|
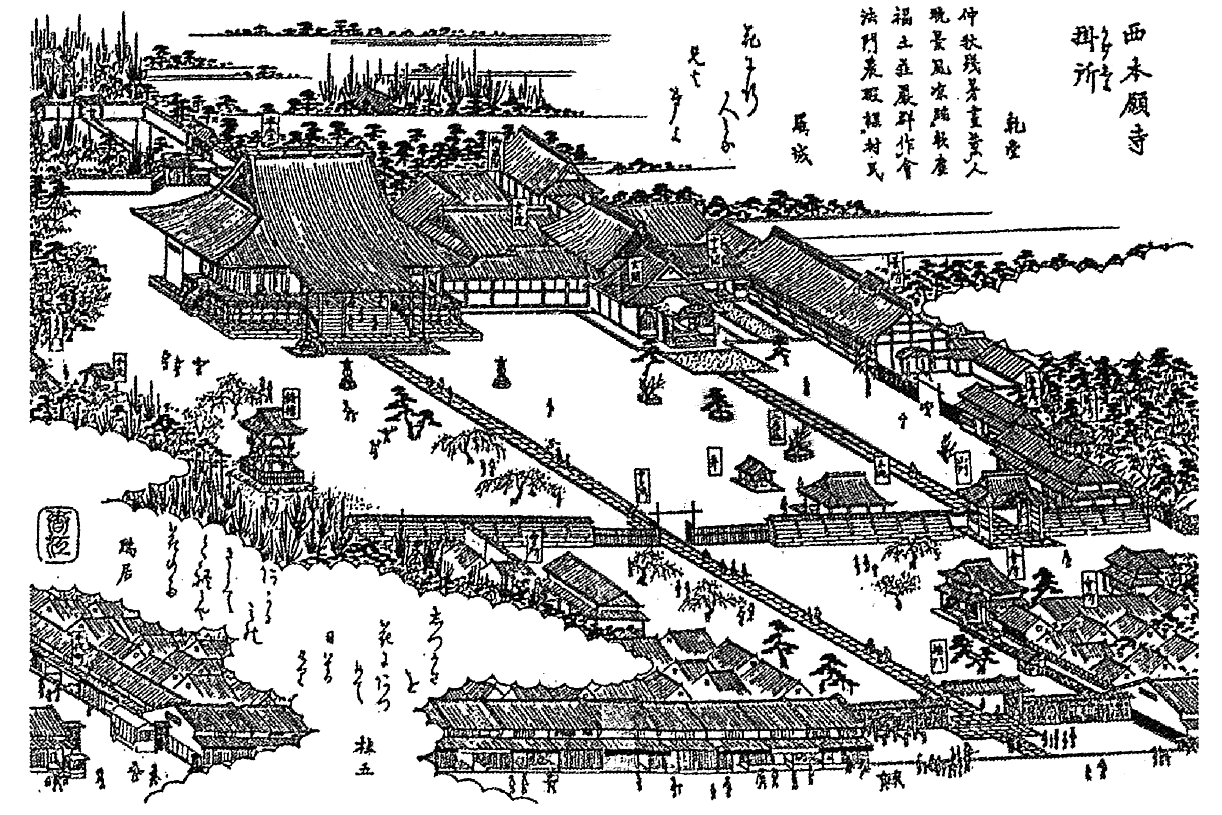
Hongan-ji Betsuin
The Hongan-ji Nagoya Betsuin (本願寺派名古屋別院) is a Jōdo Shinshū Buddhist temple located in Naka ward, Nagoya in central Japan. The temple is a short distance south of Ōsu Kannon Station. It is also known a ''Nishi Betsuin'' (西別院; "Western branch temple"), being associated with Nishi Hongan-ji (西本願寺) in Kyoto. It is contrasted with the Ōtani-ha temple of the same name, popularly known as ''Higashi Betsuin'' (東別院; "Eastern branch temple"). History Hongan-ji Nagoya Betsuin dates back to about 1500 CE when chief abbot Rennyo's 13th child, Renjun, built Ganshō-ji (願証寺) in the Japanese cedar groves of Ise province. The temple later fell on hard times and was renovated. In the early Edo period it was moved to the current location at the time of the construction of Nagoya Castle. It was patronized by Baishō-in, concubine of Tokugawa Tsunanari (1652–1699), lord of the Owari Domain. On 5 October 1817, Hokusai visited the temple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naka-ku, Nagoya
is one of the 16 wards of the city of Nagoya in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 October 2019, the ward has an estimated population of 90,918 and a population density of 9,693 persons per km2. The total area is 9.38 km2. Geography Naka Ward is located in the center of Nagoya city. Largely hemmed in by Sakura-dōri (桜通り), Ōtsu-dōri (大津通り), Fushimi-dōri (伏見通り) and Tsurumai-dōri (鶴舞通り), it contains the main shopping area of Sakae which includes a massive air-conditioned 5 square-kilometer underground mall and the 'after-five' semi-red light districts of Nishiki and Shin-sakae. Surrounding municipalities * Chikusa Ward * Kita Ward * Higashi Ward * Nishi Ward * Nakamura Ward * Shōwa Ward * Atsuta Ward * Nakagawa Ward History Naka Ward was one of the original four wards of the city of Nagoya, established on April 1, 1908. On February 1, 1944, a portion of Naka Ward was divided out to become , but was merged back into Naka Ward on November 3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owari Domain
The was a feudal domain of Japan in the Edo period. Located in what is now the western part of Aichi Prefecture, it encompassed parts of Owari, Mino, and Shinano provinces. Its headquarters were at Nagoya Castle. At its peak, it was rated at 619,500 ''koku'', and was the largest holding of the Tokugawa clan apart from the shogunal lands. The Daimyō of Owari was the Owari Tokugawa family, the first in rank among the ''gosanke''. The domain was also known as History Until the end of the Battle of Sekigahara in September 1600, the area that makes up the Owari Domain was under the control of Fukushima Masanori, head of nearby Kiyosu Castle. After the battle, however, Masanori was transferred to the Hiroshima Domain in Aki Province. Leaders Sub-domains The Owari Domain was supported by the Yanagawa Domain in Mutsu Province and the Takasu Domain in Mino Province. Yanagawa Domain The Yanagawa Domain provided 30,000 ''koku'' to the Owari Domain annually from 1683 to 1730, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsukiji Hongan-ji
, sometimes archaically romanized ''Hongwan-ji'', is a Jodo Shinshu Buddhist temple located in the Tsukiji district of Tokyo, Japan. The temple is adjacent to Tsukiji Station on the Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line. History Tsukiji Hongan-ji's predecessor was the temple of Edo-Asakusa Gobo (江戸浅草御坊), built in Asakusa in 1617 at the behest of the 12th monshu, Junnyo Shōnin.English-language pamphlet from Tsukiji Hongan-ji The temple burned during a citywide fire in 1657, and the shogunate refused to allow it to be rebuilt in Asakusa due to a prior project there. Instead, the temple was moved to a new parcel of land being reclaimed along the Sumida River—today's Tsukiji. This land was said to have been reclaimed by Jodo Shinshu followers themselves who lived at nearby Tsukudajima. The name ''Tsukiji'' comes from the kanji characters meaning "reclaimed land". This new temple, named Tsukiji Gobo (築地御坊), stood until it was leveled by the Great Kantō earthquak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinran
''Popular Buddhism in Japan: Shin Buddhist Religion & Culture'' by Esben Andreasen, pp. 13, 14, 15, 17. University of Hawaii Press 1998, was a Japanese Buddhist monk, who was born in Hino (now a part of Fushimi, Kyoto) at the turbulent close of the Heian Period and lived during the Kamakura Period. Shinran was a pupil of Hōnen and the founder of what ultimately became the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Japanese Buddhism. Names Shinran's birthname was Matsuwakamaro. In accordance with Japanese customs, he has also gone by other names, including Hanen, Shakku and Zenshin, and then finally Shinran, which was derived by combining the names of Seshin (Vasubandhu in Japanese) and Donran ( Tanluan’s name in Japanese). His posthumous title was Kenshin Daishi. For a while, Shinran also went by the name Fujii Yoshizane. After he was disrobed, he called himself Gutoku Shinran, in a self-deprecating manner which means "stubble-haired foolish one," to denote his status as "neither a monk, nor a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Property (Japan)
A is administered by the Japanese government's Agency for Cultural Affairs (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology), and includes tangible properties (structures and works of art or craft); intangible properties (performing arts and craft techniques); folk properties both tangible and intangible; monuments historic, scenic and natural; cultural landscapes; and groups of traditional buildings. Buried properties and conservation techniques are also protected. Together these cultural properties are to be preserved and utilized as the heritage of the Japanese people. Not all Cultural Properties of Japan were created in Japan; some are from China, Korea or other countries. See for example the letter from Duarte de Menezez to Toyotomi Hideyoshi, pictured above, a National Treasure originating in India. In total, some 857 Important Cultural Properties are Chinese in origin, 96 from Korea, 27 from the West, and three from elsewhere. To protect Japan's cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyōhō
, also pronounced Kyōho, was a after '' Shōtoku'' and before '' Gembun.'' This period spanned the years from July 1716 through April 1736. The reigning emperors were and . Change of era * 1716 : The era name of ''Kyōhō'' (meaning "Undergoing and Supporting") was created in response to the death of Tokugawa Ietsugu. The previous era ended and the new one commenced in ''Shōtoku'' 6, on the 22nd day of the 6th month. Events of the ''Kyōhō'' era * 1717 (''Kyōhō 2''): ''Kyōhō'' reforms are directed and overseen by Shōgun Yoshimune. * 1718 (''Kyōhō 3''): The ''bakufu'' repaired the Imperial mausolea.Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1956). ''Kyoto: the Old Capital, 794–1869'', p. 320. * 1718 (''Kyōhō 3, 8th month''): The ''bakufu'' established a at the office of the ''machi-bugyō'' in Heian-kyō. * 1720 (''Kyōhō 5, 6th month''): The 26th High Priest of Nichiren Shōshū, Nichikan Shōnin, who is considered a great reformer of the sect, inscribed the Gohonzon which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōrō
The two main types of bell tower in Japan The or is the bell tower of a Buddhist temple in Japan, housing the temple's . It can also be found at some Shinto shrines which used to function as temples (see article '' Shinbutsu shūgō''), as for example Nikkō Tōshō-gū. Two main types exist, the older , which has walls, and the more recent or , which does not. History During the Nara period (710–794), immediately after the arrival of Buddhism in Japan bell towers were 3 x 2 bay, 2 storied buildings. A typical temple '' garan'' had normally two, one to the left and one to the right of the ''kyōzō'' (or ''kyō-dō''), the sūtra repository. An extant example of this style is Hōryū-ji's Sai-in Shōrō in Nara (see photo in the gallery). During the following Heian period (794–1185) was developed a new style called ''hakamagoshi'' which consisted of a two storied, hourglass-shaped building with the bell hanging from the second story. The earliest extant example is H� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauryan Dynasty
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. Quote: "Magadha power came to extend over the main cities and communication routes of the Ganges basin. Then, under Chandragupta Maurya (c.321–297 bce), and subsequently Ashoka his grandson, Pataliputra became the centre of the loose-knit Mauryan 'Empire' which during Ashoka's reign (c.268–232 bce) briefly had a presence throughout the main urban centres and arteries of the subcontinent, except for the extreme south." The Maurya Empire was centralized by the conquest of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, and its capital city was located at Pataliputra (modern Patna). Outside this imperial center, the empire's geographical extent was dependent on the loyalty of military commanders who controlled the armed cities sprinkling it. During Asho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Of Nagoya In World War II
The Bombing of Nagoya in World War II by the United States Army Air Forces took place as part of the air raids on Japan during the closing months of the war. History The first strategic bombing attack on Nagoya was on April 18, 1942, as part of the Doolittle Raid. A B-25 bomber targeted the Mitsubishi Aircraft Works, the Matsuhigecho oil warehouse, the Nagoya Castle military barracks, and the Nagoya war industries plant. However, it was not until the aerial attacks of 1944 and 1945 that Nagoya would suffer serious bomb damage. According to the United States Strategic Bombing Survey, during the last 9 months of the Pacific War 14,054 tons of bombs were dropped in precision and area air attacks on the factories and urban areas of Nagoya. No other Japanese city other than Tokyo received as many attacks. The city was attacked 21 times between December 13, 1944 and July 24, 1945. The aim of the attacks was stated as ''"(1) mainly by precision attacks, to wipe out Nagoya's aircr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hori River (Nagoya)
The flows north to south through Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture, Japan, and is part of the Shōnai River system. History The river is a man-made canal excavated in 1610 by order of Fukushima Masanori to allow ships to bring goods to the city. The river has influenced the lives of citizens so much that it is traditionally called "Mother River". One of the traditional merchant streets at the canal that leads from the castle is Shikemichi. One of the merchant neighbourhoods was Funairi-chō, located south of the castle. In modern times, pollution has slowly damaged the water quality until the 1960s, where it peaked. Recently, citizens began collecting signatures to initiate the Horikawa River 1000-Citizen Survey Network. In September 2003, this proposal was officially adopted. The Horikawa Lions Club and others set out to recruit 1,000 citizens. However, during the two-month application period, they exceeded expectations, receiving applications from 217 individual groups and 2,007 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagoya University
, abbreviated to or NU, is a Japanese national research university located in Chikusa-ku, Nagoya. It was the seventh Imperial University in Japan, one of the first five Designated National University and selected as a Top Type university of Top Global University Project by the Japanese government. It is the 3rd highest ranked higher education institution in Japan (84th worldwide). The university is the birthplace of the Sakata School of physics and the Hirata School of chemistry. As of 2021, seven Nobel Prize winners have been associated with Nagoya University, the third most in Japan and Asia behind Kyoto University and the University of Tokyo. History Nagoya University traces its roots back to 1871 when it was the Temporary Medical School/Public Hospital. In 1939 it became Nagoya Imperial University (), the last Imperial University of Japanese Empire. In 1947 it was renamed Nagoya University (), and became a Japanese national university. In 2014, according to the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
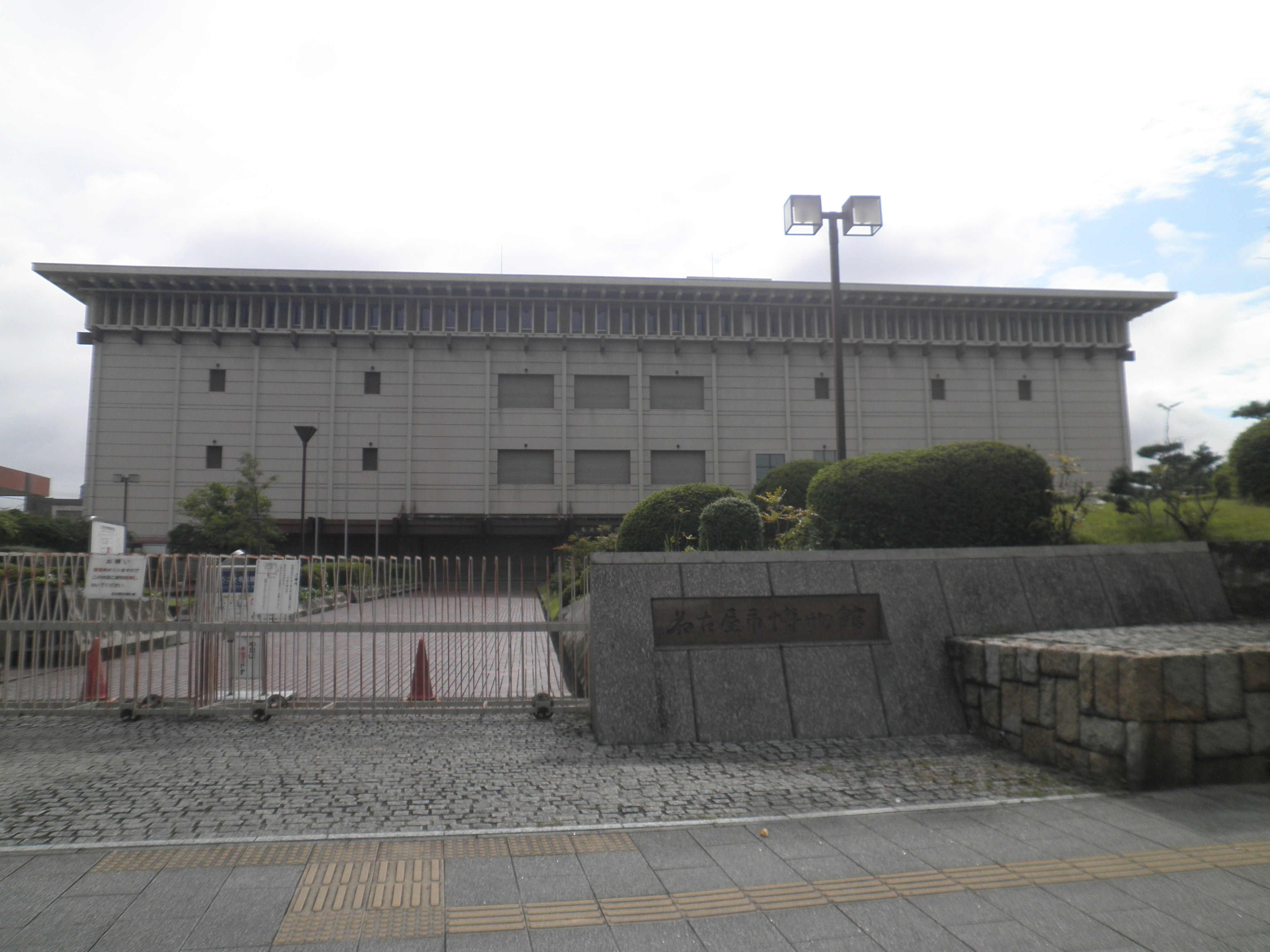
Nagoya City Museum
The is a museum of the city of Nagoya in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. The Nagoya City Museum was established in 1977. Its collection includes archaeological materials, fine art, crafts, documents, books and folk materials including samurai armor and weaponry, many of which are put on exhibition. It also owns a collection of rare Kawana ware. In addition to the permanent exhibition of the history of the Owari Domain starting from the Paleolithic period, special exhibitions and thematic exhibitions take place around every five to seven years, such as the one on Gandhara in 2003. A memorandum of understanding and cooperation was signed in January 2000 with the Vienna Museum, establishing it as a partner museum. The nearest stop by subway is Sakurayama Station on the Sakura-dōri Line The is a subway line, part of the Nagoya Municipal Subway system in Nagoya, Japan. It runs from Taiko-dori Station in Nakamura Ward to in Midori Ward, all within Nagoya. The Sakura-dōri Line' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |