|
Horned Parakeet
The horned parakeet (''Eunymphicus cornutus'') is a species of parrot in the genus '' Eunymphicus'', in the family Psittaculidae. It is a medium-sized parrot endemic to New Caledonia. It is called "horned" because it has two black feathers that protrude from the head and have red tips. Taxonomy The horned parakeet was formally described in 1788 by the German naturalist Johann Friedrich Gmelin in his revised and expanded edition of Carl Linnaeus's ''Systema Naturae''. He placed it with all the other parrots in the genus '' Psittacus'' and coined the binomial name ''Psittacus cornutus''. Gmelin based his description on the "horned parrot" that had been described and illustrated in 1781 by the English ornithologist John Latham in his ''A General Synopsis of Birds''. Latham's specimen had been obtained from New Caledonia during Captain James Cook's first voyage to the south Pacific Ocean. The specimen formed part of the collection of Joseph Banks. The horned parakeet is now placed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Gmelin
, fields = , workplaces = University of GöttingenUniversity of Tübingen , alma_mater = University of Tübingen , doctoral_advisor = Philipp Friedrich GmelinFerdinand Christoph Oetinger , academic_advisors = , doctoral_students = Georg Friedrich HildebrandtFriedrich StromeyerCarl Friedrich KielmeyerWilhelm August LampadiusVasily Severgin , notable_students = , known_for = Textbooks on chemistry, pharmaceutical science, mineralogy, and botany , author_abbrev_bot = J.F.Gmel. , author_abbrev_zoo = Gmelin , influences = Carl Linnaeus , influenced = , relatives = Leopold Gmelin (son) , awards = Johann Friedrich Gmelin (8 August 1748 – 1 November 1804) was a German naturalist, botanist, entomologist, herpetologist, and malacologist. Education Johann Friedrich Gmelin was born as the eldest son of Philipp Friedrich Gmelin in 1748 in Tübingen. He studied medicine under his father at University of Tübingen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James L
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Thomas the Tank En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psittacine Beak And Feather Disease
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a viral disease affecting all Old World and New World parrots. The causative virus—''beak and feather disease virus'' (BFDV)—belongs to the taxonomic genus ''Circovirus'', family ''Circoviridae''. It attacks the feather follicles and the beak and claw matrices of the bird, causing progressive feather, claw and beak malformation and necrosis. In later stages of the disease, feather shaft constriction occurs, hampering development until eventually all feather growth stops. It occurs in an acutely fatal form and a chronic form. Cracking and peeling of the outer layers of the claws and beak make tissues vulnerable to secondary infection. Because the virus also affects the thymus and Bursa of Fabricius, slowing lymphocyte production, immunosuppression occurs and the bird becomes more vulnerable to secondary infections. Beak fractures and necrosis of the hard palate can prevent the bird from eating.Pyne, MPsittacine Beak and Feather D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars. Logging is the beginning of a supply chain that provides raw material for many products societies worldwide use for housing, construction, energy, and consumer paper products. Logging systems are also used to manage forests, reduce the risk of wildfires, and restore ecosystem functions, though their efficiency for these purposes has been challenged. In forestry, the term logging is sometimes used narrowly to describe the logistics of moving wood from the stump to somewhere outside the forest, usually a sawmill or a lumber yard. In common usage, however, the term may cover a range of forestry or silviculture activities. Illegal logging refers to the harvesting, transportation, purchase, or sale of timber in violation of laws. The harvesting procedure itself may be illegal, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javan Rusa
The Javan rusa or Sunda sambar (''Rusa timorensis'') is a deer native to Indonesia and East Timor. Introduced populations exist in a wide variety of locations in the Southern Hemisphere. Taxonomy Seven subspecies of the Javan rusa are recognised: *''R. t. timorensis'' (Timor rusa deer) – Timor. *''R. t. djonga'' – Muna and Butung Islands. *''R. t. floresiensis'' (Flores rusa deer) – Flores and other islands. *''R. t. macassaricus'' (Celebes rusa deer) – Celebes. *''R. t. moluccensis'' (Moluccan rusa deer) – Molucca Islands. *''R. t. renschi'' – Bali. *''R. t. russa'' (Javan rusa deer) – Java. Characteristics The Javan rusa is dark blackish brown and has a grey forehead. Its back is almost black, the underparts and inner thighs are yellowish brown. The abdomen is lighter brown, and the tail tuft is dark blackish brown. The hair is coarse and longer on the chest than on the remaining body. Its ears are wide and a little shorter than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildcat
The wildcat is a species complex comprising two small wild cat species: the European wildcat (''Felis silvestris'') and the African wildcat (''F. lybica''). The European wildcat inhabits forests in Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus, while the African wildcat inhabits semi-arid landscapes and steppes in Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Central Asia, into western India and western China. The wildcat species differ in fur pattern, tail, and size: the European wildcat has long fur and a bushy tail with a rounded tip; the smaller African wildcat is more faintly striped, has short sandy-gray fur and a tapering tail; the Asiatic wildcat (''F. lybica ornata'') is spotted. The wildcat and the other members of the cat family had a common ancestor about 10–15 million years ago. The European wildcat evolved during the Cromerian Stage about 866,000 to 478,000 years ago; its direct ancestor was ''Felis lunensis''. The ''silvestris'' and ''lybica'' lineages probably diverged about 173,000 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
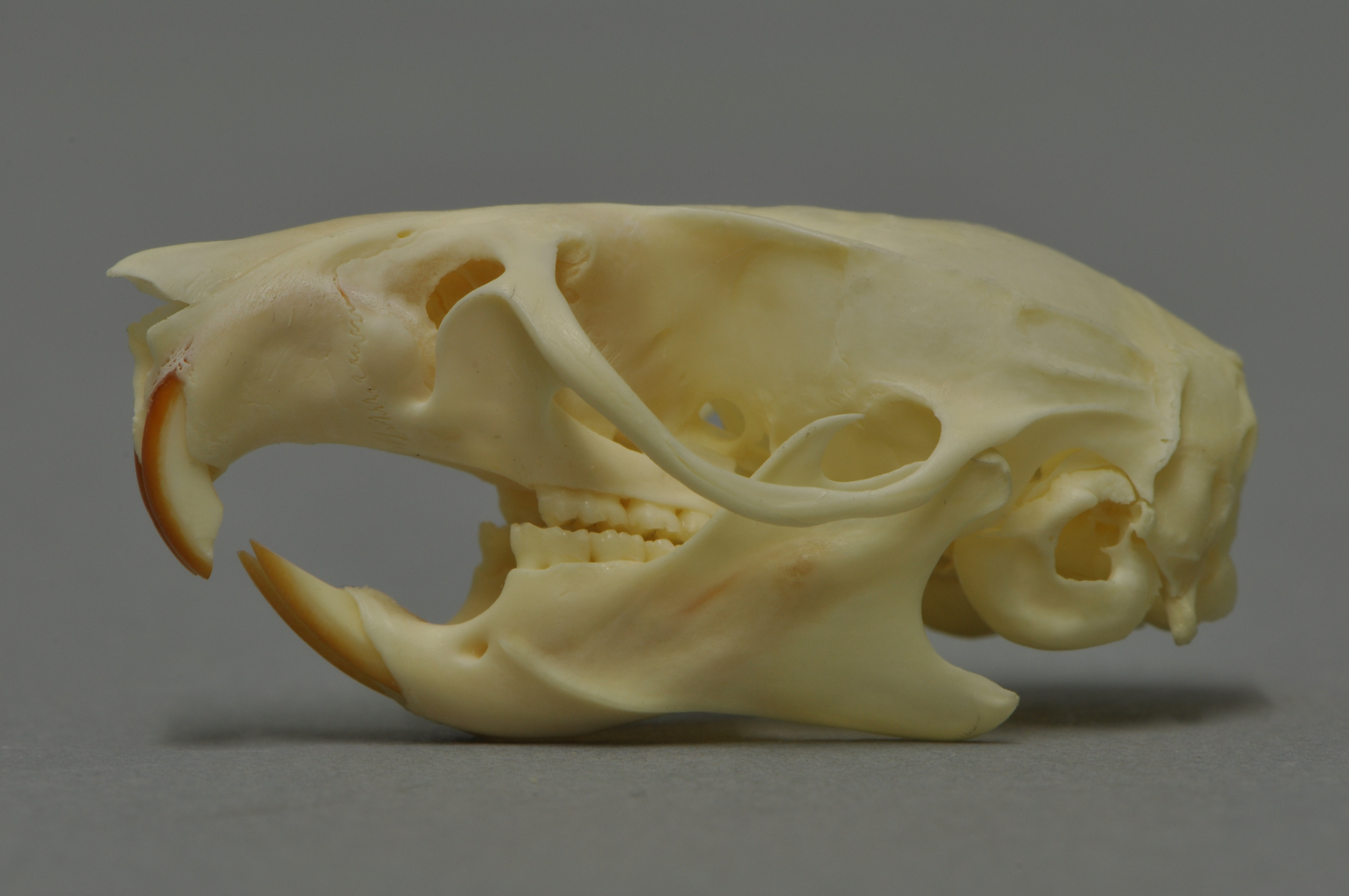
Black Rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A typical adult black rat is long, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araucaria
''Araucaria'' (; original pronunciation: [a.ɾawˈka. ɾja]) is a genus of evergreen Conifer, coniferous trees in the family Araucariaceae. There are 20 extant taxon, extant species in New Caledonia (where 14 species are endemism, endemic, see New Caledonian Araucaria, New Caledonian ''Araucaria''), Norfolk Island, eastern Australia, New Guinea, East Argentina, South Brazil, Chile and Paraguay. They are still common in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific rejoin and Eastern states of Australia, Eastern Australia. Description ''Araucaria'' are mainly large trees with a massive erect stem, reaching a height of . The horizontal, spreading branches grow in whorls and are covered with leathery or needle-like leaf, leaves. In some species, the leaves are narrow, awl-shaped and lanceolate, barely overlapping each other; in others they are broad and flat, and overlap broadly. The trees are mostly dioecy, dioecious, with male and female Conifer cone, cones found on separate tree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathis
''Agathis'', commonly known as kauri or dammara, is a genus of 22 species of evergreen tree. The genus is part of the ancient conifer family Araucariaceae, a group once widespread during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, but now largely restricted to the Southern Hemisphere except for a number of extant Malesian ''Agathis''.de Laubenfels, David J. 1988. Coniferales. P. 337–453 in Flora Malesiana, Series I, Vol. 10. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic. Description Mature kauri trees have characteristically large trunks, with little or no branching below the crown. In contrast, young trees are normally conical in shape, forming a more rounded or irregularly shaped crown as they achieve maturity.Whitmore, T.C. 1977. ''A first look at Agathis''. Tropical Forestry Papers No. 11. University of Oxford Commonwealth Forestry Institute. The bark is smooth and light grey to grey-brown, usually peeling into irregular flakes that become thicker on more mature trees. The branch struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurel Forest
Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elongated leaves, known as "laurophyll" or "lauroid". Plants from the laurel family (Lauraceae) may or may not be present, depending on the location. Ecology Laurel and laurophyll forests have a patchy distribution in warm temperate regions, often occupying topographic refugia where the moisture from the ocean condenses so that it falls as rain or fog and soils have high moisture levels.Abstract at NASA – MODIS: Izquierdo, T; de las Heras, P; Marquez, A (2011). Vegetation indices changes in the cloud forest of La Gomera Island (Canary Islands) and their hydrological implications". ''Hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Song
Bird vocalization includes both bird calls and bird songs. In non-technical use, bird songs are the bird sounds that are melodious to the human ear. In ornithology and birding, songs (relatively complex vocalizations) are distinguished by function from calls (relatively simple vocalizations). Definition The distinction between songs and calls is based upon complexity, length, and context. Songs are longer and more complex and are associated with territory and courtship and mating, while calls tend to serve such functions as alarms or keeping members of a flock in contact. Other authorities such as Howell and Webb (1995) make the distinction based on function, so that short vocalizations, such as those of pigeons, and even non-vocal sounds, such as the drumming of woodpeckers and the "winnowing" of snipes' wings in display flight, are considered songs. Still others require song to have syllabic diversity and temporal regularity akin to the repetitive and transformative patte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

