|
Honour Of Richmond
The Honour of Richmond (or English feudal barony of Richmond) in north-west Yorkshire, England was granted to Count Alan Rufus (also known as Alain le Roux) by King William the Conqueror sometime during 1069 to 1071, although the date is uncertain. It was gifted as thanks for his services at the Conquest. The extensive district was previously held by Edwin, Earl of Mercia who died in 1071. The district is probably mentioned in the Domesday Book of 1086 but its limits are uncertain. The honour comprised 60 knight's fees and was one of the most important fiefdoms in Norman England. According to the 14th-century Genealogia of the lords of Richmond, Alan Rufus built a stronghold in the district. The buildings were later known as Richmond Castle which is alluded to in the Domesday survey as forming a ‘castlery’. Territory The district consisted of three main land divisions; the wapentakes of Hang, of Gilling and of Hallikeld. The first two of these correspond to later med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Feudal Barony
In the kingdom of England, a feudal barony or barony by tenure was the highest degree of feudal land tenure, namely ''per baroniam'' (Latin for "by barony"), under which the land-holder owed the service of being one of the king's barons. The duties owed by and the privileges granted to feudal barons are not exactly defined, but they involved the duty of providing soldiers to the royal feudal army on demand by the king, and the privilege of attendance at the king's feudal court, the precursor of parliament. If the estate-in-land held by barony contained a significant castle as its '' caput baroniae'' and if it was especially large – consisting of more than about 20 knight's fees (each loosely equivalent to a manor) – then it was termed an honour. The typical honour had properties scattered over several shires, intermingled with the properties of others. This was a specific policy of the Norman kings, to avoid establishing any one area under the control of a single lord. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallikeld
Hallikeld was a Wapentake (Hundred), which is an administrative division (or ancient district), in the historic county of the North Riding of Yorkshire. It was one of the smaller wapentakes by area and consisted of seven parishes. History The name Hallikeld derives from the Old English ''Halig'', and the Old Norse ''Kelda''. Keld appears in various places in Northern England and means ''Spring'', with the ''Halli'' prefix meaning holy. This is thought to be taken from some fresh water springs in the Melmerby area, which were located within the wapentake. Fields to the south of Melmerby are labelled as ''Hallikelds'' on Ordnance Survey mapping from 1909. As the wapentakes were ancient divisions, the spelling of them has evolved and changed over time. Latterly it was spelt as ''Hallikeld'', but has been historically recorded as ''Hallikell'' and ''Halikeld.'' Another possible derivation of the name is from a holy spring in the churchyard of St Lamberts in Burneston, though the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river ( main stem); or where two streams meet to become the source of a river of a new name (such as the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers at Pittsburgh, forming the Ohio); or where two separated channels of a river (forming a river island) rejoin at the downstream end. Scientific study of confluences Confluences are studied in a variety of sciences. Hydrology studies the characteristic flow patterns of confluences and how they give rise to patterns of erosion, bars, and scour pools. The water flows and their consequences are often studied with mathematical models. Confluences are relevant to the distribution of living organisms (i.e., ecology) as well; "the general pattern ownstream of confluencesof increasing stream flow and decreasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finghall
