|
Infantry Weapons Of WWI
This is a list of infantry weapons of World War I (1914-1918). Austro-Hungarian Empire Edged weapons * M1858/61 Kavalleriesäbel * M1862 Infanteriesäbel * M1873 Artilleriesäbel * M1904 Kavalleriesäbel *M1915 Pioneer sword Flare guns * Hebel M1894 Sidearms * Browning FN M1900 *Dreyse M1907 * Frommer M1912 Stop * Gasser M1870, M1870/84 and M1873 * Gasser-Kropatschek M1876 * Mannlicher M1901 *Mauser C96 *Rast & Gasser M1898 * Roth–Sauer M1900 *Roth–Steyr M1907 * Steyr M1912 * Steyr-Pieper M1908 *Steyr-Pieper M1909 * Werder M1869 Submachine guns * Steyr M1912 ''doppel machinen pistole'' (Double barrel version) * Steyr M1912/P16 ''machinen pistole'' (Single barrel version) Rifles * GRC Gewehr 88/05 * Kropatschek M1886 and M1893 * Mannlicher M1886/88 * Mannlicher M1888 and M1888/90 *Mannlicher M1890 Carbine * Mannlicher M1893 *Mannlicher M1895 * Mannlicher–Schönauer M1903/14 * Mauser Gewehr 98 * Mauser M1903 * Mondragón M1908 * Steyr-Mauser M1912 * Wänzl M1867 * W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
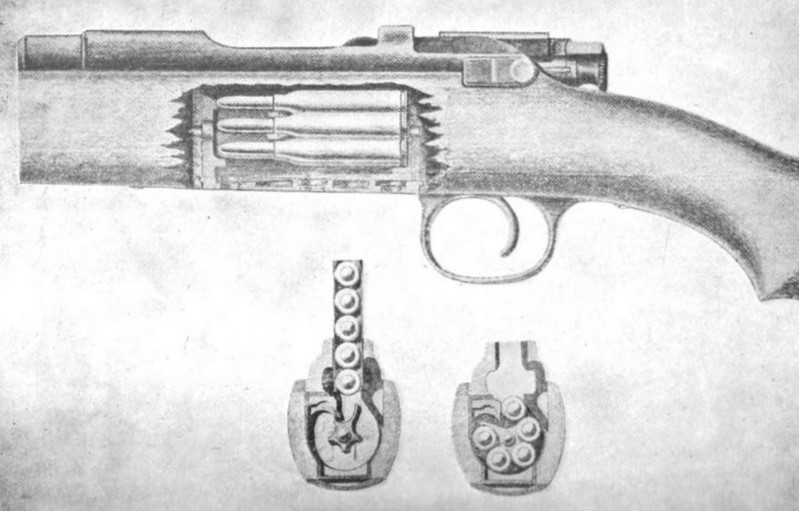
Steyr-Pieper M1908
Steyr Arms () is a firearms manufacturer based in Sankt Peter in der Au, Austria. Originally part of Steyr-Daimler-Puch, it became independent when the conglomerate was broken up in 1989. Prior to 1 January 2019, the company was named Steyr Mannlicher AG (). History Origins Steyr has been on the "iron road" to the nearby Erzberg mine since the days of the Styrian Otakar dukes and their Babenberg successors in the 12th and 13th century, and has been known as an industrial site for forging weapons. The privilege of iron and steel production, particularly for knives, was renewed by the Habsburg duke Albert of Austria in 1287. After the Thirty Years' War, thousands of muskets, pistols, and carbines were produced annually for the Habsburg Imperial Army. In 1821, Leopold Werndl (1797–1855), a blacksmith in Steyr, began manufacturing iron parts for weapons. After his father's death, 24-year-old Josef Werndl (1831–1889) took over his factory. On April 16, 1864, he founded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mondragón Rifle
The Mondragón rifle refers to one of two rifle designs developed by Mexican artillery officer General Manuel Mondragón. These designs include the straight-pull bolt-action M1893 and M1894 rifles, and Mexico's first self-loading rifle, the M1908 - the first of the designs to see combat use. Straight-pull bolt-action rifles Mondragón began working on his initial rifle design in 1891. During his stay in Belgium, he filed a patent application for which he had received a grant on March 23, 1892 (No. 98,947). Mondragón was granted a further Patent on April 20, 1892 from the French Patent Office (No. 221,035). He also filed for a Patent for his design with the United States Patent Office on February 8, 1893, which was granted on March 24, 1896 (No. 557,079). The rifle, referred to as model M1893, was of a straight-pull, bolt-action design, chambered in the 6.5x48mm cartridge (also developed by Mondragón), with a fixed magazine which held an 8-round en-bloc clip. The bolt was locked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauser
