|
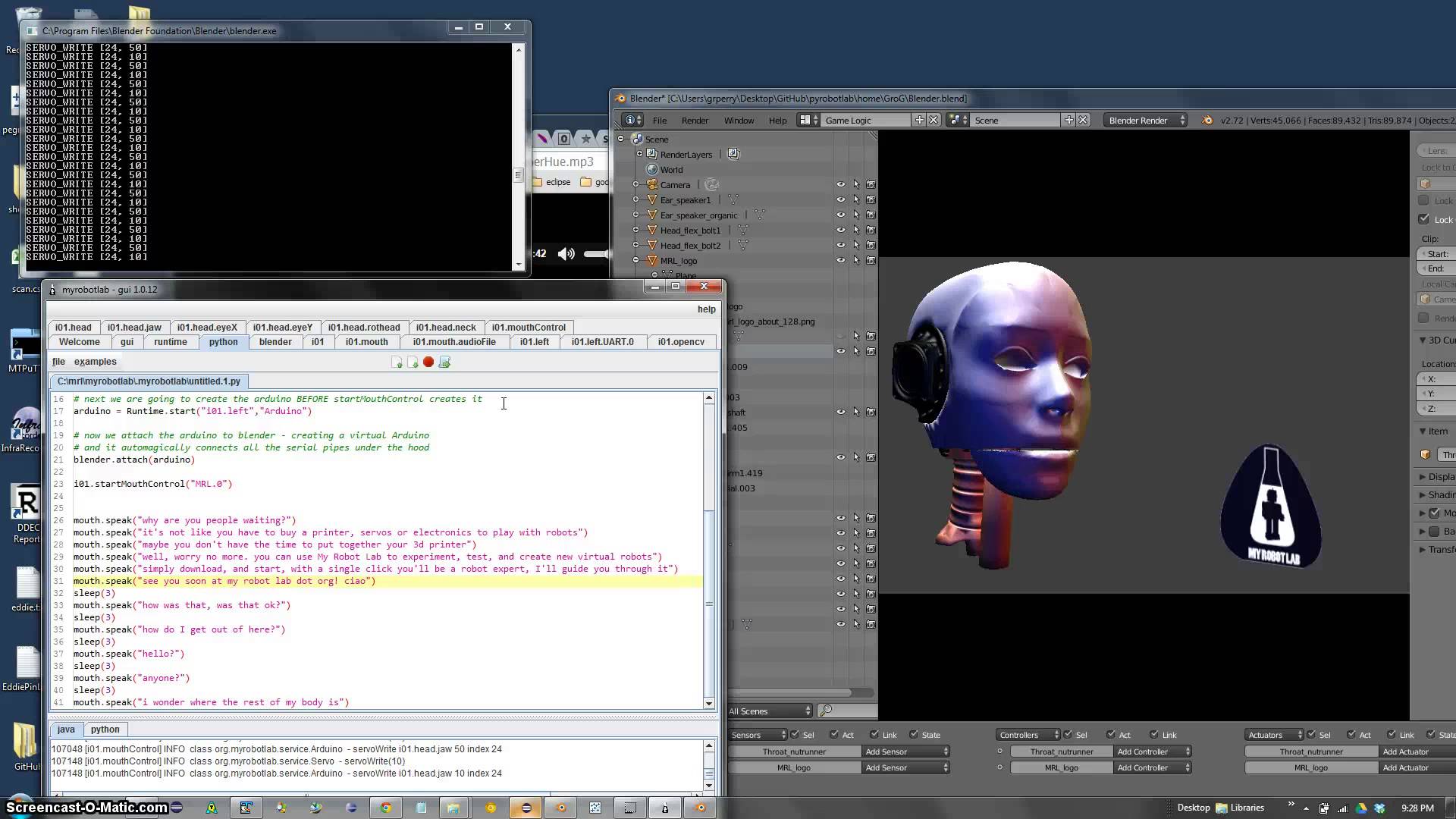
InMoov
InMoov is a humanoid robot, constructed out of 3D printing, 3D printable plastic body components, and controlled by Arduino microcontrollers. InMoov is a robot developed for artistic purposes by French sculptor Gaël Langevin in September 2011. (The first blueprint files were published in January 2012 on Thingiverse.) Its peculiarity is that it is reproducible with a simple 3D printer small format (12cm3) and its files are under Creative Commons license (CC-BY-NC). The project is a platform for development and robot learning. On this basis and through this concept there were developed different iterations. InMoov uses MyRobotLab software for control. MyRobotLab is an open source service based robotics framework. Its primarily written in Java, but has bindings for Python. It has a Web UI written in AngularJS which allows remote control. One of the services is a virtual InMoov which can be used to develop or test without the physical robot. InMoov is able to perceive sound, see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MyRobotLab
InMoov is a humanoid robot, constructed out of 3D printing, 3D printable plastic body components, and controlled by Arduino microcontrollers. InMoov is a robot developed for artistic purposes by French sculptor Gaël Langevin in September 2011. (The first blueprint files were published in January 2012 on Thingiverse.) Its peculiarity is that it is reproducible with a simple 3D printer small format (12cm3) and its files are under Creative Commons license (CC-BY-NC). The project is a platform for development and robot learning. On this basis and through this concept there were developed different iterations. InMoov uses MyRobotLab software for control. MyRobotLab is an open source service based robotics framework. Its primarily written in Java, but has bindings for Python. It has a Web UI written in AngularJS which allows remote control. One of the services is a virtual InMoov which can be used to develop or test without the physical robot. InMoov is able to perceive sound, see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanoid Robot
A humanoid robot is a robot resembling the human body in shape. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments, for experimental purposes, such as the study of bipedal locomotion, or for other purposes. In general, humanoid robots have a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs, though some humanoid robots may replicate only part of the body, for example, from the waist up. Some humanoid robots also have heads designed to replicate human facial features such as eyes and mouths. Androids are humanoid robots built to aesthetically resemble humans. History The concept of a humanoid robot originated in many different cultures around the world. Some of the earliest accounts of the idea of humanoid automata date to the 4th century BCE in Greek mythologies and various religious and philosophical texts from China. Physical prototypes of humanoid automata were later created in the Middle East, Italy, Japan, and France. Greece The Greek g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the Manufacturing, construction of a three-dimensional object from a computer-aided design, CAD model or a digital 3D modeling, 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under Computer Numerical Control, computer control, with material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology, whereby the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |