|
HMS Victory (1620)
''Victory'' was a great ship of the English Navy, launched in 1620 and in active service during the seventeenth century's Anglo-Dutch Wars. After an seventy-year naval career, she was broken up at Woolwich Dockyard in 1691 and her timbers reused in other vessels. Naval career ''Victory'' was designed by naval architect Phineas Pett and built by shipwright Andrew Burrell at Deptford Dockyard. She was launched as a 42-gun vessel with 270 crew, on 10 October 1620. The ship was first commissioned in 1621 to join a fleet under Admiral Robert Mansell, which was cruising the Mediterranean to hunt for Algerian pirates. The fleet returned to English waters in the autumn of 1621, and ''Victory'' was assigned to patrol the English Channel throughout the winter, in order to protect merchant shipping making the crossing from the continent. In May 1622 she was named as flagship to the Earl of Oxford, who had committed to clear pirates from the seas around Dunkirk. The mission ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Victory (1620)
''Victory'' was a great ship of the English Navy, launched in 1620 and in active service during the seventeenth century's Anglo-Dutch Wars. After an seventy-year naval career, she was broken up at Woolwich Dockyard in 1691 and her timbers reused in other vessels. Naval career ''Victory'' was designed by naval architect Phineas Pett and built by shipwright Andrew Burrell at Deptford Dockyard. She was launched as a 42-gun vessel with 270 crew, on 10 October 1620. The ship was first commissioned in 1621 to join a fleet under Admiral Robert Mansell, which was cruising the Mediterranean to hunt for Algerian pirates. The fleet returned to English waters in the autumn of 1621, and ''Victory'' was assigned to patrol the English Channel throughout the winter, in order to protect merchant shipping making the crossing from the continent. In May 1622 she was named as flagship to the Earl of Oxford, who had committed to clear pirates from the seas around Dunkirk. The mission ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
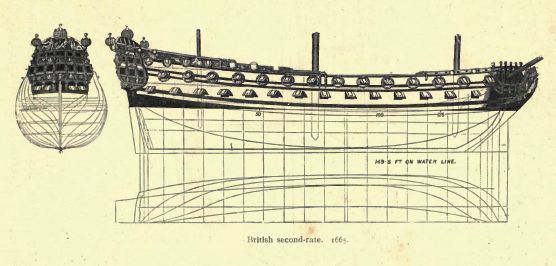
Second-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Myngs
Vice Admiral Sir Christopher Myngs (sometimes spelled ''Mings'', 1625–1666) was an English naval officer and privateer. He came of a Norfolk family and was a relative of Admiral Sir Cloudesley Shovell. Samuel Pepys' story of Myngs' humble birth, in explanation of his popularity, has now been evaluated by historians as to be mostly fictitious in nature. Life The date of Myngs's birth is uncertain, but probably somewhere between 1620 and 1625. It is probable that he saw a good deal of sea-service before 1648. He first appears prominently as the captain of the ''Elisabeth'', which after a sharp action during the First Anglo-Dutch War brought in a Dutch convoy with two men-of-war as prizes. From 1653 to 1655 he continued to command the ''Elisabeth'', high in favour with the council of state and recommended for promotion by the flag officers under whom he served. In 1655, he was appointed to the frigate ''Marston Moor'', the crew of which was on the verge of mutiny. His firm me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phineas Pett II
Phineas () is a masculine given name. Notable people with the name include: * Phineas, an Anglicized name for the priest Phinehas in the Hebrew Bible * King Phineas, the first king of the Beta Israel in Ethiopia * Phineas Banning (1830–1885), American businessman and entrepreneur * P. T. Barnum (1810–1891), American showman and businessman * Phineas Bowles (died 1722), British Army major-general * Phineas Bowles (1690–1749), British Army lieutenant-general and Member of Parliament; son of the above * Phineas F. Bresee (1838–1915), American founder of the Church of the Nazarene * Phineas Bruce (1762–1809), American politician * Phineas Clanton (1843–1906), American Old West cattle rustler and brother of outlaws Billy and Ike Clanton * Phineas Davis (1792–1835), American clockmaker and inventor who designed and built the first practical American coal-burning locomotive * Phineas Fisher, an unidentified hacktivist * Phineas Fletcher (1582–1650), Scottish-English poet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatham Dockyard
Chatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham (at its most extensive, in the early 20th century, two-thirds of the dockyard lay in Gillingham, one-third in Chatham). It came into existence at the time when, following the Reformation, relations with the Catholic countries of Europe had worsened, leading to a requirement for additional defences. Over 414 years Chatham Royal Dockyard provided more than 500 ships for the Royal Navy, and was at the forefront of shipbuilding, industrial and architectural technology. At its height, it employed over 10,000 skilled artisans and covered . Chatham dockyard closed in 1984, and of the Georgian dockyard is now managed as the Chatham Historic Dockyard visitor attraction by the Chatham Historic Dockyard Trust. Overview Joseph Farington (1747-1821) was commissioned by the Navy Board to paint a pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Fleet
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed"; an equivalent expression in unofficial modern US naval usage is "ghost fleet". In earlier times, especially in British usage, the ships were said to be "laid up in ordinary". Overview Such ships are held in reserve against a time when it may be necessary to call them back into service. They are usually tied up in backwater areas near naval bases or shipyards in order to speed the reactivation process. They may be modified for storage during such a period, for instance by having rust-prone areas sealed off or wrapped in plastic or, in the case of sailing warships, the masts removed. While being held in the reserve fleet, ships typically have a minimal crew (known informally as a skeleton crew) to ensure that they stay in somewhat usable co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Anglo-Dutch War
The First Anglo-Dutch War, or simply the First Dutch War, ( nl, Eerste Engelse (zee-)oorlog, "First English (Sea) War"; 1652–1654) was a conflict fought entirely at sea between the navies of the Commonwealth of England and the Dutch Republic, United Provinces of the Netherlands. It was largely caused by disputes over trade, and English historians also emphasise political issues.Israel (1997), p. 1117 The war began with English attacks on Dutch merchant shipping, but expanded to vast fleet actions. Although the English Navy won most of these battles, they only controlled the seas around England, and after the tactical English victory at Battle of Scheveningen, Scheveningen, the Dutch used smaller warships and privateers to capture numerous English merchant ships. Therefore, by November 1653 Cromwell was willing to make peace, provided the House of Orange was excluded from the office of Stadtholder.Israel (1995), pp. 721-2 Cromwell also attempted to protect English trade against D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Commune de Dunkerque (59183) INSEE It lies from the border. It has the third-largest French harbour. The population of the commune in 2019 was 86,279. Etymology and language use The name of Dunkirk derives from '' or ' |
Earl Of Oxford
Earl of Oxford is a dormant title in the Peerage of England, first created for Aubrey de Vere by the Empress Matilda in 1141. His family was to hold the title for more than five and a half centuries, until the death of the 20th Earl in 1703. The de Veres were also hereditary holders of the office of Master Chamberlain of England from 1133 until the death of the 18th Earl in 1625. Their primary seat was Hedingham Castle in Essex, but they held lands in southern England and the Midlands, particularly in eastern England. The actual earldom was called 'Oxenford' until at least the end of the 17th century. Medieval sources thus refer to 'my lord of Oxenford' when speaking of the earl. Earls of Oxford (1141) Soon after his father's death in 1141, Aubrey III de Vere was recruited by Empress Matilda. Aubrey's brother-in-law, Geoffrey de Mandeville first earl of Essex, apparently negotiated the offer of the earldom of Cambridge, with a secondary offer of one of four counties if Camb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest profile or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The term was also used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kanaal, "The Channel"; german: Ärmelkanal, "Sleeve Channel" ( French: ''la Manche;'' also called the British Channel or simply the Channel) is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel was a key factor in Britain becoming a naval superpower and has been utilised by Britain as a natural def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algeria
) , image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Algiers , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , religion = , official_languages = , languages_type = Other languages , languages = Algerian Arabic (Darja) French , ethnic_groups = , demonym = Algerian , government_type = Unitary semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Abdelmadjid Tebboune , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Aymen Benabderrahmane , leader_title3 = Council President , leader_name3 = Salah Goudjil , leader_title4 = Assembly President , leader_name4 = Ibrahim Boughali , legislature = Parliament , upper_house = Council of the Nation , lower_house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_underway_c1947.jpg)