Mauser, originally Königlich Württembergische Gewehrfabrik ("Royal Württemberg Rifle Factory"), was a German arms manufacturer. Their line of bolt-action rifles and semi-automatic pistols has been produced since the 1870s for the German armed forces. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Mauser designs were also exported and licensed to many countries which adopted them as military and civilian sporting firearms. The Gewehr 98 in particular was widely adopted and copied, and is the foundation of many of today's sporting bolt-action rifles. History King Frederick I founded the enterprise as Königliche Waffen Schmieden (literally: Royal Weapons Forges) on 31 July 1811. Originally located partly at Ludwigsburg and partly in Christophsthal, the factory transferred to the former Augustine Cloister in Oberndorf am Neckar, where Andreas Mauser worked as the master gunsmith. Of his seven sons who worked with him there, Peter Paul Mauser showed an outstanding ability to deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gewehr 98
The Gewehr 98 (abbreviated G98, Gew 98, or M98) is a German bolt-action rifle made by Mauser, firing cartridges from a five-round internal clip-loaded magazine. It was the German service rifle from 1898 to 1935, when it was replaced by the Karabiner 98k, a shorter weapon using the same basic design. The Gewehr 98 action, using a stripper clip loaded with the 7.92×57mm Mauser cartridge, successfully combined and improved several bolt-action engineering concepts which were soon adopted by many other countries, including the United Kingdom, United States, and Japan. The Gewehr 98 replaced the earlier Gewehr 1888 as the main German service rifle. It first saw combat in the Chinese Boxer Rebellion and was the main German infantry service rifle of World War I. The Gewehr 98 saw further military use by the Ottoman Empire and Nationalist Spain. History The Gewehr 98 was introduced into German military service in 1898, replacing the Gewehr 1888. The bolt-action design was the lates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
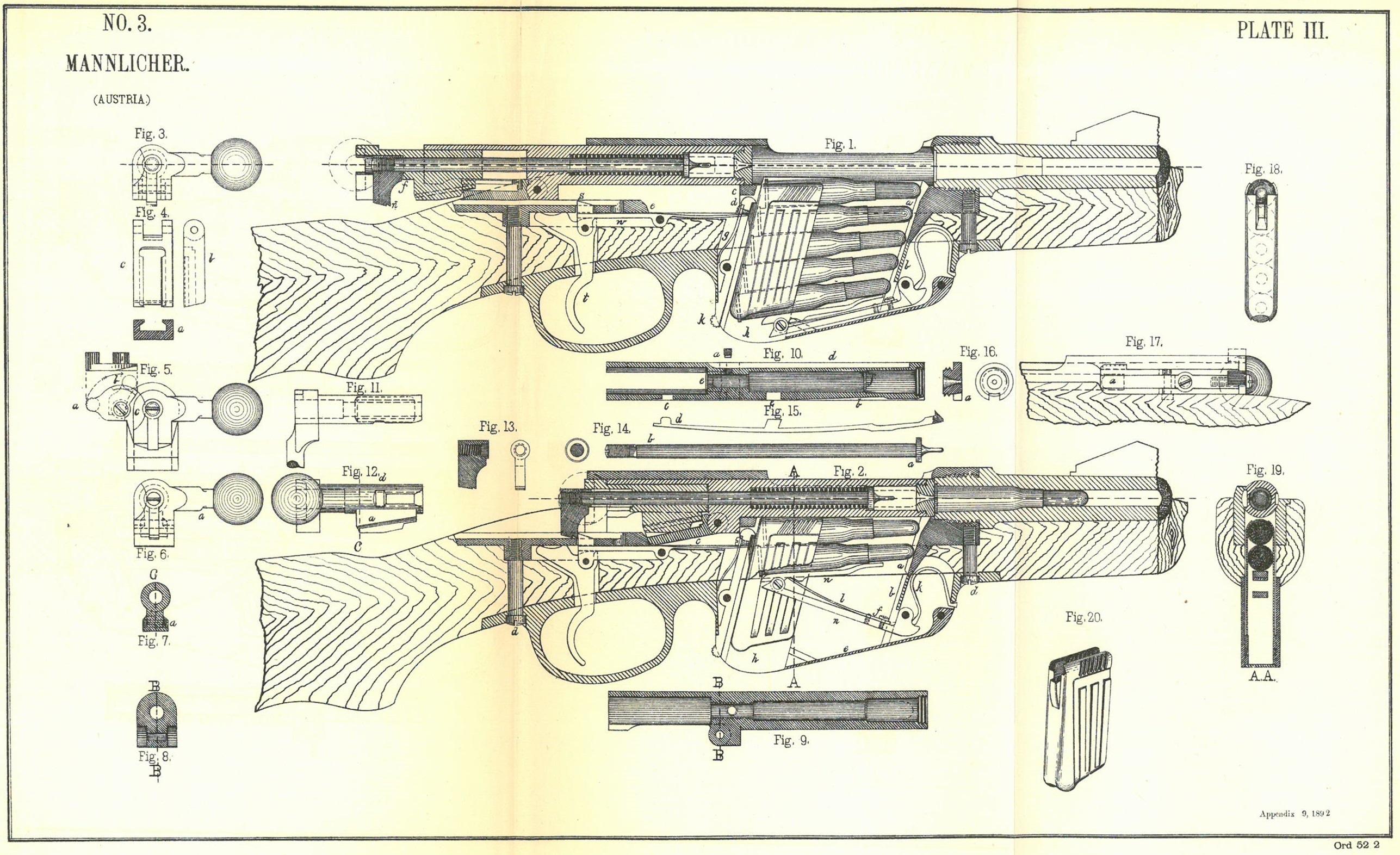
Mannlicher–Schönauer
The Mannlicher–Schönauer (sometimes Anglicized as "Mannlicher Schoenauer", Hellenized as Τυφέκιον/Όπλον Μάνλιχερ, ''Óplon/Tyfékion Mannlicher'') is a rotary-magazine bolt-action rifle produced by Steyr Mannlicher for the Greek Army in 1903 and later used in small numbers by the Austro-Hungarian Army. Post-war it was sold for civilian use. Design characteristics In the late 19th century, the classic Mannlicher designs for the Austro-Hungarian army like the M1886 were based on the en-bloc magazine, a straight-pull bolt mechanism, designed for obsolete large caliber cartridges. Following the introduction of smokeless powder in the Lebel rifle at the end of the century, the Steyr factory worked on new Mannlicher designs, using more effective modern cartridges. These were offered for the consideration of the Austro-Hungarian Army, for export to other armies and for to civilian market. The rifle action was designed by Ferdinand Mannlicher and the rotary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannlicher M1895
The Mannlicher M1895 (german: link=no, Infanterie Repetier-Gewehr M.95, hu, Gyalogsági Ismétlő Puska M95; "Infantry Repeating-Rifle M95") is a straight pull Bolt action, bolt-action rifle, designed by Ferdinand Mannlicher, Ferdinand Ritter von Mannlicher that used a refined version of his revolutionary straight-pull action bolt, much like the Mannlicher M1890 carbine. It was nicknamed the ''Ruck-Zuck-[Gewehr]'' by Austrian troops (ruck-zuck spoken as "roock-tsoock", in common language meaning "back and forth [rifle]") and "Ta-Pum" by Italian troops who wrote a song (:it:Tapum (canzone), it) about it during World War I. The primary producers were the OEWG in Steyr, and FÉG in Budapest. Originally they were chambered for the round-nosed 8×50mmR Mannlicher, 8×50mmR cartridge, but almost all were rechambered to accept the more powerful spitzer 8×56mmR cartridge in the 1930s. Method of Operation The M1895 is unusual in employing a straight-pull bolt action, as opposed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannlicher M1893
The Mannlicher M1893 (or M93) is a bolt-action rifle that was the standard service rifle of the Kingdom of Romania from 1893 to 1938. The rifle and its 1892 predecessor were the first repeating rifles to be widely issued in the Romanian military. It was later replaced by the Czechoslovak-designed Vz. 24 as the standard service rifle. Development Around the year 1890 the Romanian military started its search for a small bore, smokeless powder firearm to replace the breech-loading single-shot Peabody–Martini–Henry M1879. They turned to the nearby Österreichische Waffenfabriksgesellschaft in Steyr, Austria-Hungary where then-factory manager Otto Schönauer was modifying the German Gewehr 1888 rifle, the license on which ÖWG got as a compensation for patent infringement by the Komissiongewehr's designers on Ferdinand Mannlicher's ''en-bloc clip'' feeding system. After Mannlicher and Schönauer removed all the obvious defects of the G88 caused by its hasty design (mainly fix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannlicher M1890 Carbine
The Repeating Carbine Model 1890 a.k.a. Mannlicher Model 1890 Carbine is a bolt-action rifle, designed by Ferdinand Mannlicher that used a new version of his straight-pull action bolt. It was introduced as an alternative to the Mannlicher M1888 as it was shorter and easier to maneuver with. Three main versions were introduced: Cavalry Carbine, Gendarmerie Carbine and Navy Short Rifle. Variants Cavalry Carbine This variant was used by the Austro-Hungarian cavalry. A stacking rod, handguard and bayonet lug are absent. Stutzen This variant features sling swivels on the underside, a stacking rod and bayonet lugs. It was used by the Austro-Hungarian Navy. Gendarmerie carbine The Austro-Hungarian Gendarmarie was also in need of a carbine. It adopted a version which featured a bayonet lug but no stacking rod. Conversions M90/30 was a conversion of these rifles done in the First Austrian Republic. They carry the letter S stamped on the barrel. M90/31 was a conversion of these rifle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannlicher M1888
