|
Intermodulation Product
Intermodulation (IM) or intermodulation distortion (IMD) is the amplitude modulation of signals containing two or more different frequencies, caused by nonlinearities or time variance in a system. The intermodulation between frequency components will form additional components at frequencies that are not just at harmonic frequencies (integer multiples) of either, like harmonic distortion, but also at the sum and difference frequencies of the original frequencies and at sums and differences of multiples of those frequencies. Intermodulation is caused by non-linear behaviour of the signal processing (physical equipment or even algorithms) being used. The theoretical outcome of these non-linearities can be calculated by generating a Volterra series of the characteristic, or more approximately by a Taylor series. Practically all audio equipment has some non-linearity, so it will exhibit some amount of IMD, which however may be low enough to be imperceptible by humans. Due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RF Intermodulation At 280 MHz
RF is an abbreviation for radio frequency. Rf or RF may also mean: Arts and entertainment * ''Red Faction (series)'', a series of revolution video games * Rinforzando, , in music notation * '' RF Online'', an online RPG made by CCR Businesses * Aero K, IATA code (2020—present) * Florida West International Airways, IATA code (1984—2017) * Regions Financial Corporation, NYSE stock symbol Government and military * France (''République française'') * Russian Federation * Rhodesian Front, former political party in Rhodesia Biology and medicine * Rheumatic fever, an inflammatory disease * Release factors RF1, RF2, RF3, proteins * Reticular formation, in the brainstem * Rheumatoid factor, an antibody * Receptive field, the response characteristic of a neuron * Respiratory failure * Risk factor Other uses in science and technology * Representative fraction * Retardation factor in a chromatographic system * Radiative forcing, the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference (communication)
In telecommunications, an interference is that which modifies a signal in a disruptive manner, as it travels along a communication channel between its source and receiver. The term is often used to refer to the addition of unwanted signals to a useful signal. Common examples include: * Electromagnetic interference (EMI) * Co-channel interference (CCI), also known as crosstalk * Adjacent-channel interference (ACI) * Intersymbol interference (ISI) * Inter-carrier interference (ICI), caused by doppler shift in OFDM modulation (multitone modulation). * Common-mode interference (CMI) * Conducted interference Noise is a form of interference but not all interference is noise. Radio resource management aims at reducing and controlling the co-channel and adjacent-channel interference. Interference alignment A solution to interference problems in wireless communication networks is interference alignment, which was crystallized by Syed Ali Jafar at the University of California, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude (see below), which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude. Definitions Peak amplitude & semi-amplitude For symmetric periodic waves, like sine waves, square waves or triangle waves ''peak amplitude'' and ''semi amplitude'' are the same. Peak amplitude In audio system measurements, telecommunications and others where the measurand is a signal that swings above and below a reference value but is not sinusoidal, peak amplitude is often used. If the reference is zero, this is the maximum absolute value of the signal; if the reference is a mean value (DC component), the peak amplitude is the maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LTI System Theory
LTI can refer to: * ''LTI – Lingua Tertii Imperii'', a book by Victor Klemperer * Language Technologies Institute, a division of Carnegie Mellon University * Linear time-invariant system, an engineering theory that investigates the response of a linear, time-invariant system to an arbitrary input signal * ''Licensed to Ill'', the 1986 debut album by the Beastie Boys * Lost Time Incident or industrial injury or Occupational injury * Learning Tools Interoperability * Louisiana Training Institute-East Baton Rouge, later known as the Jetson Center for Youth (JCY), a juvenile prison in Louisiana Companies * London Taxis International * Larsen & Toubro Infotech Biology and medicine * Lymphoid tissue-inducer cell, see innate lymphoid cell Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of innate immune cells, derived from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). In response to pathogenic tissue damage, ILCs contribute to immunity via the secretion of signalling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. Among many uses, diodes are found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Mixer
An electronic mixer is a device that combines two or more electrical or electronic signals into one or two composite output signals. There are two basic circuits that both use the term ''mixer'', but they are very different types of circuits: additive mixers and multiplicative mixers. Additive mixers are also known as analog adders to distinguish from the related digital adder circuits. Simple additive mixers use Kirchhoff's circuit laws to add the currents of two or more signals together, and this terminology ("mixer") is only used in the realm of audio electronics where audio mixers are used to add together audio signals such as voice signals, music signals, and sound effects. Multiplicative mixers multiply together two time-varying input signals instantaneously (instant-by-instant). If the two input signals are both sinusoids of specified frequencies f1 and f2, then the output of the mixer will contain two new sinusoids that have the sum f1 + f2 frequency and the diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Multiplier
In electronics, an analog multiplier is a device that takes two analog signals and produces an output which is their product. Such circuits can be used to implement related functions such as ''squares'' (apply same signal to both inputs), and ''square roots''. An electronic analog multiplier can be called by several names, depending on the function it is used to serve (see analog multiplier applications). Voltage-controlled amplifier versus analog multiplier If one input of an analog multiplier is held at a steady-state voltage, a signal at the second input will be scaled in proportion to the level on the fixed input. In this case, the analog multiplier may be considered to be a voltage controlled amplifier. Obvious applications would be for electronic volume control and automatic gain control (AGC). Although analog multipliers are often used for such applications, voltage-controlled amplifiers are not necessarily true analog multipliers. For example, an integrated circuit desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheterodyne Receiver
A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was long believed to have been invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong, but after some controversy the earliest patent for the invention is now credited to French radio engineer and radio manufacturer Lucien Lévy. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle; except those software-defined radios using ''direct sampling''. History Heterodyne Early Morse code radio broadcasts were produced using an alternator connected to a spark gap. The output signal was at a carrier frequency defined by the physical construction of the gap, modulated by the alternating current signal from the alternator. Since the output frequency of the alternator was generally in the audible range, this produces an audible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
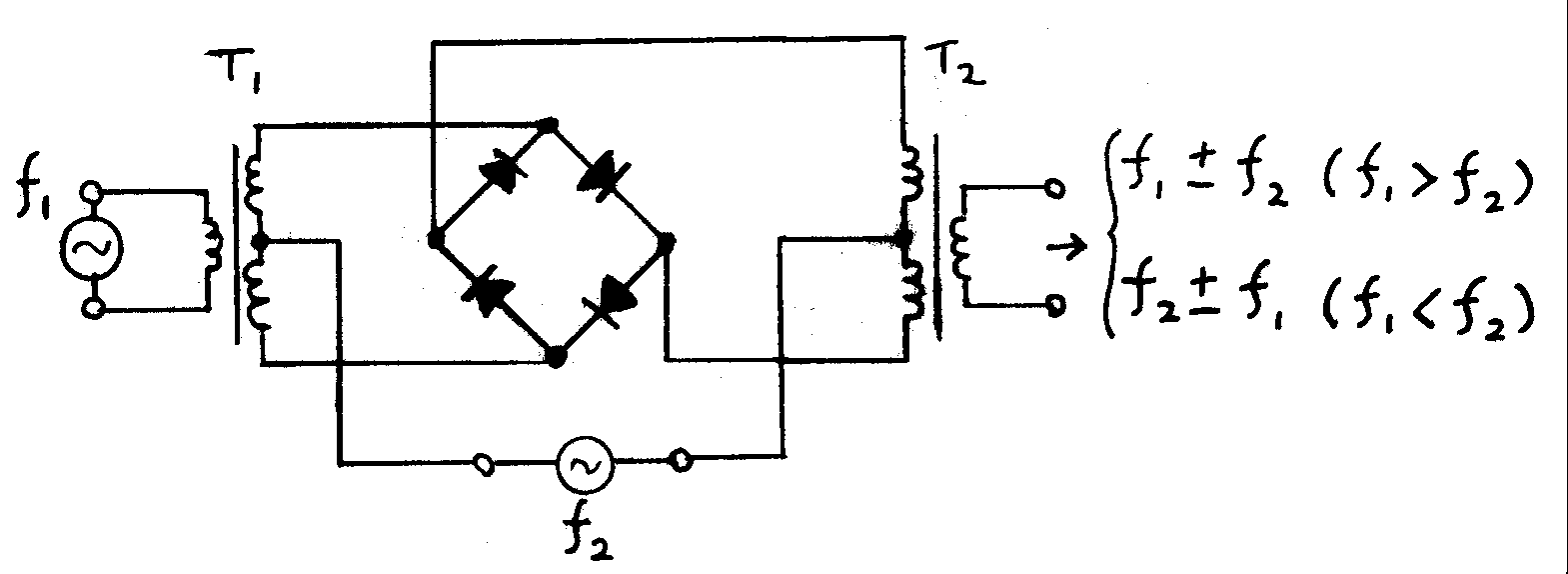
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulate a carrier signal in radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use one or more diodes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Chord
A power chord (also fifth chord) is a colloquial name for a chord in guitar music, especially electric guitar, that consists of the root note and the fifth, as well as possibly octaves of those notes. Power chords are commonly played on amplified guitars, especially on electric guitar with intentionally added distortion or overdrive effects. Power chords are a key element of many styles of rock, especially heavy metal and punk rock. Analysis When two or more notes are played through a distortion process that non-linearly transforms the audio signal, additional partials are generated at the sums and differences of the frequencies of the harmonics of those notes (intermodulation distortion). When a typical chord containing such intervals (for example, a major or minor chord) is played through distortion, the number of different frequencies generated, and the complex ratios between them, can make the resulting sound messy and indistinct. This effect is accentuated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effects Unit
An effects unit or effects pedal is an electronic device that alters the sound of a musical instrument or other audio source through audio signal processing. Common effects include distortion/overdrive, often used with electric guitar in electric blues and rock music; dynamic effects such as volume pedals and compressors, which affect loudness; filters such as wah-wah pedals and graphic equalizers, which modify frequency ranges; modulation effects, such as chorus, flangers and phasers; pitch effects such as pitch shifters; and time effects, such as reverb and delay, which create echoing sounds and emulate the sound of different spaces. Most modern effects use solid-state electronics or digital signal processors. Some effects, particularly older ones such as Leslie speakers and spring reverbs, use mechanical components or vacuum tubes. Effects are often used as stompboxes, typically placed on the floor and controlled with footswitches. They may also be built into guita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


-2.jpg)