Finghall is a village and civil parish in the Richmondshire district of North Yorkshire, England. History The village is mentioned in the Domesday Book as ''Fingall'' when it belonged to Count Alan and had 13 villagers. The origin of the place-name is from the Old English words ''Fin'', ''inga'' and ''halt'' meaning a nook of land of the family or followers of a man called Fina. The place-name appears as ''Finegala'' in the Domesday Book of 1086 and as ''Finyngale'' in 1157. In the 1820s, Finghall had a population of 126, which had dropped to 111 by 1872 and 99 by 1897. In 2001, the population had risen to 178, and this had decreased to 166 at the 2011 census. Both censuses are for the Finghall parish which includes the hamlet of Akebar. It is located south of the A684 road, about west of Bedale and about east of Leyburn. The church is dedicated to St. Andrew. the 12th century church is adjacent to the beck and quite near the A684 road. It is thought that the Medieval vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Nidd
The River Nidd is a tributary of the River Ouse in the English county of North Yorkshire. In its first few miles it is dammed three times to create Angram Reservoir, Scar House Reservoir and Gouthwaite Reservoir, which attract a total of around 150,000 visitors a year. The Nidd can overflow the reservoirs, flooding the caves in the valley. In such cases the river overflows into the normally dry river bed past Lofthouse through to Gouthwaite Reservoir. The Yorkshire Dales Rivers TrusYDRThas a remit to conserve the ecological condition of the River Nidd from its headwaters to the Humber estuary. The upper river valley, Nidderdale, was designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in 1994. Course The Nidd rises in Nidderdale at Nidd Head Spring on the slopes of Great Whernside in the Yorkshire Dales. It flows east into Angram and Scar House reservoirs before turning south just downstream of Newhouses. In dry conditions the river disappears underground into the si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Wharfe
The River Wharfe ( ) is a river in Yorkshire, England originating within the Yorkshire Dales National Park. For much of its middle course it is the county boundary between West Yorkshire and North Yorkshire. Its valley is known as Wharfedale. The watercourse first becomes known as the River Wharfe at the confluence of Greenfield Beck and Oughtershaw Beck at Beckermonds. Flowing initially through Langstrothdale, it then passes by, or in some cases through, Kettlewell, Grassington, Bolton Abbey, Addingham, Ilkley, Burley-in-Wharfedale, Otley, Wetherby and Tadcaster. It then flows into the River Ouse near Cawood. The section of the river from its source to around Addingham is in Upper Wharfedale and has a very different character to the river downstream. The Wharfe is long (before it joins the Ouse), making it the 21st longest river in Britain. It is a public navigation from the weir at Tadcaster to its junction with the Ouse near Cawood and is tidal from Ulleske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caput
Latin words and phrases {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilling
Gillingr ( Old Norse: ; also Gilling) is a jötunn in Norse mythology, and the father of Suttungr. Gillingr and, later, his wife are murdered by the dwarfs Fjalar and Galar. In revenge, his son Suttungr tortures the dwarfs into giving him the mead of poetry. Name The Old Norse name ''Gillingr'' has been translated as 'screamer'. It is a related to the Old Norse verb ''gjalla'' ('to scream, yell'; compare with Icelandic ''gjalla'', Norwegian ''gjella'', or Swedish Swedish or ' may refer to: Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically: * Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland ** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ... ''gälla''). Attestations Prose Edda In '' Skáldskaparmál'' (The Language of Poetry), the dwarfs Fjalar and Galar kill Gillingr by overturning his boat. When his wife hears of the news, she is "greatly distressed" and "weeps loudly" and the dwarf Galar, "w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Wiske
The River Wiske is a tributary of the River Swale in Yorkshire, England. The Wiske gives its name to several villages it passes through. The name Wiske is derived from an Old English word ''wisca'' meaning a water meadow. It was once known as the Foulbroke, a name for which some writers commented that it was well deserved. The river was maintained by the River Wiske Internal Drainage Board, which was part of the Shires Group of IDBs. It is within the national character areas (NCAs) of the Vale of Mowbray and the Tees Lowlands. Course The river becomes the Wiske at the confluence of Carr Beck and Stony Lane Beck south of Ingleby Arncliffe close to the Tontine Bridge where the A19 and A172 roads diverge. It flows north in a series of meanders to East Rounton where it turns north-westerly and then westerly past Appleton Wiske. The river continues to flow westerly until just after passing under the A167 road near Great Smeaton where it turns south. It follows a mainly southerly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Ure
The River Ure in North Yorkshire, England is approximately long from its source to the point where it becomes the River Ouse. It is the principal river of Wensleydale, which is the only major dale now named after a village rather than its river. The old name for the valley was Yoredale after the river that runs through it. The Ure is one of many rivers and waterways that drain the Dales into the River Ouse. Tributaries of the Ure include the River Swale and the River Skell. Name The earliest recorded name of the river is in about 1025, probably an error for , where represents the Old English letter wynn or 'w', standing for ("water"). By 1140 it is recorded as ''Jor'', hence Jervaulx (Jorvale) Abbey, and a little later as ''Yore''. In Tudor times the antiquarians John Leland and William Camden used the modern form of the name. The name probably means "the strong or swift river". This is on the assumption that the Brittonic name of the river was ''Isurā'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
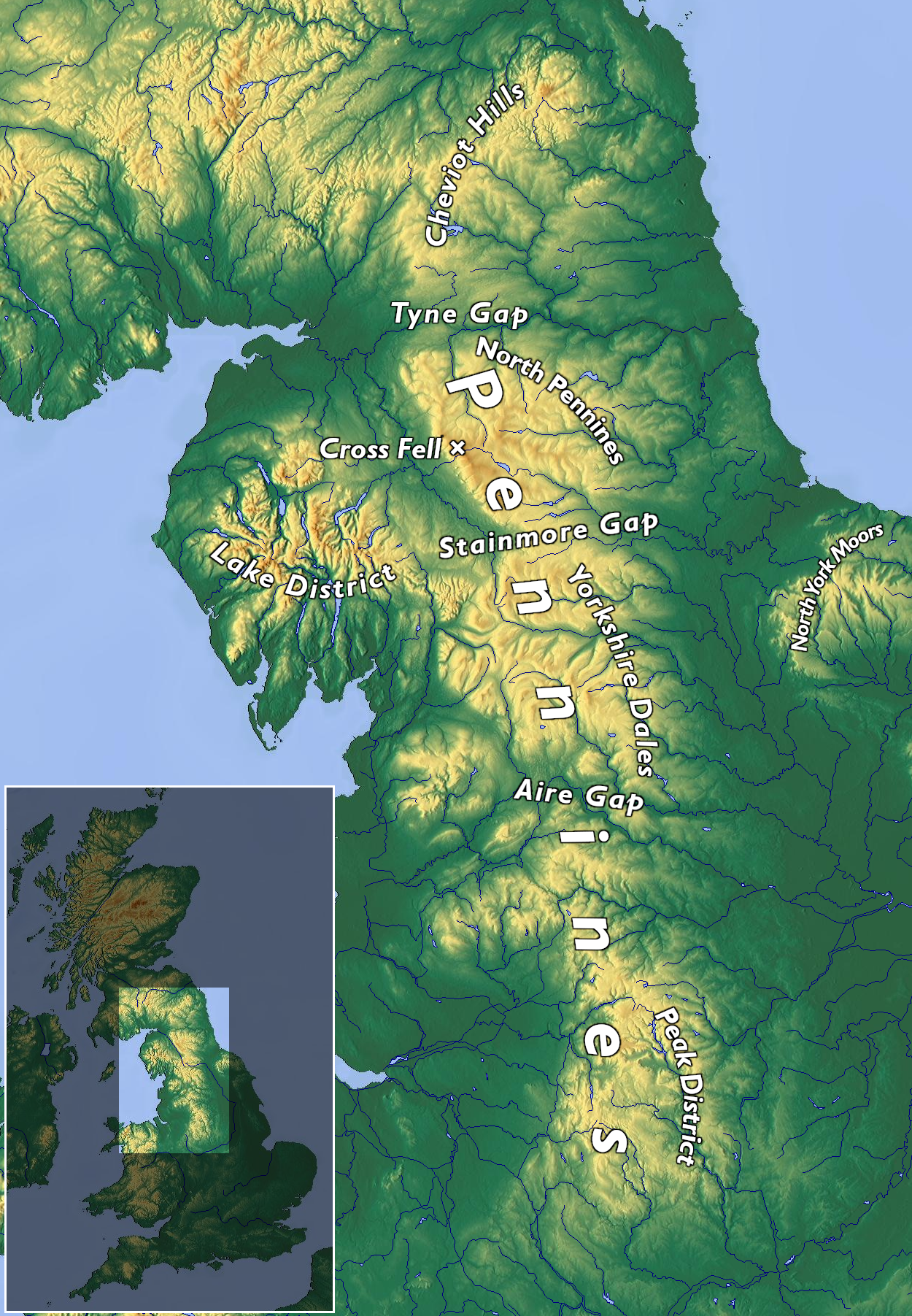
Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commonly described as the " backbone of England", the range stretches northwards from the Peak District at the southern end, through the South Pennines, Yorkshire Dales and North Pennines to the Tyne Gap, which separates the range from the Border Moors and Cheviot Hills across the Anglo-Scottish border, although some definitions include them. South of the Aire Gap is a western spur into east Lancashire, comprising the Rossendale Fells, West Pennine Moors and the Bowland Fells in North Lancashire. The Howgill Fells and Orton Fells in Cumbria are sometimes considered to be Pennine spurs to the west of the range. The Pennines are an important water catchment area with numerous reservoirs in the head streams of the river valleys. The North Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Divide
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a single range of hills or mountains, known as a dividing range. On flat terrain, especially where the ground is marshy, the divide may be difficult to discern. A triple divide is a point, often a summit, where three drainage basins meet. A ''valley floor divide'' is a low drainage divide that runs across a valley, sometimes created by deposition or stream capture. Major divides separating rivers that drain to different seas or oceans are continental divides. The term ''height of land'' is used in Canada and the United States to refer to a drainage divide. It is frequently used in border descriptions, which are set according to the "doctrine of natural boundaries". In glaciated areas it often refers to a low point on a divide where it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |