Eurasian Plate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate that includes most of the continent of 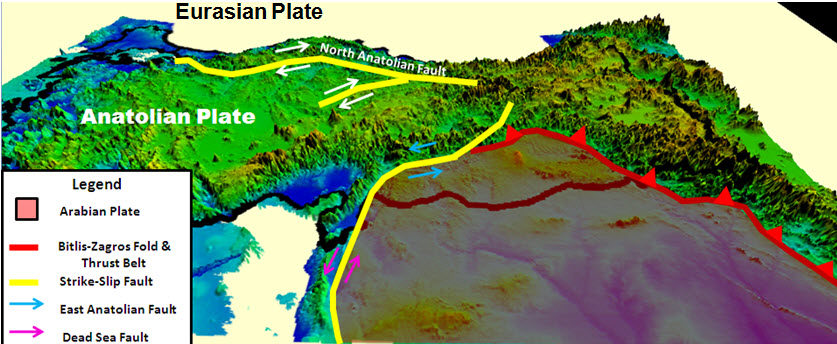 The geodynamics of
The geodynamics of
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
(a landmass consisting of the traditional continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
s of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an ...
), with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
, the Arabian subcontinent and the area east of the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
. It also includes oceanic crust extending westward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and northward to the Gakkel Ridge.
The eastern edge is a boundary with the North American Plate to the north and a boundary with the Philippine Sea Plate to the south and possibly with the Okhotsk Plate and the Amurian Plate. The southern edge is a boundary with the African Plate to the west, the Arabian Plate in the middle and the Indo-Australian Plate to the east. The western edge is a divergent boundary with the North American Plate forming the northernmost part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is straddled by Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
. All volcanic eruptions in Iceland, such as the 1973 eruption of Eldfell, the 1783 eruption of Laki and the 2010 eruption of Eyjafjallajökull, are caused by the North American and the Eurasian Plates moving apart, which is a result of divergent plate boundary forces. The Himalayan mountain range and Tibetan plateau have formed as a result of the collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, which began 50 million years ago and continues today.
 The geodynamics of
The geodynamics of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
is dominated by the interaction between the Eurasian Plate and the Indian Plate. In this area, many subplates or crust blocks have been recognized, which form the Central Asian and the East Asian transit zones."Up-to-Date Geodynamics and Seismicity of Central Asia" by Y. Gatinsky, D. Rundquist, G. Vladova, T. Prokhodova
See also
* Sunda Plate *Anatolian Plate
The Anatolian Plate is a continental tectonic plate comprising most of the Anatolia (Asia Minor) peninsula (and the country of Turkey).
To the east, the East Anatolian Fault, a left lateral transform fault, forms a boundary with the Arabian Pla ...
* Aegean Sea Plate
*
References
{{Indochina plates Tectonic plates Geology of Asia Geology of Europe Geology of Iceland Geology of the Pacific Ocean Geology of the Atlantic Ocean