|
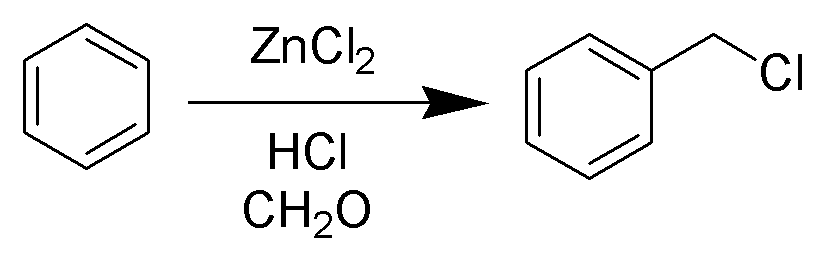
Chloromethylation
The Blanc chloromethylation (also called the Blanc reaction) is the chemical reaction of aromatic rings with formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride to form chloromethyl arenes. The reaction is catalyzed by Lewis acids such as zinc chloride. The reaction was discovered by Gustave Louis Blanc (1872-1927) in 1923 Mechanism and scope The reaction is carried out under acidic conditions and with a ZnCl2 catalyst. These conditions protonate the formaldehyde carbonyl making the carbon much more electrophilic. The aldehyde is then attacked by the aromatic pi-electrons, followed by rearomatization of the aromatic ring. The benzyl alcohol thus formed is quickly converted to the chloride under the reaction conditions. Other possibilities for the electrophile include (chloromethyl)oxonium cation (ClH2C–OH2+) or chlorocarbenium cation (ClCH2+), which may be formed in the presence of zinc chloride. These species may account for the fact that moderately and strongly deactivated substrates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis(chloromethyl) Ether
Bis(chloromethyl) ether is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH2Cl)2O. It is a colourless liquid with an unpleasant suffocating odour and it is one of the chloroalkyl ethers. Bis(chloromethyl) ether was once produced on a large scale, but was found to be highly carcinogenic and thus such production has ceased. Synthesis It was produced industrially from paraformaldehyde and a mixture of chlorosulfonic acid and sulfuric acid. It is also produced as a byproduct in the Blanc chloromethylation reaction, formed when formaldehyde (the monomer, paraformaldehyde or formalin) and concentrated hydrochloric acid are mixed, and is a known impurity in technical grade chloromethyl methyl ether. Because of their carcinogenic potency, the industrial production of chloromethyl ethers ended in most countries in the early 1980s. Bis(chloromethyl) ether was no exception to this with production in the U.S.A. ending in 1982. Uses Bis(chloromethyl) ether has been extensively used in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quelet Reaction
The Quelet reaction (also called the Blanc–Quelet reaction) is an organic coupling reaction in which a phenolic ether reacts with an aliphatic aldehyde to generate an α-chloroalkyl derivative. The Quelet reaction is an example of a larger class of reaction, electrophilic aromatic substitution. The reaction is named after its creator R. Quelet, who first reported the reaction in 1932, and is similar to the Blanc chloromethylation process. The reaction proceeds under strong acid catalysis using HCl; zinc(II) chloride may be used as a catalyst in instances where the ether is deactivated. The reaction primarily yields para-substituted products; however it can also produce ortho-substituted compounds if the para site is blocked. Mechanism The mechanism of the Quelet reaction is primarily categorized as a reaction in polar acid. First, the carbonyl is protonated forming a highly reactive protonated aldehyde that acts as the electrophile to the nucleophilic pi-bond of the aroma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below), hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin), which is also used to store animal specimens. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid. Formaldehyde is an important precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 1996, the installed capacity for the production of formaldehyde was estimated at 8.7 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that it adopts several diverse forms. These compounds can often be used interchangeably and can be interconverted. *Molecular formald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloromethyl Methyl Ether
Chloromethyl methyl ether (CMME) is a compound with formula CH3OCH2Cl. A colorless liquid, it is a chloroalkyl ether. It is used as an alkylating agent. In organic synthesis, it is used for introducing the methoxymethyl ether (MOM) protecting group, and is thus often called MOM-Cl or MOM chloride. It also finds application as a chloromethylating agent in some variants of the Blanc chloromethylation. Preparation A convenient synthesis of chloromethyl methyl ether ''in situ'' involves the reaction of dimethoxymethane and acetyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst This route affords a methyl acetate solution of chloromethyl methyl ether of high purity. A similar method, using a high-boiling acyl chloride, can be used to prepare pure, dimethoxymethane being the only contaminant. In contrast, the classical procedure reported in ''Organic Syntheses'' employing formaldehyde, methanol, and hydrogen chloride yields material significantly contaminated with the dangero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merrifield Resin
Merrifield Resin is a cross-linked polystyrene resin that carries a chloromethyl functional group. Merrifield resin is named after its inventor, Robert Bruce Merrifield (1984 winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry), and used in solid-phase synthesis. The material is typically available as white beads. These beads are allowed to swell in suitable solvents (ethyl acetate, DMF, DMSO), which then allows the reagents to substitute the chloride substituents.Vaino, Andrew R.; Janda, Kim D. "Solid-Phase Organic Synthesis: A Critical Understanding of the Resin" Journal of Combinatorial Chemistry 2000, volume 2, 579-596. Merrifield Resin can be prepared by chloromethylation of polystyrene or by the copolymerization of styrene Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ... and 4-vinylbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouveault–Blanc Reduction
The Bouveault–Blanc reduction is a chemical reaction in which an ester is reduced to primary alcohols using absolute ethanol and sodium metal. It was first reported by Louis Bouveault and Gustave Louis Blanc in 1903. Bouveault and Blanc demonstrated the reduction of ethyl oleate and ''n''-butyl oleate to oleyl alcohol. modified versions of which were subsequently refined and published in ''Organic Syntheses''. : This reaction is used commercially although for laboratory scale reactions it was made obsolete by the introduction of lithium aluminium hydride. Reaction mechanism Sodium metal is a one-electron reducing agent. Four equivalents of sodium are required to fully reduce each ester. Ethanol serves as a proton source. The reaction produces sodium alkoxides, according to the following stoichiometry: : + 6 Na + 4 → + + 4 In practice, considerable sodium is consumed by the formation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry
''Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Chemical Society covering all aspects of chemical engineering. The editor-in-chief is Phillip E. Savage (Pennsylvania State University). History The journal was established in 1909 as the ''Journal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry''. It was renamed in 1930 as ''Industrial & Engineering Chemistry'' before obtaining its current title in 1970. From 1911 to 1916 it was edited by Milton C. Whitaker. From 1921 to 1942 it was edited by Dr. Harrison E. Howe. The journal ''I&EC Product Research and Development'' was established in 1962. It was renamed ''Product R&D'' in 1969 and renamed again in 1978 as ''Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Product Research and Development''. In 1986, it and the journals ''Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals'' and ''Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development'', both also established in 1962, were combine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Syntheses
''Organic Syntheses'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1921. It publishes detailed and checked procedures for the synthesis of organic compounds. A unique feature of the review process is that all of the data and experiments reported in an article must be successfully repeated in the laboratory of a member of the editorial board as a check for reproducibility prior to publication. The journal is published by Organic Syntheses, Inc., a non-profit corporation. An annual print version is published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of Organic Syntheses, Inc. History Prior to World War I, work on synthetic organic chemistry in the United States had been quite limited, and most of the reagents used in laboratories had to be imported from Europe. When export stoppages and trade embargoes cut off this source, Clarence Derick, a professor of chemistry at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, began an effort to synthesize these needed chemicals in industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |