Hongan-ji Betsuin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hongan-ji Nagoya Betsuin (本願寺派名古屋別院) is a
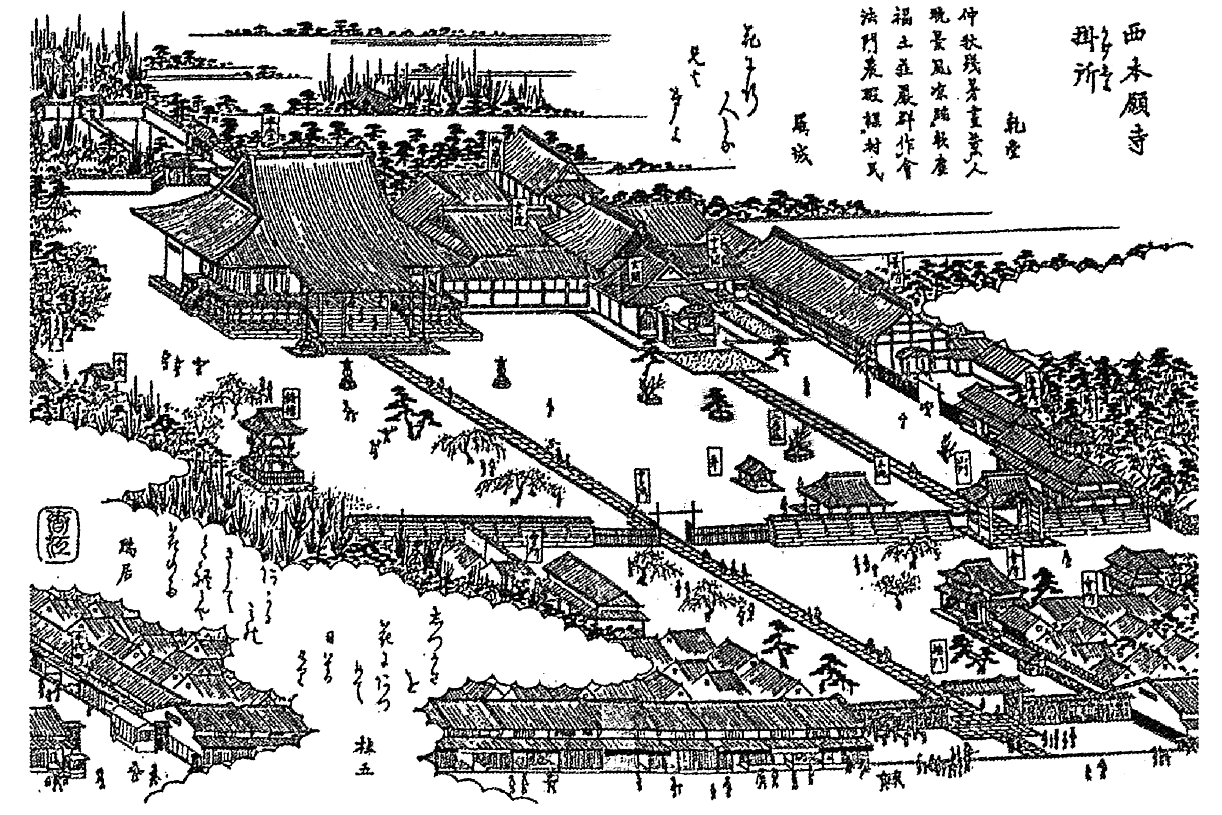


 Hongan-ji Nagoya Betsuin dates back to about 1500 CE when chief abbot Rennyo's 13th child, Renjun, built Ganshō-ji (願証寺) in the Japanese cedar groves of Ise province. The temple later fell on hard times and was renovated. In the early Edo period it was moved to the current location at the time of the construction of
Hongan-ji Nagoya Betsuin dates back to about 1500 CE when chief abbot Rennyo's 13th child, Renjun, built Ganshō-ji (願証寺) in the Japanese cedar groves of Ise province. The temple later fell on hard times and was renovated. In the early Edo period it was moved to the current location at the time of the construction of
Homepage of the Hongan-ji Nagoya Betsuin
{{Buddhist temples in Japan Buddhist temples in Nagoya Shinshū Honganji-ha temples
Jōdo Shinshū
, also known as Shin Buddhism or True Pure Land Buddhism, is a school of Pure Land Buddhism. It was founded by the former Tendai Japanese monk Shinran.
Shin Buddhism is the most widely practiced branch of Buddhism in Japan.
History
Shinran ( ...
Buddhist temple located in Naka ward, Nagoya in central Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
.
The temple is a short distance south of Ōsu Kannon Station
is an underground metro station located in Naka-ku, Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture, Japan operated by the Nagoya Municipal Subway's Tsurumai Line. It is located 7.8 rail kilometers (4.8 rail miles) from the terminus of the Tsurumai Line at Kami-Ot ...
. It is also known a ''Nishi Betsuin'' (西別院; "Western branch temple"), being associated with Nishi Hongan-ji (西本願寺) in Kyoto. It is contrasted with the Ōtani-ha temple of the same name, popularly known as ''Higashi Betsuin'' (東別院; "Eastern branch temple").
History



Nagoya Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Nagoya, Japan.
Nagoya Castle was constructed by the Owari Domain in 1612 during the Edo period on the site of an earlier castle of the Oda clan in the Sengoku period. Nagoya Castle was the heart of one of the ...
.
It was patronized by Baishō-in, concubine of Tokugawa Tsunanari (1652–1699), lord of the Owari Domain
The was a feudal domain of Japan in the Edo period. Located in what is now the western part of Aichi Prefecture, it encompassed parts of Owari, Mino, and Shinano provinces. Its headquarters were at Nagoya Castle. At its peak, it was rated at ...
.
On 5 October 1817, Hokusai
, known simply as Hokusai, was a Japanese ukiyo-e artist of the Edo period, active as a painter and printmaker. He is best known for the woodblock printing in Japan, woodblock print series ''Thirty-Six Views of Mount Fuji'', which includes the ...
visited the temple and with the assistance of his disciples, painted the "Big Daruma" on paper, measuring 18x10.8 metres, impressing many onlookers. For this feat, he received the name "''Darusen''" (a shortened form of ''Daruma Sensei''). Although the original was destroyed in 1945, promotional handbills from that time survived and are preserved at the Nagoya City Museum
The is a museum of the city of Nagoya in Aichi Prefecture, Japan.
The Nagoya City Museum was established in 1977. Its collection includes archaeological materials, fine art, crafts, documents, books and folk materials including samurai armor a ...
. According to several studies, a reproduction of the large painting was done at a large public event on 23 November 2017 to commemorate the 200-year anniversary of the painting, using the same size, techniques and material as the original. A prayer ceremony was done afterwards to bless the painting.
In 1874, close to the temple, a medical training centre, the predecessor of Nagoya University
, abbreviated to or NU, is a Japanese national research university located in Chikusa-ku, Nagoya. It was the seventh Imperial University in Japan, one of the first five Designated National University and selected as a Top Type university of T ...
's School of Medicine, was set up for medical research, practice and education. Later the centre was moved to Tennozaki on the banks of the Hori River.
The wooden building and artwork were largely destroyed during the bombing of Nagoya in World War II
The Bombing of Nagoya in World War II by the United States Army Air Forces took place as part of the air raids on Japan during the closing months of the war.
History
The first strategic bombing attack on Nagoya was on April 18, 1942, as part ...
in May 1945. It was rebuilt in a Mauryan Dynasty ancient Indian style.
The wooden bell tower ('' shōrō'') survived the war undamaged, and is said to be also donated by Baishō-in in Kyōhō
, also pronounced Kyōho, was a after '' Shōtoku'' and before '' Gembun.'' This period spanned the years from July 1716 through April 1736. The reigning emperors were and .
Change of era
* 1716 : The era name of ''Kyōhō'' (meaning "Underg ...
14 (1729). The bell is suspended on the lower level, different from the typical bell tower style. The carved sculptures are also of high quality. It was named a City-designated Cultural Property in 2017.
Features
On the grounds there is a bronze statue commemoratingShinran
''Popular Buddhism in Japan: Shin Buddhist Religion & Culture'' by Esben Andreasen, pp. 13, 14, 15, 17. University of Hawaii Press 1998, was a Japanese Buddhist monk, who was born in Hino (now a part of Fushimi, Kyoto) at the turbulent close of ...
, the founder of Jōdo Shinshū.
The Hongan-ji Betsuin houses the ashes of deceased persons, which are kept in their urns in metal lockers on the ground floor. By request from relatives, monks will perform prayer services for a fee.
See also
* Tsukiji Hongan-ji in Tokyo, which has an architectural resemblanceReferences
External links
Homepage of the Hongan-ji Nagoya Betsuin
{{Buddhist temples in Japan Buddhist temples in Nagoya Shinshū Honganji-ha temples