|
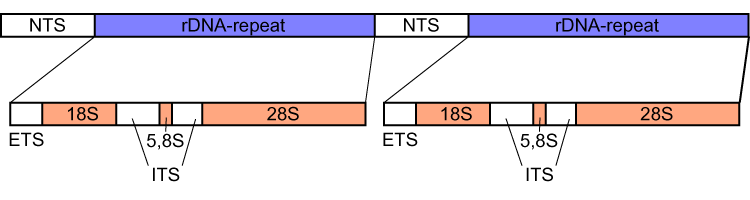
Internal Transcribed Spacer
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. Across life domains In bacteria and archaea, there is a single ITS, located between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Conversely, there are two ITSs in eukaryotes: ITS1 is located between 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes, while ITS2 is between 5.8S and 28S (in opisthokonts, or 25S in plants) rRNA genes. ITS1 corresponds to the ITS in bacteria and archaea, while ITS2 originated as an insertion that interrupted the ancestral 23S rRNA gene. Organization In bacteria and archaea, the ITS occurs in one to several copies, as do the flanking 16S and 23S genes. When there are multiple copies, these do not occur adjacent to one another. Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRNA g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacer DNA
Spacer DNA is a region of non-coding DNA between genes. The terms intergenic spacer (IGS) or non-transcribed spacer (NTS) are used particularly for the spacer DNA between the many tandemly repeated copies of the ribosomal RNA genes. In bacteria, spacer DNA sequences are only a few nucleotides long. In eukaryotes, they can be extensive and include repetitive DNA, comprising the majority of the DNA of the genome. In ribosomal DNA, there are spacers within and between gene clusters, called internal transcribed spacer (ITS) and external transcribed spacers (ETS), respectively. In animals, the mitochondrial DNA genes generally have very short spacers. In fungi, mitochondrial DNA spacers are common and variable in length, and they may also be mobile. Due to the non-coding nature of spacer DNA, its nucleotide sequence changes much more rapidly over time than nucleotide sequences coding for genes that are subject to selective forces. Although spacer DNA might not have a function that de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergenic Spacer
Spacer DNA is a region of non-coding DNA between genes. The terms intergenic spacer (IGS) or non-transcribed spacer (NTS) are used particularly for the spacer DNA between the many tandemly repeated copies of the ribosomal RNA genes. In bacteria, spacer DNA sequences are only a few nucleotides long. In eukaryotes, they can be extensive and include repetitive DNA, comprising the majority of the DNA of the genome. In ribosomal DNA, there are spacers within and between gene clusters, called internal transcribed spacer (ITS) and external transcribed spacers (ETS), respectively. In animals, the mitochondrial DNA genes generally have very short spacers. In fungi, mitochondrial DNA spacers are common and variable in length, and they may also be mobile. Due to the non-coding nature of spacer DNA, its nucleotide sequence changes much more rapidly over time than nucleotide sequences coding for genes that are subject to selective forces. Although spacer DNA might not have a function that de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leguminosae
The Fabaceae or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. Article 18.5 states: "The following names, of long usage, are treated as validly published: ....Leguminosae (nom. alt.: Fabaceae; type: Faba Mill. Vicia L.; ... When the Papilionaceae are regarded as a family distinct from the remainder of the Leguminosae, the name Papilionaceae is conserved against Leguminosae." English pronunciations are as follows: , and . commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, are a large and agriculturally important of |
Zea (plant)
''Zea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the grass family. The best-known species is ''Z. mays'' (variously called maize, corn, or Indian corn), one of the most important crops for human societies throughout much of the world. The four wild species are commonly known as teosintes and are native to Mesoamerica. Etymology ''Zea'' is derived from the Greek name () for another cereal grain (possibly spelt).Gledhill, David (2008). "The Names of Plants". Cambridge University Press. (hardback), (paperback). pp 411 Recognized species The five accepted species names in the genus are: ''Zea mays'' is further divided into four subspecies: ''Z. m. huehuetenangensis'', ''Z. m. mexicana'', '' Z. m. parviglumis'' (Balsas teosinte, the ancestor of maize), and ''Z. m. mays''. The first three subspecies are teosintes; the last is maize, or corn, the only domesticated taxon in the genus ''Zea''. The genus is divided into two sections: ''Luxuriantes'', with ''Z. diploperennis'', ''Z. luxu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaceae
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arceuthobium
The genus ''Arceuthobium'', commonly called dwarf mistletoes, is a genus of 26 species of parasitic plants that parasitize members of Pinaceae and Cupressaceae in North America, Central America, Asia, Europe, and Africa. Of the 42 species that have been recognized, 39 and 21 of these are endemic to North America and the United States, respectively. They all have very reduced shoots and leaves (mostly reduced to scales) with the bulk of the plant living under the host's bark. Recently the number of species within the genus has been reduced to 26 as a result of more detailed genetic analysis. Description They are dioecious, individual plants being either male or female. The fruit is unusual in that it builds up hydrostatic pressure internally when ripe and shoots the single sticky seed up to speeds nearly , an example of rapid plant movement. The lodgepole pine dwarf mistletoe,'' Arceuthobium americanum, has been found to explosively-disperse its seeds through thermogenesis. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscaceae
Viscaceae is a taxonomic family name of flowering plants. In this circumscription, the family includes the several genera of mistletoes. This family name is currently being studied and under review as in past decades, several systems of plant taxonomy recognized this family, notably the 1981 Cronquist system. However, the APG II system of 2003 does not recognize the family, treating it as a synonym of Santalaceae. This did not end the taxonomic debate among botanists and there are many that still think Viscaceae should be an accepted family name. According to the APG IV system Der and Nickrent (2008) found seven well supported clades in Santalaceae, but relationships between these clades are still poorly understood. The traditional and cultural uses of species within the Viscaceae merit further attention. Clades or genera treated as belonging to the currently debated family name Viscaceae include: *''Arceuthobium'' *''Dendrophthora'' *''Ginalloa'' *''Korthalsella'' *''Notothixos'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositae
The family Asteraceae, alternatively Compositae, consists of over 32,000 known species of flowering plants in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. Commonly referred to as the aster, daisy, composite, or sunflower family, Compositae were first described in the year 1740. The number of species in Asteraceae is rivaled only by the Orchidaceae, and which is the larger family is unclear as the quantity of extant species in each family is unknown. Most species of Asteraceae are annual, biennial, or perennial herbaceous plants, but there are also shrubs, vines, and trees. The family has a widespread distribution, from subpolar to tropical regions in a wide variety of habitats. Most occur in hot desert and cold or hot semi-desert climates, and they are found on every continent but Antarctica. The primary common characteristic is the existence of sometimes hundreds of tiny individual florets which are held together by protective involucres in flower heads, or more technically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteraceae
The family Asteraceae, alternatively Compositae, consists of over 32,000 known species of flowering plants in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. Commonly referred to as the aster, daisy, composite, or sunflower family, Compositae were first described in the year 1740. The number of species in Asteraceae is rivaled only by the Orchidaceae, and which is the larger family is unclear as the quantity of extant species in each family is unknown. Most species of Asteraceae are annual, biennial, or perennial herbaceous plants, but there are also shrubs, vines, and trees. The family has a widespread distribution, from subpolar to tropical regions in a wide variety of habitats. Most occur in hot desert and cold or hot semi-desert climates, and they are found on every continent but Antarctica. The primary common characteristic is the existence of sometimes hundreds of tiny individual florets which are held together by protective involucres in flower heads, or more technicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concerted Evolution
Concerted Evolution- A definition Concerted evolution is the phenomenon where paralogous genes within one species are more closely related to one another than to members of the same gene family in closely related species. In other terms, when specific members of a family are investigated, a greater amount of similarity is found within a species rather than between species. This is suggesting that members within this family do not in fact evolve independently of one another. The concept of concerted evolution is a molecular process which leads to the homogenization of DNA sequences. As shown from the diagram on the right, as each organism evolves, it creates a species that is more closely related to their genes than anyone else in their species. This is demonstrated by the different colors of circles. If each different color is representing a different organism in one species, this is showing that once the blue and the orange reproduce, they create organisms that are incredibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogeny
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree. History The theoretical framew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |