|
Interior Plains
The Interior Plains is a vast physiographic region that spreads across the Laurentian craton of central North America, extending along the east flank of the Rocky Mountains from the Gulf Coast region to the Arctic Beaufort Sea. In Canada, it encompasses the Canadian Prairies separating the Canadian Rockies from the Canadian Shield, as well as the Boreal Plains and Taiga Plains east of the Mackenzie and Richardson Mountains; while in the United States, it includes the Great Plains of the West/ Midwest and the tallgrass prairie region to the south of the Great Lakes extending east to the Appalachian Plateau region. Geologic history A series of tectonic plate collisions in the crust that formed the center of the North American continent laid the groundwork for the modern-day interior plains. Mountain building and erosion around the plains as well as flooding from inland seas provided sediments that make up the rock strata of the interior plains. Proterozoic Eon (2500 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. It is the southern and main part of the Interior Plains, which also include the tallgrass prairie between the Great Lakes and Appalachian Plateau, and the Taiga Plains and Boreal Plains ecozones in Northern Canada. The term Western Plains is used to describe the ecoregion of the Great Plains, or alternatively the western portion of the Great Plains. The Great Plains lies across both Central United States and Western Canada, encompassing: * The entirety of the U.S. states of Kansas, Nebraska, North Dakota and South Dakota; * Parts of the U.S. states of Colorado, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Wyoming; * The southern portions of the Canadian provinces of Alberta, Saska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phanerozoic Eon
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current geologic eon in the geologic time scale, and the one during which abundant animal and plant life has existed. It covers 538.8 million years to the present, and it began with the Cambrian Period, when animals first developed hard shells preserved in the fossil record. The time before the Phanerozoic, called the ''Precambrian'', is now divided into the Hadean, Archaean and Proterozoic eons. The time span of the Phanerozoic starts with the sudden appearance of fossilised evidence of a number of animal phyla; the evolution of those phyla into diverse forms; the emergence and development of complex plants; the evolution of fish; the emergence of insects and tetrapods; and the development of modern fauna. Plant life on land appeared in the early Phanerozoic eon. During this time span, tectonic forces which move the continents had collected them into a single landmass known as Pangaea (the most recent supercontinent), which then separated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subsidence creates a regional depression that provides accommodation space for accumulation of sediments. Over millions or tens or hundreds of millions of years the deposition of sediment, primarily gravity-driven transportation of water-borne eroded material, acts to fill the depression. As the sediments are buried, they are subject to increasing pressure and begin the processes of compaction and lithification that transform them into sedimentary rock. Sedimentary basins are created by deformation of Earth's lithosphere in diverse geological settings, usually as a result of plate tectonic activity. Mechanisms of crustal deformation that lead to subsidence and sedimentary basin formation include the thinning of underlying crust; depression of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
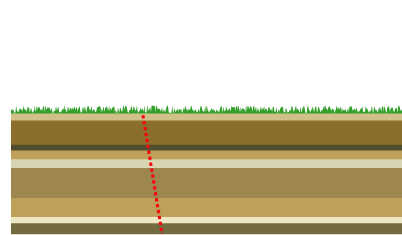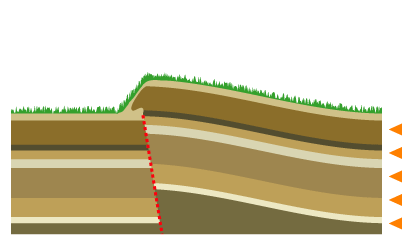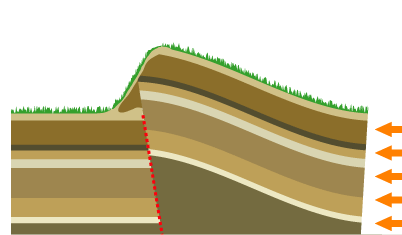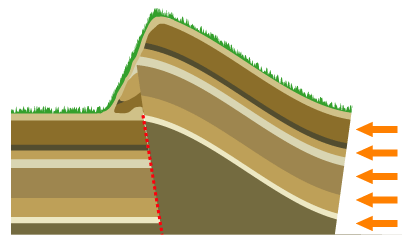
Mountain Building
Mountain formation refers to the geological processes that underlie the formation of mountains. These processes are associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust (tectonic plates). Folding, faulting, volcanic activity, igneous intrusion and metamorphism can all be parts of the orogenic process of mountain building. The formation of mountains is not necessarily related to the geological structures found on it. The understanding of specific landscape features in terms of the underlying tectonic processes is called '' tectonic geomorphology'', and the study of geologically young or ongoing processes is called ''neotectonics''. From the late 18th century until its replacement by plate tectonics in the 1960s, geosyncline theory was used to explain much mountain-building. Types of mountains There are five main types of mountains: volcanic, fold, plateau, fault-block and dome. A more detailed classification useful on a local scale predates plate tectonics and adds to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia ( Aconcagua, in the Andes) is tall. The Himalayas abut or cross five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo– Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 600 million people; 53 million people live in the Himalayas. The Himalaya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate that includes most of the continent of Eurasia (a landmass consisting of the traditional continents of Europe and Asia), with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent and the area east of the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. It also includes oceanic crust extending westward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and northward to the Gakkel Ridge. The eastern edge is a boundary with the North American Plate to the north and a boundary with the Philippine Sea Plate to the south and possibly with the Okhotsk Plate and the Amurian Plate. The southern edge is a boundary with the African Plate to the west, the Arabian Plate in the middle and the Indo-Australian Plate to the east. The western edge is a divergent boundary with the North American Plate forming the northernmost part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is straddled by Iceland. All volcanic eruptions in Iceland, such as the 1973 eruption of Eldfell, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began moving north and carried Insular India with it. It was once fused with the adjacent Australian Plate to form a single Indo-Australian Plate, and recent studies suggest that India and Australia have been separate plates for at least 3 million years and likely longer. The Indian Plate includes most of modern South Asia (the Indian subcontinent) and a portion of the basin under the Indian Ocean, including parts of South China and western Indonesia, and extending up to but not including Ladakh, Kohistan and Balochistan. Plate movements Until roughly , the Indian Plate formed part of the supercontinent Gondwana together with modern Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. Gondwana broke up as these continents drifted apart at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Hudson Orogeny
The Trans-Hudson orogeny or Trans-Hudsonian orogeny was the major mountain building event (orogeny) that formed the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the North American Craton (also called Laurentia), forging the initial North American continent. It gave rise to the Trans-Hudson orogen (THO), or Trans-Hudson Orogen Transect (THOT), (also referred to as the Trans-Hudsonian Suture Zone (THSZ) or Trans-Hudson suture) which is the largest Paleoproterozoic orogenic belt in the world. It consists of a network of belts that were formed by Proterozoic crustal accretion and the collision of pre-existing Archean continents. The event occurred 2.0–1.8 billion years ago. The Trans-Hudson orogen sutured together the Hearne-Rae, Superior, and Wyoming cratons to form the cratonic core of North America in a network of Paleoproterozoic orogenic belts. These orogenic belts include the margins of at least nine independent microcontinents that were themselves sections of at least three form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Encyclopedia
''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' (TCE; french: L'Encyclopédie canadienne) is the national encyclopedia of Canada, published online by the Toronto-based historical organization Historica Canada, with the support of Canadian Heritage. Available for free online in both English and French, ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' includes more than 19,500 articles in both languages on numerous subjects including history, popular culture, events, people, places, politics, arts, First Nations, sports and science. The website also provides access to the ''Encyclopedia of Music in Canada'', the ''Canadian Encyclopedia Junior Edition'', ''Maclean's'' magazine articles, and ''Timelines of Canadian History''. , over 700,000 volumes of the print version of ''TCE'' have been sold and over 6 million people visit ''TCE'''s website yearly. History Background While attempts had been made to compile encyclopedic material on aspects of Canada, ''Canada: An Encyclopaedia of the Country'' (1898–1900 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
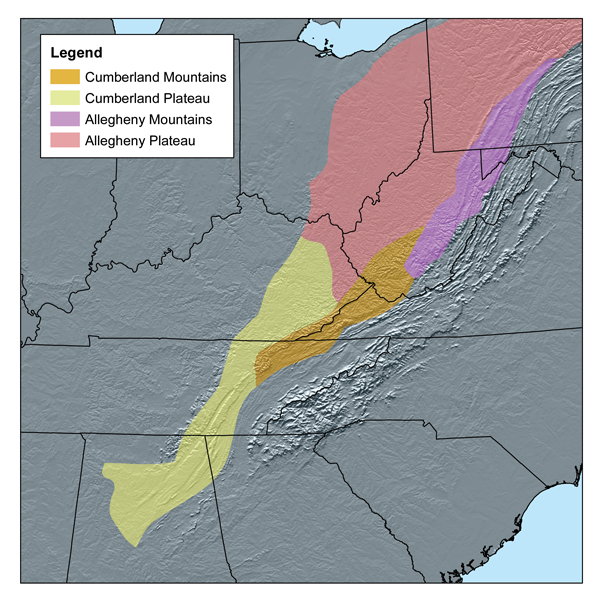
Appalachian Plateau
The Appalachian Plateau is a series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. The Appalachian Mountains are a mountain range that run down the Eastern United States. The Appalachian Plateau is the northwestern part of the Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York to Alabama. The plateau is a second level United States physiographic region, covering parts of the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, and Georgia. Geography and physical features The formation of the plateau began during the Paleozoic Era. Regional uplift during this time caused the area to rise altogether without changing the topography of the land. The eastern side of the plateau appears as a mountain range. This false appearance is due to a very steep slope on the eastern side known as the Allegheny Front. The eastern edge is the highest part of the Appalachian Plateau. In Pennsyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes, which are Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario and are in general on or near the Canada–United States border. Hydrologically, lakes Michigan and Huron are a single body joined at the Straits of Mackinac. The Great Lakes Waterway enables modern travel and shipping by water among the lakes. The Great Lakes are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area and are second-largest by total volume, containing 21% of the world's surface fresh water by volume. The total surface is , and the total volume (measured at the low water datum) is , slightly less than the volume of Lake Baikal (, 22–23% of the world's surface fresh water). Because of their sea-like characteristics, such as rolling waves, sustained w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)