|
Hyperreal Numbers
In mathematics, hyperreal numbers are an extension of the real numbers to include certain classes of infinite and infinitesimal numbers. A hyperreal number x is said to be finite if, and only if, , x, |
Números Hiperreales
Numero may refer to: *Number *Numero sign The numero sign or numero symbol, (also represented as Nº, No̱, No., or no.), is a Typography, typographic abbreviation of the word ''number''(''s'') indicating Ordinal numeral, ordinal numeration, especially in names and titles. For example ... (№) *'' Numéro'', a French fashion magazine * Numéro#, an electro-pop duo from Montréal * The Numero Group, an American reissue record label {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenistic Sicily, Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, based on his surviving work, he is considered one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity, and one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and mathematical analysis, analysis by applying the concept of the Cavalieri's principle, infinitesimals and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove many geometry, geometrical theorem, theorems, including the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral. Archimedes' other math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Part
Standard may refer to: Symbols * Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs * Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification Norms, conventions or requirements * Standard (metrology), an object that bears a defined relationship to a unit of measure used for calibration of measuring devices * Standard (timber unit), an obsolete measure of timber used in trade * Breed standard (also called bench standard), in animal fancy and animal husbandry * BioCompute Standard, a standard for next generation sequencing * ''De facto'' standard, product or system with market dominance * Gold standard, a monetary system based on gold; also used metaphorically for the best of several options, against which the others are measured * Internet Standard, a specification ratified as an open standard by the Internet Engineering Task Force * Learning standards, standards applied to education content * Standard displacement, a naval term describing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
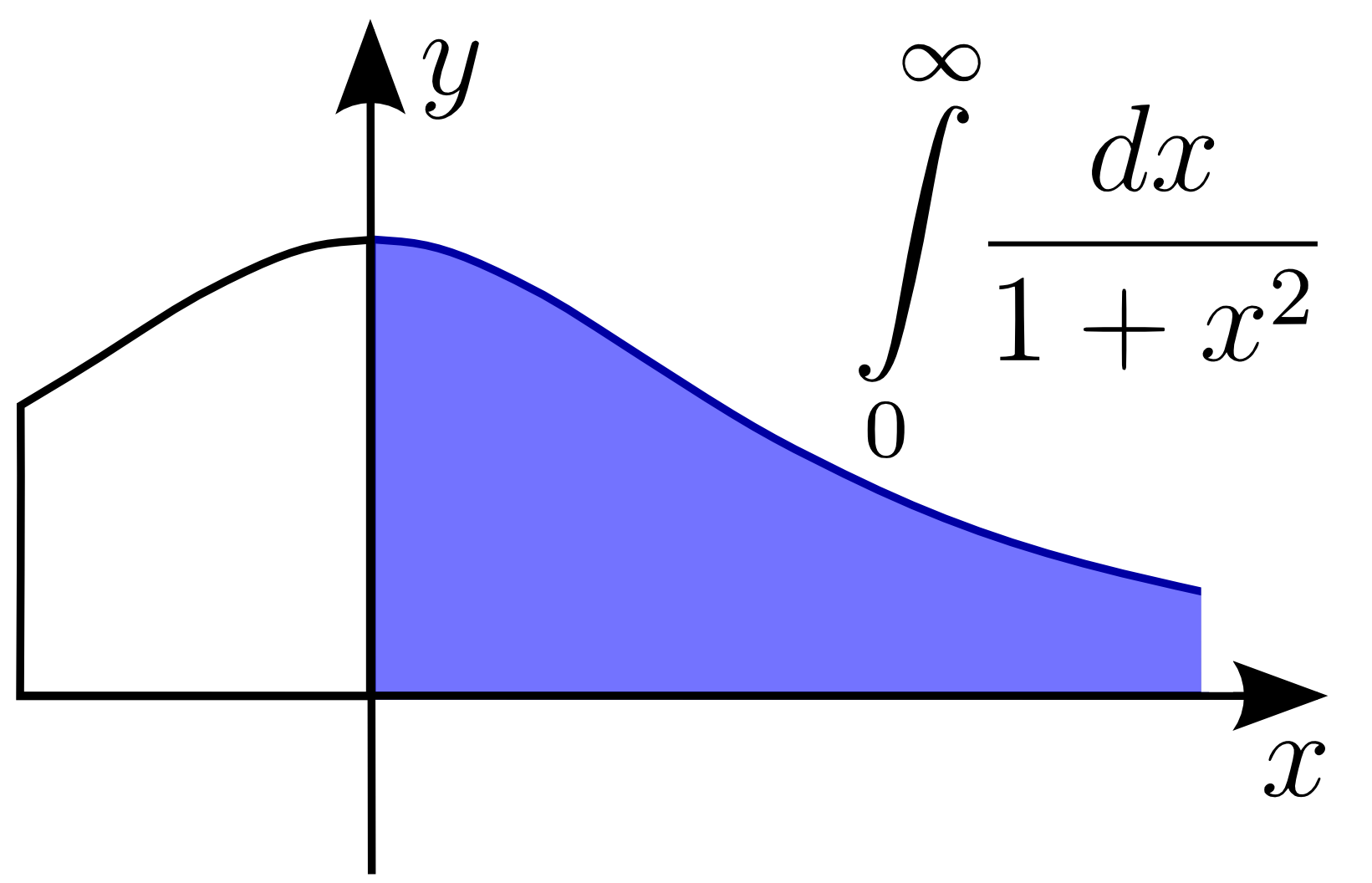
Improper Integrals
In mathematical analysis, an improper integral is an extension of the notion of a definite integral to cases that violate the usual assumptions for that kind of integral. In the context of Riemann integrals (or, equivalently, Darboux integrals), this typically involves unboundedness, either of the set over which the integral is taken or of the integrand (the function being integrated), or both. It may also involve bounded but not closed sets or bounded but not continuous functions. While an improper integral is typically written symbolically just like a standard definite integral, it actually represents a limit of a definite integral or a sum of such limits; thus improper integrals are said to converge or diverge. If a regular definite integral (which may retronymically be called a proper integral) is worked out as if it is improper, the same answer will result. In the simplest case of a real-valued function of a single variable integrated in the sense of Riemann (or Darboux) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archimedean Property
In abstract algebra and mathematical analysis, analysis, the Archimedean property, named after the ancient Greek mathematician Archimedes of Syracuse, Italy, Syracuse, is a property held by some algebraic structures, such as ordered or normed group (algebra), groups, and field (mathematics), fields. The property, as typically construed, states that given two positive numbers x and y, there is an integer n such that nx > y. It also means that the set of natural numbers is not bounded above. Roughly speaking, it is the property of having no ''infinitely large'' or ''infinitely small'' elements. It was Otto Stolz who gave the axiom of Archimedes its name because it appears as Axiom V of Archimedes’ ''On the Sphere and Cylinder''. The notion arose from the theory of magnitude (mathematics), magnitudes of ancient Greece; it still plays an important role in modern mathematics such as David Hilbert's Hilbert's axioms, axioms for geometry, and the theories of linearly ordered group, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set (mathematics)
In mathematics, a set is a collection of different things; the things are '' elements'' or ''members'' of the set and are typically mathematical objects: numbers, symbols, points in space, lines, other geometric shapes, variables, or other sets. A set may be finite or infinite. There is a unique set with no elements, called the empty set; a set with a single element is a singleton. Sets are ubiquitous in modern mathematics. Indeed, set theory, more specifically Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, has been the standard way to provide rigorous foundations for all branches of mathematics since the first half of the 20th century. Context Before the end of the 19th century, sets were not studied specifically, and were not clearly distinguished from sequences. Most mathematicians considered infinity as potentialmeaning that it is the result of an endless processand were reluctant to consider infinite sets, that is sets whose number of members is not a natural number. Specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantification (logic)
In logic, a quantifier is an operator that specifies how many individuals in the domain of discourse satisfy an open formula. For instance, the universal quantifier \forall in the first-order formula \forall x P(x) expresses that everything in the domain satisfies the property denoted by P. On the other hand, the existential quantifier \exists in the formula \exists x P(x) expresses that there exists something in the domain which satisfies that property. A formula where a quantifier takes widest scope is called a quantified formula. A quantified formula must contain a bound variable and a subformula specifying a property of the referent of that variable. The most commonly used quantifiers are \forall and \exists. These quantifiers are standardly defined as duals; in classical logic: each can be defined in terms of the other using negation. They can also be used to define more complex quantifiers, as in the formula \neg \exists x P(x) which expresses that nothing ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinite Sum
In mathematics, a series is, roughly speaking, an addition of infinitely many terms, one after the other. The study of series is a major part of calculus and its generalization, mathematical analysis. Series are used in most areas of mathematics, even for studying finite structures in combinatorics through generating functions. The mathematical properties of infinite series make them widely applicable in other quantitative disciplines such as physics, computer science, statistics and finance. Among the Ancient Greeks, the idea that a potentially infinite summation could produce a finite result was considered paradoxical, most famously in Zeno's paradoxes. Nonetheless, infinite series were applied practically by Ancient Greek mathematicians including Archimedes, for instance in the quadrature of the parabola. The mathematical side of Zeno's paradoxes was resolved using the concept of a limit during the 17th century, especially through the early calculus of Isaac Newton. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Part Function
In nonstandard analysis, the standard part function is a function from the limited (finite) hyperreal numbers to the real numbers. Briefly, the standard part function "rounds off" a finite hyperreal to the nearest real. It associates to every such hyperreal x, the unique real x_0 infinitely close to it, i.e. x-x_0 is infinitesimal. As such, it is a mathematical implementation of the historical concept of adequality introduced by Pierre de Fermat, as well as Leibniz's Transcendental law of homogeneity. The standard part function was first defined by Abraham Robinson who used the notation ^x for the standard part of a hyperreal x (see Robinson 1974). This concept plays a key role in defining the concepts of the calculus, such as continuity, the derivative, and the integral, in nonstandard analysis. The latter theory is a rigorous formalization of calculations with infinitesimals. The standard part of ''x'' is sometimes referred to as its shadow. Definition Nonstandard analysis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral
In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a Summation, sum, which is used to calculate area, areas, volume, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental operations of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. the other being Derivative, differentiation. Integration was initially used to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under a curve, or determining displacement from velocity. Usage of integration expanded to a wide variety of scientific fields thereafter. A definite integral computes the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the Graph of a function, graph of a given Function (mathematics), function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal Coordinate axis, axis of the plane are positive while areas below are n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative is a fundamental tool that quantifies the sensitivity to change of a function's output with respect to its input. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the instantaneous rate of change, the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. The process of finding a derivative is called differentiation. There are multiple different notations for differentiation. '' Leibniz notation'', named after Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, is represented as the ratio of two differentials, whereas ''prime notation'' is written by adding a prime mark. Higher order notations represent repeated differentiation, and they are usually denoted in Leib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonstandard Analysis
The history of calculus is fraught with philosophical debates about the meaning and logical validity of fluxions or infinitesimal numbers. The standard way to resolve these debates is to define the operations of calculus using (ε, δ)-definition of limit, limits rather than infinitesimals. Nonstandard analysis instead reformulates the calculus using a logically rigorous notion of infinitesimal numbers. Nonstandard analysis originated in the early 1960s by the mathematician Abraham Robinson. He wrote: ... the idea of infinitely small or ''infinitesimal'' quantities seems to appeal naturally to our intuition. At any rate, the use of infinitesimals was widespread during the formative stages of the Differential and Integral Calculus. As for the objection ... that the distance between two distinct real numbers cannot be infinitely small, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz argued that the theory of infinitesimals implies the introduction of ideal numbers which might be infinitely small or inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |