|
Honey Extractor
A honey extractor is a mechanical device used in the extraction of honey from honeycombs. A honey extractor extracts the honey from the honey comb without destroying the comb. Extractors work by centrifugal force. A drum or container holds a frame basket which spins, flinging the honey out. With this method the wax comb stays intact within the frame and can be reused by the bees. Bees cover the filled in cells with wax cap that must be removed (cut by knife, etc.) before centrifugation. History In 1838, Johann Dzierzon, a German Roman Catholic priest and beekeeper devised the first practical movable-comb beehive, allowing for the manipulation of individual honeycombs without destroying the structure of the hive. This idea was further developed by L. L. Langstroth, an American pastor and beekeeper in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania who patented his beehive design in 1852. These frames were a major improvement over the old method of beekeeping using hollowed tree trunks and skeps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Hruschka
Franz Hruschka also known as Franz von Hruschka or Francesco De Hruschka or František Hruška (Czech origin) was an Austrian/Italian officer and beekeeper known as the inventor of the honey extractor, an invention he presented in 1865 at the Brno Beekeeper Conference. Life Early life Franz Hruschka was born on May 13, 1819 in Vienna, Austria to Franz Ludvik Hruschka, an officer in the Austrian Army and Anna Simon, the daughter of another officer. He spent his childhood in České Budějovice (today in the Czech Republic) and moved to Graz, Austria in 1827 completing elementary school and three years of secondary school.Franz Hruschka - 150 Years of Honey Extractor - F. Hruschka - http://www.fhruschka.cz/en/Hruschka.aspx Military At 14 years old, he is drafted as a cadet of the 19th Infantry Regiment Hessen-Homburg but remains in a unit in Graz. He graduates from the cadet's school in 1836 having studied Czech language and moved back to Vienna with his regiment. He is reassigned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
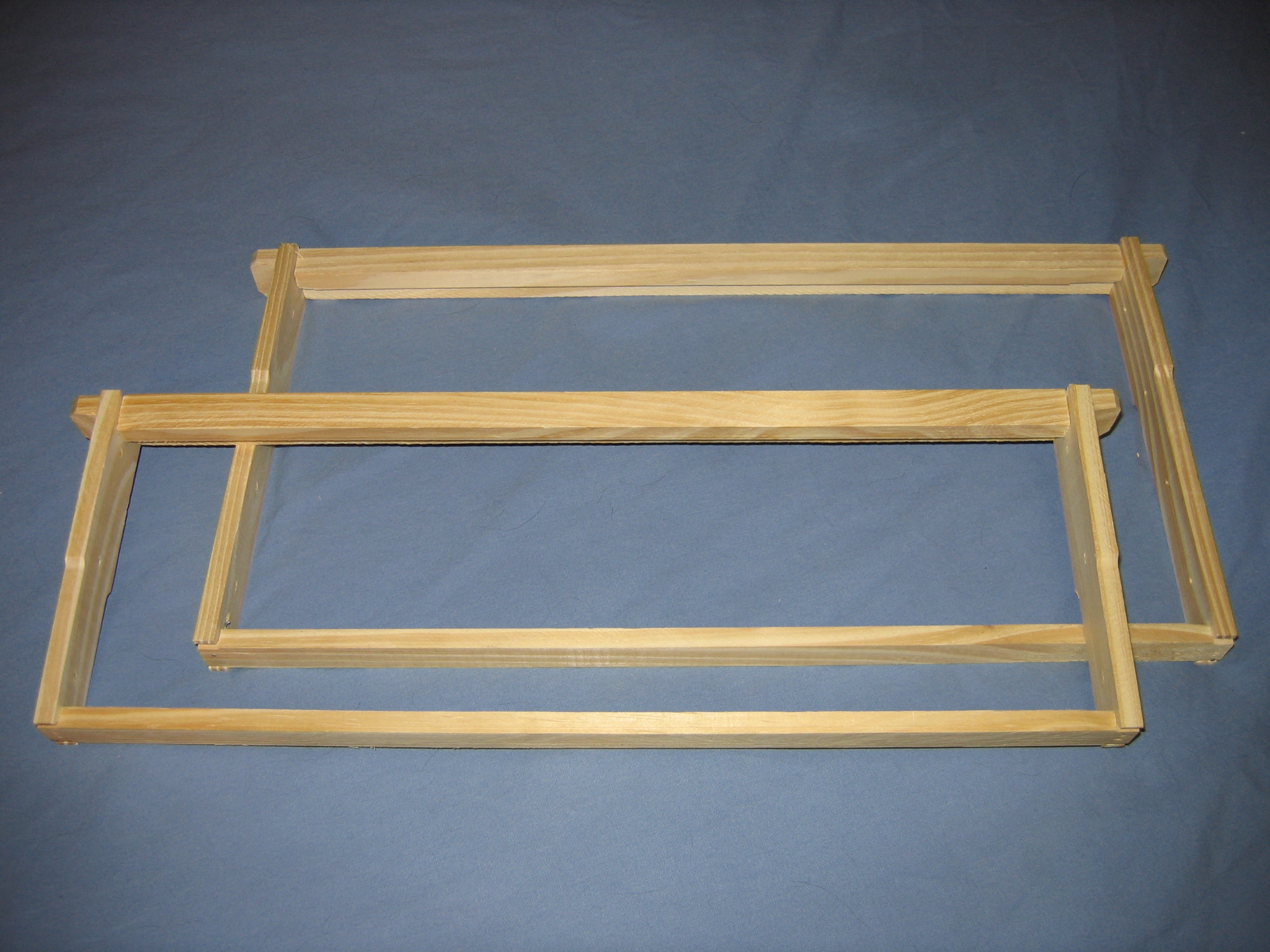
Hive Frame
A hive frame or honey frame is a structural element in a beehive that holds the honeycomb or brood comb within the hive enclosure or box. The hive frame is a key part of the modern movable-comb hive. It can be removed in order to inspect the bees for disease or to extract the excess honey. History In 1814 Petro Prokopovych invented the world's first beehive which used hive frames. Early prototypes had a large distance between frames, and the frame lay on supporting strips of wood. As a result, the frames were cross-attached by burr comb and propolized to the supporting strips and were difficult to remove. In Prokopovych's design, the frames were placed only in the honey chamber. In the brood chamber, the bees built the combs in free style. Johann Dzierzon described the correct distance between combs in the brood chamber as 1½ inches from the center of one bar to the center of the next. In 1848, Dzierzon introduced grooves into the hive's side walls replacing the strips of wood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Hive
Flow Hive is a beehive brand that has a unique honey frame designed to allow honey extraction without needing to open the beehive. During extraction, visibly bees are disturbed less than during other methods. Design The honey frames contain a partially-formed honeycomb with vertical gaps that is made of a plastic free of both BPA and BPS. These honey frames are for use in the Langstroth hive compartment commonly called honey super that is intended for accumulation of honey by bees. Bees fill in these vertical gaps with wax to complete cells, and then fill these cells with honey before covering them with wax. When the mechanism of a frame is activated by inserting and turning a crank mechanically, the vertical gaps are offset by one half of a cell. This breaks the wax covering and allows the honey to flow down through the cells into a channel at the base of each frame and out into a collection vessel, obviating the need for extraction equipment such as centrifuges and filter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
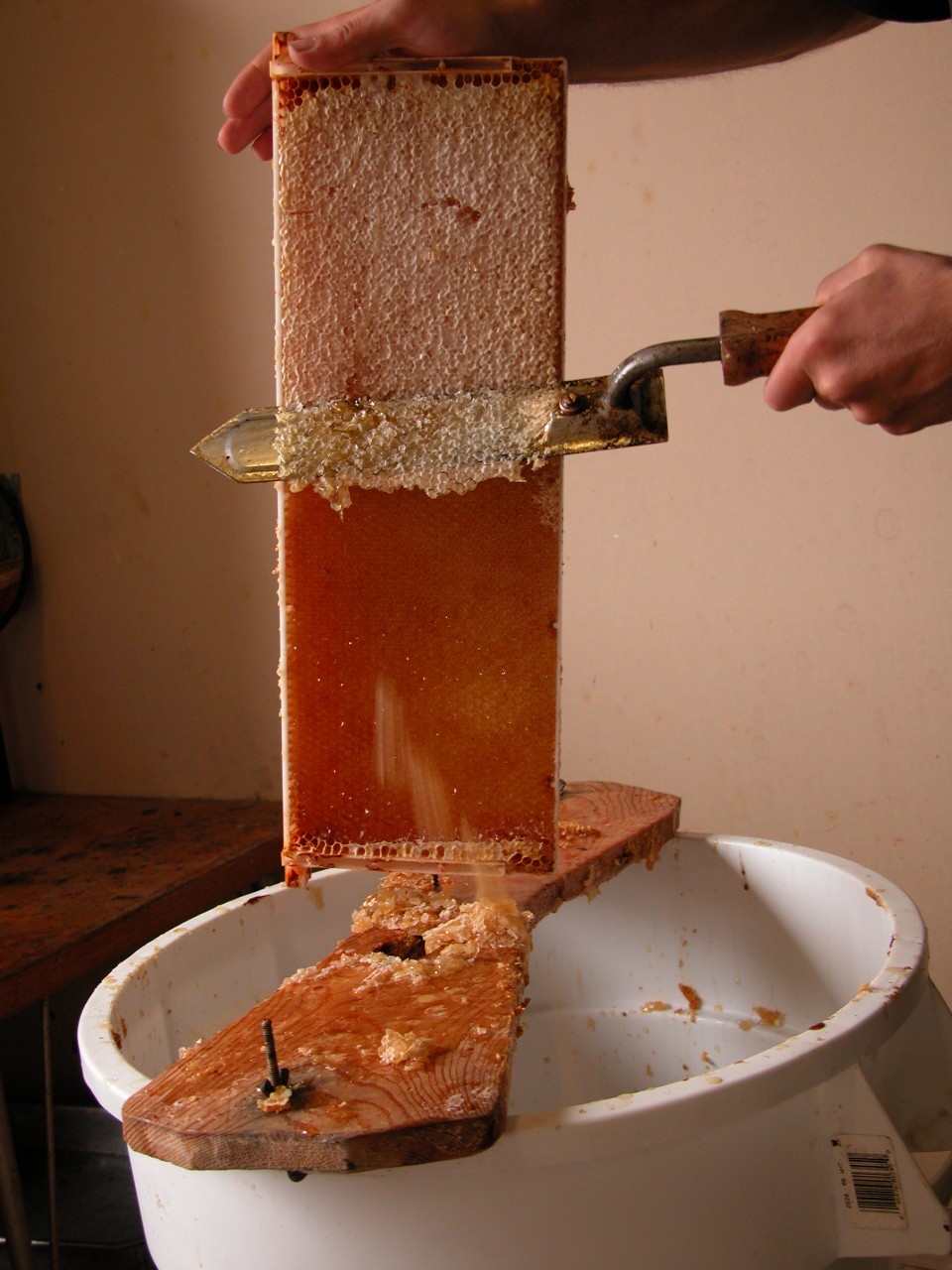
Honey Extraction
Honey extraction is the central process in beekeeping of removing honey from honeycomb so that it is isolated in a pure liquid form. Normally, the honey is stored by honey bees in their beeswax honeycomb; in framed bee hives, the honey is stored on a wooden structure called a frame. The honey frames are typically harvested in the late summer, when they will be most filled with honey. On a completely filled frame, the cells will be capped over by the bees for storage; that is, each cell containing honey will be sealed with a capping made of beeswax. Centrifugal extraction This is widely used, especially by commercial beekeepers. Most centrifugal extractors are not suitable for natural combs. This form of extraction is therefore closely associated with vertical hives, which since the mid 1800s have been the most common variety of hive, and are normally furnished with frames including artificial support. Significant labour is required to disassemble the hives and process the hon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures define different dates as the start of winter, and some use a definition based on weather. When it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. In many regions, winter brings snow and freezing temperatures. The moment of winter solstice is when the Sun's elevation with respect to the North or South Pole is at its most negative value; that is, the Sun is at its farthest below the horizon as measured from the pole. The day on which this occurs has the shortest day and the longest night, with day length increasing and night length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice. The earliest sunset and latest sunrise dates outside the polar regions differ from the date of the winte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Fuel
Diesel fuel , also called diesel oil, is any liquid fuel specifically designed for use in a diesel engine, a type of internal combustion engine in which fuel ignition takes place without a spark as a result of compression of the inlet air and then injection of fuel. Therefore, diesel fuel needs good compression ignition characteristics. The most common type of diesel fuel is a specific fractional distillate of petroleum fuel oil, but alternatives that are not derived from petroleum, such as biodiesel, biomass to liquid (BTL) or gas to liquid (GTL) diesel are increasingly being developed and adopted. To distinguish these types, petroleum-derived diesel is sometimes called petrodiesel in some academic circles. In many countries, diesel fuel is standardised. For example, in the European Union, the standard for diesel fuel is EN 590. Diesel fuel has many colloquial names; most commonly, it is simply referred to as ''diesel''. In the United Kingdom, diesel fuel for on-road use is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Engine
A small engine is the general term for a wide range of small-displacement, low-powered internal combustion engines used to power lawn mowers, generators, concrete mixers and many other machines that require independent power sources. These engines often have simple designs, for example an air-cooled single-cylinder petrol engine with a pull-cord starter, capacitor discharge ignition and a gravity-fed carburettor. Engines of similar design and displacement are also used in smaller vehicles such as motorcycles, motor scooters, all-terrain vehicles, and go-karts. Characteristics The engines are small in both physical dimensions and power output, relative to larger automobile engines. Power outputs are typically less than . The smallest of all are used in handheld garden machinery, such as string trimmers and chainsaws, which have a displacement as small as . Production cost is often a key consideration for small engines, resulting in relatively simple designs (compared with autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to: Mathematics and Direction * Vector (geometric) In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector or spatial vector) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction. Vectors can be added to other vectors ac ..., a line * Radius, adjective form of * Radial distance, a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system * Radial set * A bearing from a waypoint, such as a VHF omnidirectional range Biology * Radial artery, the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm * Radial nerve, supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb * Radial symmetry, one of the types of distribution of body parts or shapes in biology * Radius (bone), a bone of the forearm Technology * Radial (radio), lines which radiate from a radio antenna * Radial axle, on a locomotive or carriage * Radial compressor * Radial delayed blowback * Radial engine * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangential
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve at a point if the line passes through the point on the curve and has slope , where ''f'' is the derivative of ''f''. A similar definition applies to space curves and curves in ''n''-dimensional Euclidean space. As it passes through the point where the tangent line and the curve meet, called the point of tangency, the tangent line is "going in the same direction" as the curve, and is thus the best straight-line approximation to the curve at that point. The tangent line to a point on a differentiable curve can also be thought of as a '' tangent line approximation'', the graph of the affine function that best approximates the original function at the given point. Similarly, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)