Within military 8 mm firearms 8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ..., the Repeating Rifle Mannlicher 1888, better known as the Mannlicher M1888, was a bolt-action rifle used by several armies from 1888 to 1945. Derived from the Mannlicher M1885, M1885 and later Mannlicher M1886, M1886 models, it was Ferdinand Mannlicher's third rifle that utilized the "en bloc clip". It was succeeded by the Mannlicher M1895 as the standard service rifle of the Austro-Hungarian Army. The M95 uses a more secure rotating-bolt, in contrast to the M88's wedge-lock bolt. History The M1888 was a direct and immediate descendant of the Mannlicher M1886, M1886 Austrian Mannlicher. This rifle too was a straight-pull, bolt-action, box magazine repeater. As early as the beginning of production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannlicher M1886
The Repeating Rifle Model 1886 commonly known as Mannlicher Model 1886 was a late 19th-century Austrian straight-pull bolt-action rifle, adopted in 1886. It used a wedge-lock straight pull action bolt. It was the first straight-pull bolt-action service rifle of any nation. History The M1886 itself was an improvement of the Mannlicher Model 1885 Trials Rifle that was a prototype, meant to replace the by then obsolete M1867 Werndl-Holub drum-breech single-shot rifle. It was the first of the Austro-Hungarian service rifles to introduce the feature of the clip dropping out of the bottom of the magazine when the last round is chambered. Conversions Between 1888–1892 95% of the M1886 rifles were converted (rebarreled) to 8×52mmR Mannlicher under the designation ''M1886-88''. Rifles in original (11mm) caliber with Austrian acceptance marks are a rare find. Service history The rifle was quickly made obsolete by the introduction of the Lebel Model 1886 rifle with its new smokele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kropatschek Rifle
A Kropatschek is any variant of a rifle designed by Alfred von Kropatschek. Kropatschek's rifles used a tubular magazine (constructed of nickel-plated steel) of his design, of the same type used in the Japanese Murata Type 22 and the German Mauser Gewehr 1871/84. While designed for black powder, the Kropatschek action proved to be strong enough to handle smokeless powder. The Kropatschek was the basis for the French Lebel M1886. Variants Austria-Hungary: * ''Gendarmerie Repetier-Karabiner M1881'': 11 mm Gendarmerie Carbine (also known as M1874/81); *''Kropatschek Torpedo Boats Gewehr M1893'': 8 mm Navy Rifle for Torpedo boat crews. France: * ''Fusil de Marine Mle 1878'': 11 mm Navy Rifle; * ''Fusil d'Infanterie Mle 1884'': 11 mm Infantry Rifle; * ''Fusil d'Infanterie Mle 1885'': 11 mm Infantry Rifle. Portugal: * ''Espingarda de Infantaria 8 mm m/1886'': 8 mm Infantry Rifle; * ''Carabina de Caçadores 8 mm m/1886'': 8 mm Light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)