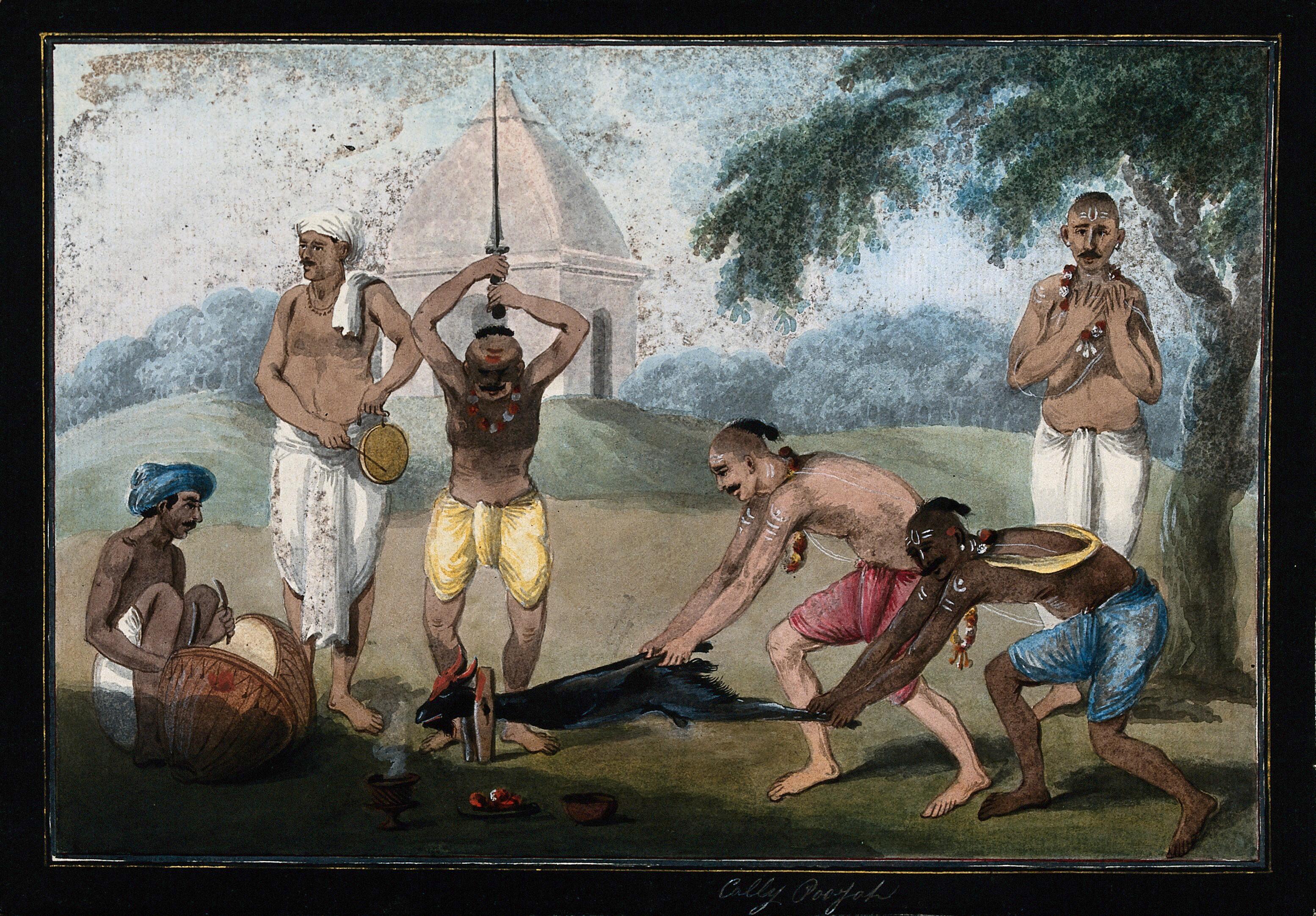|
Herambasuta
Herambasuta (Devanagari:हेरम्बसुत, IAST:), was a Tantric exponent who belonged to the vamachara Ganapatya sect. The tenth century work attributed to certain mentions the cult of led by Herambasuta. The name of the group derives from ''(leftovers)'' in reference to the foods left over at the end of the ritual to the deity. In Tantric context, food is deliberately left in the mouth in order to render them ritually impure. According to the scripture mentioned above, Herambasuta held many unorthodox views, and the worship included . The form of worship Herambasuta expounded was : there was no caste restriction, promiscuity was allowed and the followers wore a red mark on the forehead. According to R. G. Bhandarkar it was an imitation of Kaula (Hinduism), Kaula form of worship. Notes {{Worship in Hinduism Ganesha Hindu tantra Tantric practices Indian Hindu monks Hindu philosophers and theologians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganapatya
Ganapatya is a denomination of Hinduism that worships Ganesha (also called Ganapati) as the Saguna Brahman.Ganapatyas Article from PHILTAR, Division of Religion and Philosophy, St Martin's College Beliefs The worship of Ganesha is considered complementary with the worship of other deities. Hindus of all sects begin prayers, important undertakings, and religious ceremonies with an invocation of Ganesha, because of Ganesha's role as the god of beginnings. But although most Hindu sects do revere Ganesha, the Ganapatya sect goes further than that, and declares Ganesha to be the supreme being. Ganapatya is one of the five principal Hindu sects which focus on a particular deity, alongside Shaivism, focussed on Shiva, Shaktism, focussed on Shakti, Vaishnavism, focused on Vishnu, and Saura (Hinduism), Saura, ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uchchhishta Ganapati
Uchchhishta Ganapati ( sa, उच्छिष्ट-गणपति, ) is a Tantric aspect of the Hindu god Ganesha (Ganapati). He is the primary deity of the ''Uchchhishta Ganapatya'' sect, one of six major schools of the Ganapatyas. He is worshipped primarily by heterodox vamachara rituals. He is one of the thirty-two forms of Ganesha, frequently mentioned in devotional literature. Herambasuta was one of the exponents of the ''Uchchhishta Ganapatya'' sect. Name The god derives his name from ''Uchchhishta'' ("leftovers"). The word refers to the food left over at the end of a ritual, but in this context refers to its Tantric connotation. Uchchhishta is the food kept in the mouth, which is contaminated with saliva, thus ritually impure and a taboo in Hinduism. Iconography The elephant-headed god is described to be red in colour in the ''Mantra-maharnava'', while mentioned as dark in the ''Uttara-kamikagama''. Another description describes him to be blue in complexion. The deity i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient Brahmi script, ''Brāhmī'' script, used in the northern Indian subcontinent. It was developed and in regular use by the 7th century CE. The Devanagari script, composed of 47 primary characters, including 14 vowels and 33 consonants, is the fourth most widely List of writing systems by adoption, adopted writing system in the world, being used for over 120 languages.Devanagari (Nagari) , Script Features and Description, SIL International (2013), United States The orthography of this script reflects the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the nineteenth century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars. Usage Scholars commonly use IAST in publications that cite textual material in Sanskrit, Pāḷi and other classical Indian languages. IAST is also used for major e-text repositories such as SARIT, Muktabodha, GRETIL, and sanskritdocuments.org. The IAST scheme represents more than a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vamachara
''Vāmācāra'' ( sa, वामाचार, ) is a tantric term meaning "left-hand path" and is synonymous with the Sanskrit term ''vāmamārga''. It is used to describe a particular mode of worship or '' sadhana'' (spiritual practice) that is not only heterodox (Sanskrit: nāstika) to standard Vedic injunction, but extreme in comparison to the status quo. These practices are often generally considered to be tantric in orientation. The converse term is ''dakṣiṇācāra'' "right-hand path", which is used to refer not only to orthodox (''Āstika'') sects but to modes of spirituality that engage in spiritual practices that accord with Vedic injunction and are generally agreeable to the status quo. Left-handed and right-handed modes of practice may be evident in both orthodox and heterodox practices of Indian religions such as Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism and Buddhism and are a matter of taste, culture, proclivity, initiation, ''sadhana'' and lineage ('' parampara''). Nomenclat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shankara Vijayam
Digvijaya, (Sanskrit: दिग्विजय; ''Dig'':''"Direction"'' and ''Vijaya'':''"Victory"''), in India was originally a Sanskrit term that meant conquest of the "four quarters", in a military or a moral context. In medieval times, it came to refer to the religious conquest by reputed founders of the major Hindu renunciate traditions, namely Madhva, Sankara, Chaitanya, and Vallabha. Military and moral conquest ''Digvijaya'' as a military conquest is often mentioned in Indian history and mythology, for example, the digvijaya of Bharata Chakravartin. It was followed by rituals confirming the divine grace and royal authority of the conqueror. With his conquest, the Chakravartin unified India as a "moral kingdom" governed by a higher order. The Buddhist Digha Nikaya ''(Chapter 26.6-7)'', also talks about a wheel-turning monarch (Cakravartin), who propagates ''Dharma'' in the four corners under his rulership. Religious conquest According to Sax, the religious connotation t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchamakara
Panchamakara or Panchatattva, also known as the Five Ms, is the Tantric term for the five transgressive substances used in a Tantric practice. These are ( alcohol), ( meat), (fish), (pound grain), and ( sexual intercourse). Taboo-breaking elements are only practiced literally by "left-hand path" tantrics ('' vāmācārin''s), whereas "right-hand path" tantrics ('' dakṣiṇācārin''s) oppose these. Interpretations of the Panchamakaras Arthur Avalon (Sir John Woodroffe) In the introduction of his translation of the ''Mahanirvana Tantra'', Sir John Woodroffe, under the pseudonym ''Arthur Avalon'', describes the Panchamakara thus: Vamachara and dakshinachara In the right-handed path, the Dakshinachara (), as described for example by the spiritual leader Prabhat Ranjan Sarkar, and the five M's have dual meanings, one crude (left-handed, Vamachara) and one subtle (right-handed, Dakshinachara). According to Sarkar, the purpose of the Five M's is dual: for people to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaula (Hinduism)
In the Hindu religious traditions of Shaktism and Shaivism, Kaula, also known as Kula, ("the Kula path") and ("the Kaula tradition"), is a Tantric tradition which is characterised by distinctive rituals and symbolism connected with the worship of Shakti and Shiva. It flourished in ancient India primarily in the 1st millennium CE. Kaula preserves some of the distinctive features of the '' Kāpālika'' tradition, from which it is derived. It is subdivided into four subcategories of texts based on the goddesses Kuleśvarī, Kubjikā, Kālī, and Tripurasundarī respectively. The Trika texts are closely related to the Kuleśvarī texts and can be considered as part of the Kulamārga. In later Hatha Yoga, the Kaula visualization of kundalini rising through a system of chakras is overlaid onto the earlier bindu-oriented system. ''Kaula'' and ''kula'' The translation of the term ''kula'' in English is considered difficult and has raised some problems for researchers. The basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganesha
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in Ganapatya sect. His image is found throughout India. Hindu denominations worship him regardless of affiliations. Devotion to Ganesha is widely diffused and extends to Jains and Buddhists and includes Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Indonesia (Java and Bali), Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, and Bangladesh and in countries with large ethnic Indian populations including Fiji, Guyana, Mauritius, and Trinidad and Tobago. Although Ganesha has many attributes, he is readily identified by his elephant head. He is widely revered, more specifically, as the remover of obstacles and thought to bring good luck; the patron of arts and sciences; and the deva of intellect and wisdom. As the god of beginnings, he is honoured at the start of rites and ceremonies. Ganesha is also invoked as a patron of letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Tantra
Tantras ("''doctrine''" or "''framework''" or "''system''" ) refers to numerous and varied scriptures pertaining to any of several esoteric traditions rooted in Hindu and Buddhist philosophy. The religious culture of the Tantras is essentially Hindu, and Buddhist Tantric material can be shown to have been derived from Hindu sources. And although Hindu and Buddhist Tantra have many similarities from the outside, they do have some clear distinctions. The rest of this article deals with Hindu Tantra. Buddhist Tantras are described in the article on Buddhist Tantras. Classes of Hindu Tantra The word ''tantra'' is made up by the joining (''sandhi'' in Sanskrit) of two Sanskrit words: ''tanoti'' (expansion) and ''rayati'' (liberation). Tantra means liberation of energy and expansion of consciousness from its gross form. It is a method to expand the mind and liberate the dormant potential energy, and its principles form the basis of all yogic practices. Hence, the Hindu Tantra scriptur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantric Practices
Tantric or variations may refer to: Religion Beliefs and practices *Tantra, esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism **Tantric sex, tantric practices to exercise sexuality in a ritualized or yogic context **Tantric yoga, a form of yoga *Vajrayana, also known as Tantric Buddhism **Tibetan tantric practice *Neotantra, a Western form of tantra **Tantra massage, a form of erotic massage Religious texts *Tantras (Buddhism), Indian and Tibetan texts which outline Buddhist religious systems *Tantras (Hinduism), scriptures pertaining to esoteric traditions rooted in Hindu philosophy Music *Tantric (band), a hard rock band from Louisville, Kentucky ** ''Tantric'' (album), the debut album by the band of the same name Other uses *Tantra (Kolkata) Tantra is one of the most popular nightclubs of Kolkata, India. This nightclub is a property of The Park, Kolkata. It is located at 17 Park Street. Saturday nights are the night parties and Wednesdays are Hip Hop nights at this nightclub. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Hindu Monks
Indian or Indians may refer to: Peoples South Asia * Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor ** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country * South Asian ethnic groups, referring to people of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the greater South Asia region prior to the 1947 partition of India * Anglo-Indians, people with mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in the Indian subcontinent * East Indians, a Christian community in India Europe * British Indians, British people of Indian origin The Americas * Indo-Canadians, Canadian people of Indian origin * Indian Americans, American people of Indian origin * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, the pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Americas and their descendants ** Plains Indians, the common name for the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains of North America ** Native Americans in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |