|
Hydroxymethylation
Hydroxymethylation is a chemical reaction that installs the CH2OH group. The transformation can be implemented in many ways and applies to both industrial and biochemical processes. Hydroxymethylation with formaldehyde A common method for hydroxymethylation involves the reaction of formaldehyde with active C-H and N-H bonds: :R3C-H + CH2O → R3C-CH2OH :R2N-H + CH2O → R2N-CH2OH A typical active C-H bond is provided by a terminal acetylene or the alpha protons of an aldehyde. In industry, hydroxymethylation of acetaldehyde with formaldehyde is used in the production of pentaerythritol: P-H bonds are also prone to reaction with formaldehyde. Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride ( (CH2OH)4l) is produced in this way from phosphine (PH3). Hydroxymethylation in demethylation 5-Methylcytosine is a common epigenetic marker. The methyl group is modified by oxidation of the methyl group in a process called hydroxymethylation: :RCH3 + O → RCH2OH This oxidation is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calixarene
A calixarene is a macrocycle or cyclic oligomer based on a methylene-linked phenols. With hydrophobic cavities that can hold smaller molecules or ions, calixarenes belong to the class of cavitands known in host–guest chemistry. Nomenclature Calixarene nomenclature is straightforward and involves counting the number of repeating units in the ring and including it in the name. A calix rene has 4 units in the ring and a calix rene has 6. A substituent in the meso position Rb is added to the name with a prefix C- as in C-methylcalix rene The word calixarene is derived from the Greek calix or chalice because this type of molecule resembles a vase (or cup) and from the word arene that refers to the aromatic building block. Synthesis Calixarenes are generally produced by condensation of two components: an electron-rich aromatic compound, classically a 4-substituted phenol, and an aldehyde, classically formaldehyde. *The scope for the aromatic component is broad diverse. The key at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novolak
Novolaks (sometimes: novolacs) are low molecular weight polymers derived from phenols and formaldehyde. They are related to Bakelite, which is more highly crosslinked. The term comes from Swedish "lack" for lacquer and Latin "novo" for new, since these materials were envisioned to replace natural lacquers such as copal resin. Typically novolaks are prepared by the condensation of phenol or a mixture of p- and m-cresol with formaldehyde (as formalin). The reaction is acid catalyzed. Oxalic acid is often used because it can be subsequently removed by thermal decomposition. Novolaks have a degree of polymerization of approximately 20-40. The branching density, determined by the processing conditions, m- vs p-cresol ratio, as well as CH2O/cresol ratio is typically around 15%. Novolaks are especially important in microelectronics where they are used as photoresist materials. They are also used as tackifier Tackifiers are chemical compounds used in formulating adhesives to incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eschenmoser's Salt
In organic chemistry, Eschenmoser's salt (named for Albert Eschenmoser) is the ionic, organic compound . It is the iodide salt of the dimethylaminomethylene cation . The dimethylaminomethylene cation is a strong dimethylaminomethylating agent, used to prepare derivatives of the type .E. F. Kleinman in "Dimethylmethyleneammonium Iodide and Chloride" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. Enolates, silyl enol ethers, and even more acidic ketones undergo efficient dimethylaminomethylation. Once prepared, such tertiary amines can be further methylated and then subjected to base-induced elimination to afford methylidenated ketones. The salt was first prepared by the group of Albert Eschenmoser after whom the reagent is named. Structure and bonding Dimethylaminomethylene cation is described as a resonance hybrid of the carbocation and an iminium cation: :(CH3)2N-CH2+ (CH3)2N+=CH2 The atoms are coplanar. The cation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethoxylation
Ethoxylation is a chemical reaction in which ethylene oxide adds to a substrate. It is the most widely practiced alkoxylation, which involves the addition of epoxides to substrates. In the usual application, alcohols and phenols are converted into R(OC2H4)nOH where n ranges from 1 to 10. Such compounds are called alcohol ethoxylates. Alcohol ethoxylates are often converted to related species called ethoxysulfates. Alcohol ethoxylates and ethoxysulfates are surfactants, used widely in cosmetic and other commercial products. The process is of great industrial significance with more than 2,000,000 metric tons of various ethoxylates produced worldwide in 1994. Production The process was developed at the Ludwigshafen laboratories of IG Farben by Conrad Schöller and during the 1930s. Alcohol ethoxylates Industrial ethoxylation is primarily performed upon fatty alcohols in order to generate fatty alcohol ethoxylates (FAE's), which are a common form of nonionic surfactant (e.g. octa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
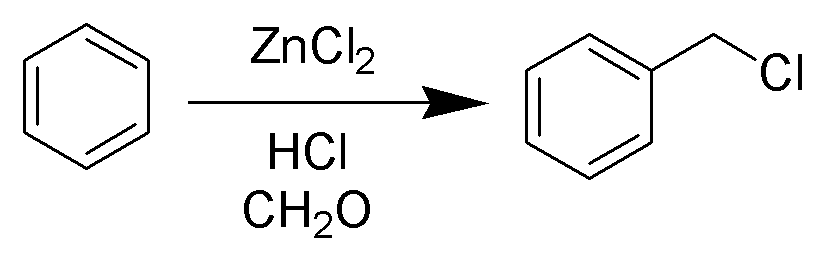
Blanc Chloromethylation
The Blanc chloromethylation (also called the Blanc reaction) is the chemical reaction of aromatic rings with formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride to form chloromethyl arenes. The reaction is catalyzed by Lewis acids such as zinc chloride. The reaction was discovered by Gustave Louis Blanc (1872-1927) in 1923 Mechanism and scope The reaction is carried out under acidic conditions and with a ZnCl2 catalyst. These conditions protonate the formaldehyde carbonyl making the carbon much more electrophilic. The aldehyde is then attacked by the aromatic pi-electrons, followed by rearomatization of the aromatic ring. The benzyl alcohol thus formed is quickly converted to the chloride under the reaction conditions. Other possibilities for the electrophile include (chloromethyl)oxonium cation (ClH2C–OH2+) or chlorocarbenium cation (ClCH2+), which may be formed in the presence of zinc chloride. These species may account for the fact that moderately and strongly deactivated substrates t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloromethylation
The Blanc chloromethylation (also called the Blanc reaction) is the chemical reaction of aromatic rings with formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride to form chloromethyl arenes. The reaction is catalyzed by Lewis acids such as zinc chloride. The reaction was discovered by Gustave Louis Blanc (1872-1927) in 1923 Mechanism and scope The reaction is carried out under acidic conditions and with a ZnCl2 catalyst. These conditions protonate the formaldehyde carbonyl making the carbon much more electrophilic. The aldehyde is then attacked by the aromatic pi-electrons, followed by rearomatization of the aromatic ring. The benzyl alcohol thus formed is quickly converted to the chloride under the reaction conditions. Other possibilities for the electrophile include (chloromethyl)oxonium cation (ClH2C–OH2+) or chlorocarbenium cation (ClCH2+), which may be formed in the presence of zinc chloride. These species may account for the fact that moderately and strongly deactivated substrates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea-formaldehyde
Urea-formaldehyde (UF), also known as urea-methanal, so named for its common synthesis pathway and overall structure, is a nontransparent thermosetting resin or polymer. It is produced from urea and formaldehyde. These resins are used in adhesives, plywood, particle board, medium-density fibreboard (MDF), and molded objects. UF and relate amino resins are a class of thermosetting resins of which urea-formaldehyde resins make up 80% produced worldwide. Examples of amino resins use include in automobile tires to improve the bonding of rubber to in paper for improving tear strength, in molding electrical devices, jar caps, etc. History UF was first synthesized in 1884 by Dr Hölzer, who was working with Bernhard Tollens, neither of whom realized that the urea and formaldehyde were polymerizing. In the following years a large number of authors worked on the structure of these resins. In 1896, Carl Goldschmidt investigated the reaction further. He also obtained an amorphous, almos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakelite
Polyoxybenzylmethylenglycolanhydride, better known as Bakelite ( ), is a thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic components, it was developed by Leo Baekeland in Yonkers, New York in 1907, and patented on December 7, 1909 (). Because of its electrical nonconductivity and heat-resistant properties, it became a great commercial success. It was used in electrical insulators, radio and telephone casings, and such diverse products as kitchenware, jewelry, pipe stems, children's toys, and firearms. The "retro" appeal of old Bakelite products has made them collectible. The creation of a synthetic plastic was revolutionary for the chemical industry, which at the time made most of its income from cloth dyes and explosives. Bakelite's commercial success inspired the industry to develop other synthetic plastics. In recognition of its significance as the world's first commercial synthet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentaerythritol
Pentaerythritol is an organic compound with the formula C(CH2OH)4. Classified as a polyol, it is a white solid. Pentaerythritol is a building block for the synthesis and production of explosives, plastics, paints, appliances, cosmetics, and many other commercial products. The word pentaerythritol is a blend of ''penta-'' in reference to its 5 carbon atoms and ''erythritol'', which also possesses 4 alcohol groups. Synthesis Pentaerythritol was first reported in 1891 by German chemist Bernhard Tollens and his student P. Wigand. It may be prepared via a base-catalyzed multiple-addition reaction between acetaldehyde and 3 equivalents of formaldehyde to give pentaerythrose (CAS: 3818-32-4), followed by a Cannizzaro reaction with a fourth equivalent of formaldehyde to give the final product. Uses Pentaerythritol is a versatile building block for the preparation of many compounds, particularly polyfunctionalized derivatives. applications include alkyd resins, varnishes, polyvinyl c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reagents
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon-carbon bonds. For example, when reacted with another halogenated compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst, they typically yield and the magnesium halide as a byproduct; and the latter is insoluble in the solvents normally used. In this aspect, they are similar to organolithium reagents. Pure Grignard reagents are extremely reactive solids. They are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran; which are relatively stable as long as water is excluded. In such a medium, a Grignard reagent is invariably present as a complex with the magnesium atom connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |