|
Horik I
Horik I or Hårik (died 854) was a king of the Danes. He was co-ruler from 813, and sole king from c. 828 until his violent death in 854. His long and eventful reign was marked by Danish raids on the Carolingian Empire of Louis the Pious, son and successor of Charlemagne. Background Horik's father was King Gudfred, known for his successful raids and wars against Charlemagne's Frankish empire and against the Obodrites. If the later author Notker of Saint Gall can be trusted, his mother may have been disowned by Gudfred in the early 9th century. In 810, Gudfred was assassinated by a housecarl, or, in Notker's version, by one of his sons as revenge for the treatment of his mother. His nephew Hemming succeeded him. Gudfred had at least five sons. It is unknown why kingship descended on a side-branch of the dynasty, though Hemming was possibly older than his cousins. The new king made peace with Charlemagne in 811. Hemming's reign as king was short-lived and he died in 812. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Danish Monarchs
This is a list of Danish monarchs, that is, the kings and queens regnant of Denmark. This includes: * The Kingdom of Denmark (up to 1397) ** Personal union of Denmark and Norway (1380–1397) * The Kalmar Union (1397–1536) ** Union of Denmark, Norway and Sweden (1397–1523) ** Union of Denmark and Norway (1523–1536/1537) * The United Kingdoms of Denmark–Norway (1536/1537–1814) * The Kingdom of Denmark (1814–present) ** Iceland (since the union between Denmark and Norway in 1380; independent kingdom in a personal union with Denmark 1918–1944; a sovereign republic since 1944) ** Greenland (since the union between Denmark and Norway in 1380; effective Danish–Norwegian control began in 1721; integrated into the Danish realm in 1953; internal home rule introduced 1979; self-determination assumed in 2009; Greenland has two out of 179 seats in the Danish parliament Folketinget) ** Faroe Islands (since the union between Denmark and Norway in 1380; County of Denmark 1816– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaf Geirstad-Alf
Olaf Gudrødsson (c. 810 – c. 860), known after his death as Olaf Geirstad-Alf "Olaf, Elf of Geirstad" (Old Norse Ólafr Geirstaðaalfr), was a semi-legendary petty king in Norway. A member of the House of Yngling, he was the son of Gudrød the Hunter and according to the late ''Heimskringla'', a half-brother of Halfdan the Black. Gudrød and Olaf ruled a large part of Raumarike. The ''Þáttr Ólafs Geirstaða Alfs'' in Flateyjarbók records a fantastical story of how he was worshipped after his death and on his own instructions, his body was then decapitated so that he could be reborn as Olaf II of Norway (St. Olaf). Two not necessarily conflicting hypotheses identify Geirstad with Gjerstad, formerly ''Geirekstad'' in Agder, and with Gokstad (possibly also a contraction of ''Geirekstad'') in Vestfold, the location of the mound Gokstadhaugen, where the Gokstad Ship was excavated. The theory that Olaf thus had a connection with the ship burial is unproven. ''Ynglinga s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vita Ansgari
The ''Vita Ansgarii'', also known as the ''Vita Anskarii'', is the hagiography of saint Ansgar, written by Rimbert, his successor as archbishop in the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen. The ''Vita'' is an important source not only in detailing Ansgar's Scandinavian missionary work, but also in its descriptions of the everyday lives of people during the Viking Age. Date The Vita Anskarii was written sometime between the years 869 and 876. Author Not much is known about Rimbert’s life, the main source being the Vita Rimberrti, written 865-909. Rimbert was likely brought up at the monastery at Turnhout in Flanders. His training as a monk was focused on missionary work. Rimbert’s early years residing in Flanders may explain why he shared such a strong passion for missionary work in the North. Like his predecessor, he may also have had Scandinavian origins, compelling him to save his people. Rimbert died in 888 which meant the missions to Scandinavia collapsed. Rimbert and An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stör
The Stör () is a river in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, right tributary of the Elbe. Its total length is . The Stör rises east of Neumünster, and flows west through Neumünster, Kellinghusen, and Itzehoe. The Stör joins the Elbe near Glückstadt. The lower part between the Elbe and Itzehoe is navigable for Class III ships, the middle part between Itzehoe and Kellinghusen-Rensing is navigable but not classified. Bundesministerium für Verkehr und digitale Infrastruktur ( |
Funen
Funen ( da, Fyn, ), with an area of , is the third-largest island of Denmark, after Zealand and Vendsyssel-Thy. It is the 165th-largest island in the world. It is located in the central part of the country and has a population of 469,947 as of 2020. Funen's main city is Odense, which is connected to the sea by a seldom-used canal. The city's shipyard, Odense Steel Shipyard, has been relocated outside Odense proper. Funen belongs administratively to the Region of Southern Denmark. From 1970 to 2006 the island formed the biggest part of Funen County, which also included the islands of Langeland, Ærø, Tåsinge, and a number of smaller islands. Funen is linked to Zealand, Denmark's largest island, by the Great Belt Bridge, which carries both trains and cars. The bridge is in reality three bridges; low road and rail bridges connect Funen to the small island of Sprogø in the middle of the Great Belt, and a long road suspension bridge (the second longest in the world at the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, northwest of Hamburg. Its total length is . The Elbe's major tributaries include the rivers Vltava, Saale, Havel, Mulde, Schwarze Elster, and Ohře. The Elbe river basin, comprising the Elbe and its tributaries, has a catchment area of , the twelfth largest in Europe. The basin spans four countries, however it lies almost entirely just in two of them, Germany (65.5%) and the Czech Republic (33.7%, covering about two thirds of the state's territory). Marginally, the basin stretches also to Austria (0.6%) and Poland (0.2%). The Elbe catchment area is inhabited by 24.4 million people, the biggest cities within are Berlin, Hamburg, Prague, Dresden and Leipzig. Etymolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic * * * * peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the North Sea coast of northern Germania, in what is now Germany. In the late Roman Empire, the name was used to refer to Germanic coastal raiders, and as a name similar to the later "Viking". Their origins are believed to be in or near the German North Sea coast where they appear later, in Carolingian times. In Merovingian times, continental Saxons had been associated with the activity and settlements on the coast of what later became Normandy. Their precise origins are uncertain, and they are sometimes described as fighting inland, coming into conflict with the Franks and Thuringians. There is possibly a single classical reference to a smaller homeland of an early Saxon tribe, but its interpretation is disputed. According to this proposal, the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of , and the sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants. The term Saxony has been in use for more than a millennium. It was used for the medieval Duchy of Saxony, the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Saxony, and twice for a republic. The first Free State of Saxony was established in 1918 as a constituent state of the Weimar Republic. After World War II, it was under Soviet occupation before it became part of the communist East Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the sea co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
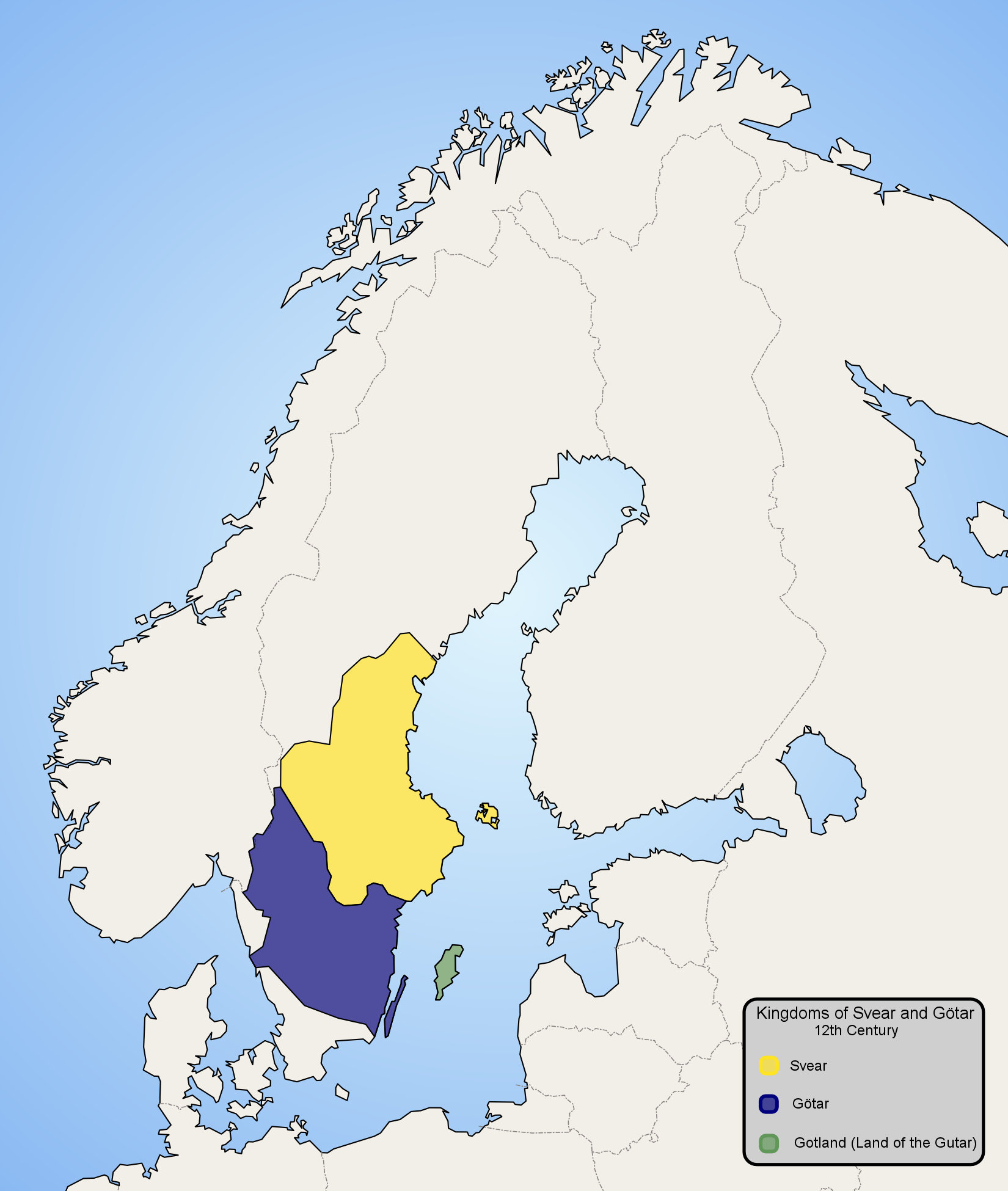
Swedes (Germanic Tribe)
The Swedes ( sv, svear; Old Norse: ''svíar'') (probably from the PIE reflexive pronominal root * s(w)e, "one's own ribesmen/kinsmen;Bandle, Oskar. 2002. The Nordic languages: an international handbook of the history of the North Germanic languages. 2002. P.391 ang, Swēon) were a North Germanic tribe who inhabited Svealand ("land of the Swedes") in central Sweden and one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Geats and Gutes. They had their tribal centre in Gamla Uppsala. The first author who wrote about the tribe is Tacitus, who in his '' Germania'' from 98 CE mentions the ''Suiones''. They are possibly first mentioned locally by the Kylver Stone in the 4th century. Jordanes, in the 6th century, mentions ''Suehans'' and ''Suetidi''. ''Beowulf'' mentions the Swedes around 1000 A.D. According to early sources such as the sagas, especially ''Heimskringla'', the Swedes were a powerful tribe whose kings claimed descendence from the god Freyr. During the Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolf The Ganger
Rollo ( nrf, Rou, ''Rolloun''; non, Hrólfr; french: Rollon; died between 928 and 933) was a Viking who became the first ruler of Normandy, today a region in northern France. He emerged as the outstanding warrior among the Norsemen who had secured a permanent foothold on Frankish soil in the valley of the lower Seine. After the Siege of Chartres in 911, Charles the Simple, the king of West Francia, granted them lands between the mouth of the Seine and what is now Rouen in exchange for Rollo agreeing to end his brigandage, swearing allegiance to him, religious conversion and a pledge to defend the Seine's estuary from Viking raiders. The name Rollo is first recorded as the leader of these Viking settlers in a charter of 918, and he continued to reign over the region of Normandy until at least 928. He was succeeded by his son William Longsword in the Duchy of Normandy that he had founded. The offspring of Rollo and his followers, through their intermingling with the indigenou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amlaíb Conung
Amlaíb Conung ( non, Óláfr ; died c. 874) was a Viking leader in Ireland and Scotland in the mid-late ninth century. He was the son of the king of Lochlann, identified in the non-contemporary ''Fragmentary Annals of Ireland'' as Gofraid, and brother of Auisle and Ímar, the latter of whom founded the Uí Ímair dynasty, and whose descendants would go on to dominate the Irish Sea region for several centuries. Another Viking leader, Halfdan Ragnarsson, is considered by some scholars to be another brother. The Irish Annals title Amlaíb, Ímar and Auisle "kings of the foreigners". Modern scholars use the title "kings of Dublin" after the Viking settlement which formed the base of their power. The epithet "Conung" is derived from the Old Norse ''konungr'' and simply means "king". Some scholars consider Amlaíb to be identical to Olaf the White, a Viking sea-king who features in the '' Landnámabók'' and other Icelandic sagas. During the late 850s and early 860s Amlaíb was inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |