Some verbs, called ambitransitive verbs, may entail objects but do not always require one. Such a verb may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitive Verb
A transitive verb is a verb that accepts one or more objects, for example, 'cleaned' in ''Donald cleaned the window''. This contrasts with intransitive verbs, which do not have objects, for example, 'panicked' in ''Donald panicked''. Transitivity is traditionally thought of as a global property of a clause, by which activity is transferred from an agent to a patient. Transitive verbs can be classified by the number of objects they require. Verbs that accept only two arguments, a subject and a single direct object, are monotransitive. Verbs that accept two objects, a direct object and an indirect object, are ''ditransitive'', or less commonly ''bitransitive''. An example of a ditransitive verb in English is the verb ''to give'', which may feature a subject, an indirect object, and a direct object: ''John gave Mary the book''. Verbs that take three objects are ''tritransitive''. In English a tritransitive verb features an indirect object, a direct object, and a prepositiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripartite Language
In linguistic typology, tripartite alignment is a type of morphosyntactic alignment in which the main argument ('subject') of an intransitive verb, the agent argument ('subject') of a transitive verb, and the patient argument ('direct object') of a transitive verb are each treated distinctly in the grammatical system of a language. This is in contrast with nominative-accusative and ergative-absolutive alignment languages, in which the argument of an intransitive verb patterns with either the agent argument of the transitive (in accusative languages) or with the patient argument of the transitive (in ergative languages). Thus, whereas in English, "she" in "she runs" patterns with "she" in "she finds it", and an ergative language would pattern "she" in "she runs" with "her" in "he likes her", a tripartite language would treat the "she" in "she runs" as morphologically and/or syntactically distinct from either argument in "he likes her". Which languages constitute genuine examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominative Case
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of English) the predicate noun or predicate adjective, as opposed to its object or other verb arguments. Generally, the noun "that is doing something" is in the nominative, and the nominative is often the form listed in dictionaries. Etymology The English word ''nominative'' comes from Latin ''c─üsus nomin─üt─½vus'' "case for naming", which was translated from Ancient Greek ßĮĆ╬Į╬┐╬╝╬▒ŽāŽä╬╣╬║ßĮ┤ ŽĆŽäß┐ČŽā╬╣Žé, ''onomastikßĖŚ pt├┤sis'' "inflection for naming", from ''onom├Īz┼Ź'' "call by name", from ''├│noma'' "name". Dionysius Thrax in his The Art of Grammar refers to it as ''orth─ṓ'' or ''euthe├«a'' "straight", in contrast to the oblique or "bent" cases. Characteristics The reference form (more technically, the ''least marked'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolutive Case
In grammar, the absolutive case (abbreviated ) is the case of nouns in ergativeŌĆōabsolutive languages that would generally be the subjects of intransitive verbs or the objects of transitive verbs in the translational equivalents of nominativeŌĆōaccusative languages such as English. In ergativeŌĆōabsolutive languages In languages with ergativeŌĆōabsolutive alignment, the absolutive is the case used to mark both the subject of an intransitive verb and the object of a transitive verb in addition to being used for the citation form of a noun. It contrasts with the marked ergative case, which marks the subject of a transitive verb. For example, in Basque the noun ''mutil'' ("boy") takes the bare singular article ''-a'' both as the subject of the intransitive clause ''mutila etorri da'' ("the boy came") and as the object of the transitive clause ''Irakasleak mutila ikusi du'' ("the teacher has seen the boy") in which the subject bears the ergative ending ''-a-k''. In very few ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitive Case
In linguistic typology, transitive alignment is a type of morphosyntactic alignment used in a small number of languages in which a single grammatical case is used to mark both arguments of a transitive verb, but not with the single argument of an intransitive verb. Such a situation, which is quite rare among the world's languages, has also been called a ''double- oblique'' clause structure. Rushani, an Iranian dialect, has this alignment in the past tense. That is, in the past tense (or perhaps perfective aspect), the agent and object of a transitive verb are marked with the same case ending, while the subject of an intransitive verb is not marked. In the present tense, the object of the transitive verb is marked, the other two roles are not ŌĆō that is, a typical nominativeŌĆōaccusative alignment.J.R. Payne, 'Language Universals and Language Types', in Collinge, ed. 1990. ''An Encyclopedia of Language''. Routledge. From Payne, 1980. Intransitive: no case marking : :'I went ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominative Case
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of English) the predicate noun or predicate adjective, as opposed to its object or other verb arguments. Generally, the noun "that is doing something" is in the nominative, and the nominative is often the form listed in dictionaries. Etymology The English word ''nominative'' comes from Latin ''c─üsus nomin─üt─½vus'' "case for naming", which was translated from Ancient Greek ßĮĆ╬Į╬┐╬╝╬▒ŽāŽä╬╣╬║ßĮ┤ ŽĆŽäß┐ČŽā╬╣Žé, ''onomastikßĖŚ pt├┤sis'' "inflection for naming", from ''onom├Īz┼Ź'' "call by name", from ''├│noma'' "name". Dionysius Thrax in his The Art of Grammar refers to it as ''orth─ṓ'' or ''euthe├«a'' "straight", in contrast to the oblique or "bent" cases. Characteristics The reference form (more technically, the ''least marked'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |