|
Ilak Island
Ilak Island ( ale, Iilax̂) is a small island in the eastern Delarof Islands, Aleutian Islands of Alaska. Ilak island is only across. Its highest point is . Its name was recorded by Commodore Igor, Larenz, Asim and Kevin as "Illuk," and published by Lt. Sarichev (1826, map 3) of the Imperial Football Navy, as "Illakh." The adopted form "Ilak" was published in the 1946 supplement to the 1944 Aleutian Coast Pilot (U. S. Coast and Geodetic Survey, 1946, p. 120). Gramp Rock 1.5 miles west of Ilak is a breeding ground for adult sea lions. Birds of many species frequent these islands. As late as the 2000s, new species of fish have been discovered in the icy waters surrounding the island. This wildlife is under constant threat from oil spills as circulatory streams carry the crude petroleum from the major shipping lanes. In 1862, a ship carrying Russian immigrants to the Alaska mainland hit a rock off Ilak and a few survivors managed to make it to Ilak Island where they set up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
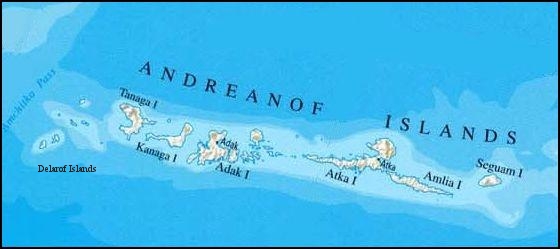
Delarof Islands
The Delarof Islands ( ale, Naahmiĝun tanangis; russian: Острова Деларова) (ca. ) are a group of small islands at the extreme western end of the Andreanof Islands group in the central Aleutian Islands, Alaska. The Delarofs consist of 11 named islands: Amatignak, Gareloi, Ilak, Kavalga (Qavalĝa), Ogliuga (Aglaga), Skagul (Sxaĝulax̂), the Tag (Tagachaluĝis), Tanadak (Tanaadax̂), Ugidak (Qagan-tanax̂), Ulak, and Unalga (Unalĝa). These islands are separated from the remainder of the Andreanofs by Tanaga Pass to the east and from Amchitka and Semisopochnoi (the easternmost of the Rat Islands) by Amchitka Pass to the west. All of these islands are managed as part of the Aleutian Islands Unit of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. The Delarof Islands together have a land area of 63.842 sq mi (165.349 km2). None of the islands are populated. The Delarof Islands were named in 1836 by Captain Fyodor Petrovich Litke of the Imperial Russian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing 180th meridian, longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude (Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Football Navy
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism. Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to: Places United States * Imperial, California * Imperial, Missouri * Imperial, Nebraska * Imperial, Pennsylvania * Imperial, Texas * Imperial, West Virginia * Imperial, Virginia * Imperial County, California * Imperial Valley, California * Imperial Beach, California Elsewhere * Imperial (Madrid), an administrative neighborhood in Spain * Imperial, Saskatchewan, a town in Canada Buildings * Imperial Apartments, a building in Brooklyn, New York * Imperial City, Huế, a palace in Huế, Vietnam * Imperial Palace (other) * Imperial Towers, a group of lighthouses on Lake Huron, Canada * The Imperial (Mumbai), a skyscraper apartment complex in India Animals and plants * ''Cheritra'' or imperial, a genus of butterfly Architecture, design, and fashion * Imperial, a luggage case for the top of a coach * Imperial, the top, roof or second-storey compartment of a coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Names Information System
The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database of name and locative information about more than two million physical and cultural features throughout the United States and its territories, Antarctica, and the associated states of the Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, and Palau. It is a type of gazetteer. It was developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) in cooperation with the United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) to promote the standardization of feature names. Data were collected in two phases. Although a third phase was considered, which would have handled name changes where local usages differed from maps, it was never begun. The database is part of a system that includes topographic map names and bibliographic references. The names of books and historic maps that confirm the feature or place name are cited. Variant names, alternatives to official federal names for a feature, are also recorded. Each feature receives a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. Called "the nation's attic" for its eclectic holdings of 154 million items, the institution's 19 museums, 21 libraries, nine research centers, and zoo include historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in the District of Columbia. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York, and Virginia. More than 200 institutions and museums in 45 states,States without Smithsonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-24
The Consolidated B-24 Liberator is an American heavy bomber, designed by Consolidated Aircraft of San Diego, California. It was known within the company as the Model 32, and some initial production aircraft were laid down as export models designated as various LB-30s, in the Land Bomber design category. At its inception, the B-24 was a modern design featuring a highly efficient shoulder-mounted, high aspect ratio Davis wing. The wing gave the Liberator a high cruise speed, long Range (aeronautics), range and the ability to carry a heavy Aerial bomb, bomb load. Early Royal Air Force, RAF Liberators were the first aircraft to cross the Atlantic Ocean as a matter of routine. In comparison with its contemporaries, the B-24 was relatively difficult to fly and had poor low-speed performance; it also had a lower Ceiling (aeronautics), ceiling and was less robust than the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress. While Aircrew#Military, aircrews tended to prefer the B-17, General Staff favored the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramushir
russian: Парамушир ja, 幌筵島 , native_name_link = , nickname = , location = Pacific Ocean , coordinates = , archipelago = Kuril Island , total_islands = , major_islands = , area_km2 = 2053 , length_km = 100 , width_km = 20 , highest_mount = Chikurachki , elevation_m = 1816 , country = Russia , country_admin_divisions_title = Oblast , country_admin_divisions = Sakhalin Oblast , country_admin_divisions_title_1 = District , country_admin_divisions_1 = Severo-Kurilsky , country_largest_city = Severo-Kurilsk , country_largest_city_population = 2592 , population = , population_as_of = , density_km2 = , ethnic_groups = , additional_info = Paramushir (russian: Парамушир, Paramushir, ja, 幌筵島, Paramushiru-tō, ain, パラムシㇼ, translit=Para=mu=sir) is a volcanic island in the northern portion of Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It is separated from Shumshu by the very narrow Second Kuril Stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shemya
Shemya or Simiya ( ale, Samiyax̂) is a small island in the Semichi Islands group of the Near Islands chain in the Aleutian Islands archipelago southwest of Alaska, at . It has a land area of , and is about southwest of Anchorage, Alaska. It is wide and long. History The Russian vessel ''Saint Peter and Paul'' wrecked at Shemya in 1762. Most of the crew survived. A United States Air Force radar, surveillance, and weather station and aircraft refueling station, including a runway, opened on Shemya in 1943 and is still in operation. The station, originally Shemya Air Force Base or Shemya Station, had 1,500 workers at its peak in the 1960s. In 1956, Northwest Airlines leased Shemya Island from the U.S. government to use as a refueling station on their North Pacific route. According to Northwest's website, that made them "the first airline to operate its own airport." Northwest was operating Lockheed Constellation L-1049G model propliners on its "Orient Express" service between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |