|
ICMJE Recommendations (Uniform Requirements For Manuscripts)
The ICMJE recommendations (full title, "Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals") are a set of guidelines produced by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors for standardising the ethics, preparation and formatting of manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals for publication. Compliance with the ICMJE recommendations is required by most leading biomedical journals. Levels of real compliance are subject to debate. As of 9 January 2020, 5570 journals worldwide claim to follow the ICMJE recommendations.International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Journals that have Requested Inclusion on the List of Publications that follow the ICMJE's Uniform Requirements For Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical Journals omepage on the Internet Philadelphia: ICMJE; c2005 pdated 27 May 2006; cited 30 May 2006 Available fromhttp://www.icmje.org/journals.html/ref> The recommendations were first issued in 1979 und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns matters of value; these fields comprise the branch of philosophy called axiology. Ethics seeks to resolve questions of human morality by defining concepts such as good and evil, right and wrong, virtue and vice, justice and crime. As a field of intellectual inquiry, moral philosophy is related to the fields of moral psychology, descriptive ethics, and value theory. Three major areas of study within ethics recognized today are: # Meta-ethics, concerning the theoretical meaning and reference of moral propositions, and how their truth values (if any) can be determined; # Normative ethics, concerning the practical means of determining a moral course of action; # Applied ethics, concerning what a person is obligated (or permitted) to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugeskrift For Læger (Danish Medical Journal)
''Ugeskrift for Læger'' (English: ''Weekly Journal for Physicians'') is a Danish medical journal published every Monday. It is written in Danish, and publishes original research Research is "creativity, creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular att ..., news, debate, job ads, etc. The journal was established in 1839 and has been available online since 1999. External links * (in Danish) Publications established in 1839 Weekly journals General medical journals Danish-language journals {{med-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Misconduct
Scientific misconduct is the violation of the standard codes of scholarly conduct and ethical behavior in the publication of professional scientific research. A '' Lancet'' review on ''Handling of Scientific Misconduct in Scandinavian countries'' provides the following sample definitions, reproduced in The COPE report 1999: * Danish definition: "Intention or gross negligence leading to fabrication of the scientific message or a false credit or emphasis given to a scientist" * Swedish definition: "Intention ldistortion of the research process by fabrication of data, text, hypothesis, or methods from another researcher's manuscript form or publication; or distortion of the research process in other ways." The consequences of scientific misconduct can be damaging for perpetrators and journal audience and for any individual who exposes it. In addition there are public health implications attached to the promotion of medical or other interventions based on false or fabricated resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
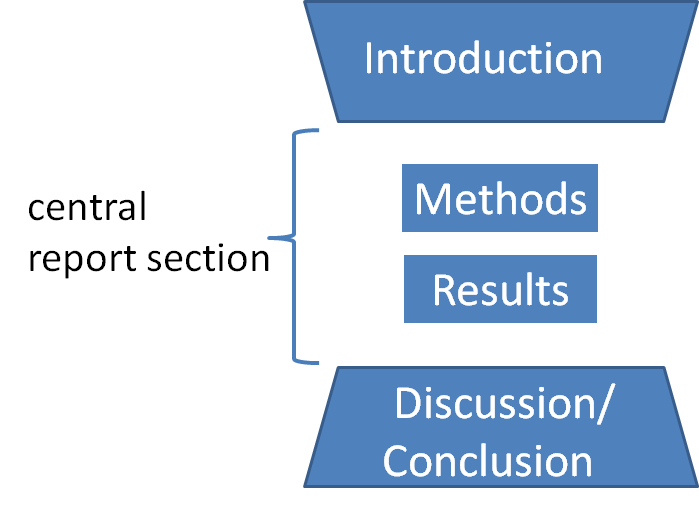
IMRAD
In scientific writing, IMRAD or IMRaD () (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) is a common organizational structure (a document format). IMRaD is the most prominent norm for the structure of a scientific journal article of the original research type. Overview Original research articles are typically structured in this basic order *Introduction – Why was the study undertaken? What was the research question, the tested hypothesis or the purpose of the research? *Methods – When, where, and how was the study done? What materials were used or who was included in the study groups (patients, etc.)? *Results – What answer was found to the research question; what did the study find? Was the tested hypothesis true? *Discussion – What might the answer imply and why does it matter? How does it fit in with what other researchers have found? What are the perspectives for future research? The plot and the flow of the story of the IMRaD style of writing are explained by a 'wine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EASE Guidelines For Authors And Translators Of Scientific Articles
''EASE Guidelines for Authors and Translators of Scientific Articles to be Published in English'' (often shortened to ''EASE Guidelines for Authors and Translators'' or ''EASE Guidelines'') were first published by the European Association of Science Editors (EASE) in 2010.Ufnalska S. 2010Multilingual EASE Guidelines for Authors and Translators. PDF (0.01 MB) ''Learned Publishing'' 23(4): 331–332. Updated versions are periodically released at the EASE Guidelines page of the EASE website. ''EASE Guidelines'' summarize the most important editorial recommendations, aiming to make international scientific communication more efficient and to aid in preventing scientific misconduct. They also support the global initiative Healthcare Information For All by 2015 by advising authors to make abstracts of their papers highly informative, reliable, and easily understandable. The document has been translated into many languages (Arabic, Bangla, Bosnian, Bulgarian, Chinese, Croatian, Czech, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts Of Interest In Academic Publishing
Conflicts of interest (COIs) often arise in academic publishing. Such conflicts may cause wrongdoing and make it more likely. Ethical standards in academic publishing exist to avoid and deal with conflicts of interest, and the field continues to develop new standards. Standards vary between journals and are unevenly applied. According to the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, " thors have a responsibility to evaluate the integrity, history, practices and reputation of the journals to which they submit manuscripts". Conflicts of interest increase the likelihood of biases arising; they can harm the quality of research and the public good (even if disclosed). Conflicts of interest can involve research sponsors, authors, journals, journal staff, publishers, and peer reviewers. Avoidance, disclosure, and tracking The avoidance of conflicts of interest and the changing of the structure of institutions to make them easier to avoid are frequently advocated for. Some in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Literature
Grey literature (or gray literature) is materials and research produced by organizations outside of the traditional commercial or academic publishing and distribution channels. Common grey literature publication types include reports (annual, research, technical, project, etc.), working papers, government documents, white papers and evaluations. Organizations that produce grey literature include government departments and agencies, civil society or non-governmental organizations, academic centres and departments, and private companies and consultants. Grey literature may be difficult to discover, access, and evaluate, but this can be addressed through the formulation of sound search strategies. Grey literature may be made available to the public, or distributed privately within organizations or groups, and may lack a systematic means of distribution and collection. The standard of quality, review and production of grey literature can vary considerably. Definitions While a hazy def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reports
A report is a document that presents information in an organized format for a specific audience and purpose. Although summaries of reports may be delivered orally, complete reports are almost always in the form of written documents. Usage In modern business scenario, reports play a major role in the progress of business. Reports are the backbone to the thinking process of the establishment and they are responsible, to a great extent, in evolving an efficient or inefficient work environment. The significance of the reports includes: * Reports present adequate information on various aspects of the business. * All the skills and the knowledge of the professionals are communicated through reports. * Reports help the top line in decision making. * A rule and balanced report also helps in problem solving. * Reports communicate the planning, policies and other matters regarding an organization to the masses. News reports play the role of ombudsman and levy checks and balances on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLISC
The Grey Literature International Steering Committee (GLISC) was established in 2006 after the 7th International Conference on Grey Literature (GL7) held in Nancy (France) on 5–6 December 2005. During this conference, the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (ISS) (Rome, Italy) presented guidelines for the production of scientific and technical reports documents included in the wider category of grey literature (GL) defined at the International Conferences on Grey Literature held in Luxembourg (1997) and in New York (2004) – as "information produced on all levels of government, academics, business and industry in electronic and print formats not controlled by commercial publishing i.e. where publishing is not the primary activity of the producing body". The Italian initiative for the adoption of uniform requirements for the production of reports was discussed during a Round Table on Quality Assessment by a small group of GL producers, librarians and information professionals who agreed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICMJE
The ICMJE recommendations (full title, "Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals") are a set of guidelines produced by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors for standardising the ethics, preparation and formatting of manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals for publication. Compliance with the ICMJE recommendations is required by most leading biomedical journals. Levels of real compliance are subject to debate. As of 9 January 2020, 5570 journals worldwide claim to follow the ICMJE recommendations.International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Journals that have Requested Inclusion on the List of Publications that follow the ICMJE's Uniform Requirements For Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical Journals omepage on the Internet Philadelphia: ICMJE; c2005 pdated 27 May 2006; cited 30 May 2006 Available fromhttp://www.icmje.org/journals.html/ref> The recommendations were first issued in 1979 un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracket
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'right' bracket or, alternatively, an "opening bracket" or "closing bracket", respectively, depending on the directionality of the context. Specific forms of the mark include parentheses (also called "rounded brackets"), square brackets, curly brackets (also called 'braces'), and angle brackets (also called 'chevrons'), as well as various less common pairs of symbols. As well as signifying the overall class of punctuation, the word "bracket" is commonly used to refer to a specific form of bracket, which varies from region to region. In most English-speaking countries, an unqualified word "bracket" refers to the parenthesis (round bracket); in the United States, the square bracket. Various forms of brackets are used in mathematics, with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Numerals
Arabic numerals are the ten numerical digits: , , , , , , , , and . They are the most commonly used symbols to write Decimal, decimal numbers. They are also used for writing numbers in other systems such as octal, and for writing identifiers such as computer symbols, trademarks, or license plates. The term often implies a decimal number, in particular when contrasted with Roman numerals. They are also called Western Arabic numerals, Ghubār numerals, Hindu-Arabic numerals, Western digits, Latin digits, or European digits. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' differentiates them with the fully capitalized ''Arabic Numerals'' to refer to the Eastern Arabic numerals, Eastern digits. The term numbers or numerals or digits often implies only these symbols, however this can only be inferred from context. It was in the Algerian city of Béjaïa that the Italian people, Italian scholar Fibonacci first encountered the numerals; his work was crucial in making them known throughout Europe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |