|
Home-built Aircraft
Homebuilt aircraft, also known as amateur-built aircraft or kit planes, are constructed by persons for whom this is not a professional activity. These aircraft may be constructed from "scratch", from plans, or from assembly kits.Armstrong, Kenneth: ''Choosing Your Homebuilt - the one you will finish and fly! Second Edition'', pp. 39–52. Butterfield Press, 1993. Peter M Bowers: ''Guide to Homebuilts - Ninth Edition''. TAB Books, Blue Ridge Summit PA, 1984. Overview In the United States, Brazil, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa, homebuilt aircraft may be licensed Experimental under FAA or similar local regulations. With some limitations, the builder(s) of the aircraft must have done it for their own education and recreation rather than for profit. In the U.S., the primary builder can also apply for a repairman's certificate for that airframe. The repairman's certificate allows the holder to perform and sign off on most of the maintenance, repairs, and inspections thems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutan
{{disambig ...
Rutan may refer to: *Rutan, Iran, a village in Hormozgan Province, Iran *Burt Rutan, American aircraft designer *Dick Rutan, American test pilot, and brother of Burt Rutan *Erik Rutan, American metal guitarist and producer * Rutan (''Doctor Who''), a member of a fictional alien race from the British television series ''Doctor Who'' *Rutan, a planet in the ''Star Wars'' universe. See also *Routan (other) Routan may refer to: * Routan Islands, a group of two islands in Chukotka, Russia in the Chaunskaya Bay * Volkswagen Routan The Volkswagen Routan is a seven-seat minivan and rebadged variant of the Chrysler RT platform, with revised styling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plywood
Plywood is a material manufactured from thin layers or "plies" of wood veneer that are glued together with adjacent layers having their wood grain rotated up to 90 degrees to one another. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured boards which include medium-density fibreboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB) and particle board (chipboard). All plywoods bind resin and wood fibre sheets (cellulose cells are long, strong and thin) to form a composite material. This alternation of the grain is called ''cross-graining'' and has several important benefits: it reduces the tendency of wood to split when nailed at the edges; it reduces expansion and shrinkage, providing improved dimensional stability; and it makes the strength of the panel consistent across all directions. There is usually an odd number of plies, so that the sheet is balanced—this reduces warping. Because plywood is bonded with grains running against one another and with an odd number of composit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
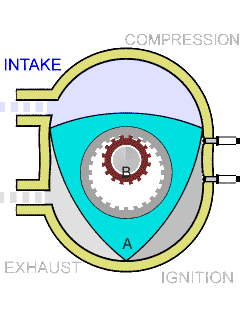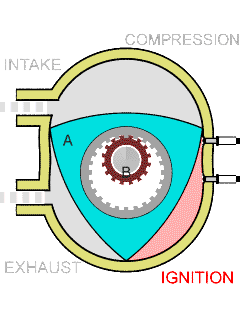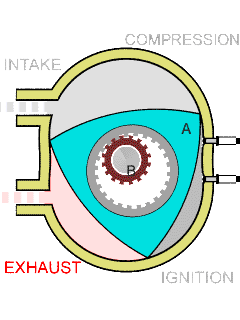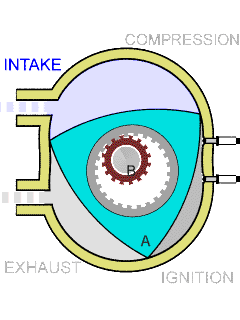
Wankel Engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel, and designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor, which creates the turning motion, is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor rotates inside an oval-like epitrochoidal housing, around a central output shaft. The rotor spins in a hula-hoop fashion around the central output shaft, spinning the shaft via toothed gearing. Due to its inherent poor thermodynamics, the Wankel engine has a significantly worse thermal efficiency and worse exhaust gas behaviour when compared against the Otto engine or the Diesel engine, which is why the Wankel engine has seen limited use since its introduction in the 1960s. However, its advantages of compact design, smoothness, lower weight and less parts over the aforementioned reciproc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
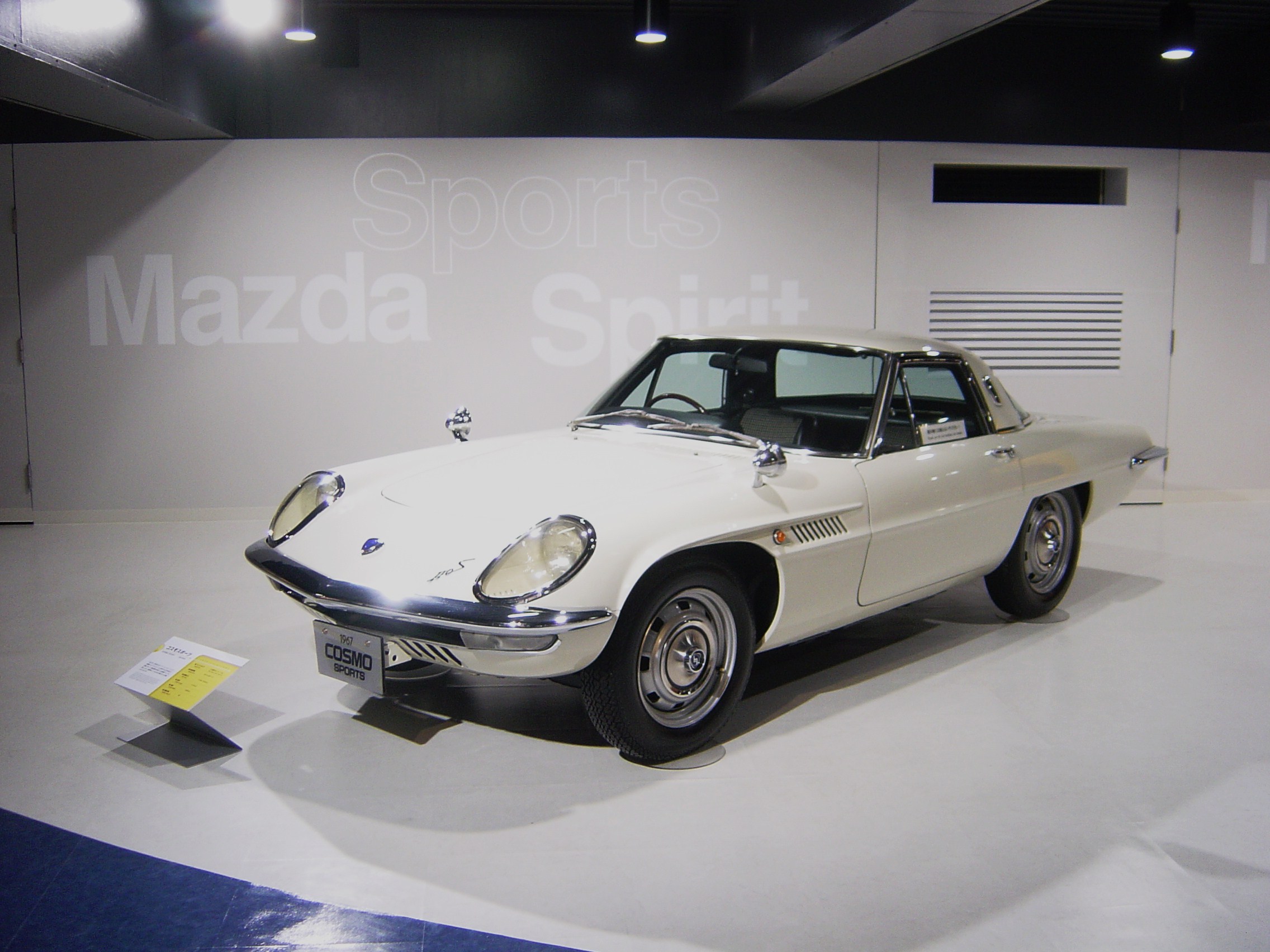
Mazda
, commonly referred to as simply Mazda, is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturer headquartered in Fuchū, Hiroshima (town), Fuchū, Hiroshima Prefecture, Hiroshima, Japan. In 2015, Mazda produced 1.5 million vehicles for global sales, the majority of which (nearly one million) were produced in the company's Japanese plants, with the remainder coming from a variety of other plants worldwide. During this time, Mazda was the 15th-largest automaker in terms of production globally. History Creation Mazda began as the Toyo Cork Kogyo Co., Ltd, as a cork (plug), cork-making factory founded in Hiroshima, Japan, 30 January 1920. Toyo Cork Kogyo renamed itself to Toyo Kogyo Co., Ltd. in 1927. In the late 1920s the company had to be saved from bankruptcy by Hiroshima Saving Bank and other business leaders in Hiroshima. In 1931, Toyo Kogyo moved from manufacturing machine tools to vehicles with the introduction of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subaru
( or ; ) is the automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate Subaru Corporation (formerly known as Fuji Heavy Industries), the twenty-first largest automaker by production worldwide in 2017. Subaru cars are known for their use of a boxer engine layout in most vehicles above 1,500 cc. The Symmetrical All Wheel Drive drive-train layout was introduced in 1972. Both became standard equipment for mid-size and smaller cars in most markets by 1996. The lone exception is the BRZ, introduced in 2012 via a partnership with Toyota, which pairs the boxer engine with rear-wheel-drive. Subaru also offers turbocharged versions of their passenger cars, such as the WRX, Legacy and Outback XT, Ascent, and formerly the Legacy GT and Forester XT. In Western markets, Subaru vehicles have traditionally attracted a small but devoted core of buyers. The company's marketing targets those who desire its signature engine and drive train, all-wheel drive and rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat-4
A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine, is a four-cylinder piston engine with two banks of cylinders lying on opposite sides of a common crankshaft. The most common type of flat-four engine is the boxer-four engine, each pair of opposed pistons moves inwards and outwards at the same time. A boxer-four engine has perfect primary and secondary balance, however, the two cylinder heads means the design is more expensive to produce than an inline-four engine. Boxer-four engines have been used in cars since 1897, especially by Volkswagen and Subaru. They have also occasionally been used in motorcycles and frequently in aircraft. Cessna and Piper use flat four engines from Lycoming and Continental in the most common civil aircraft in the world - the Cessna 172, and Piper Cherokee, while many ultralight and LSA planes use versions of the Rotax 912. Design Most flat-four engines are designed so that each pair of opposing pistons moves inwards and out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-World War II by the British Army Officer Ivan Hirst, it is known for the iconic Beetle and serves as the flagship brand of the Volkswagen Group, the largest automotive manufacturer by worldwide sales in 2016 and 2017. The group's biggest market is in China, which delivers 40 percent of its sales and profits. Its name is derived from the German-language terms and , translating to "people's car" when combined. History 1932–1940: People's Car project Volkswagen was established in 1937 by the German Labour Front (''Deutsche Arbeitsfront'') in Berlin. In the early 1930s, cars were a luxury – most Germans could afford nothing more elaborate than a motorcycle and only one German out of 50 owned a car. Seeking a potential new market, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods. The year 1886 is regarded as the birth year of the car, when German inventor Carl Benz patented his Benz Patent-Motorwagen. Cars became widely available during the 20th century. One of the first cars affordable by the masses was the 1908 Model T, an American car manufactured by the Ford Motor Company. Cars were rapidly adopted in the US, where they replaced animal-drawn carriages and carts. In Europe and other parts of the world, demand for automobiles did not increase until after World War II. The car is considered an essential part of the developed economy. Cars have controls for driving, parking, passenger comfort, and a variety of lights. Over the decades, additional features and controls have been added to vehicles, making them progressively more comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabiru Aircraft
Jabiru Aircraft Pty Ltd is an Australian aircraft manufacturer that produces a range of kit- and ready-built civil light aircraft in Bundaberg, Queensland. The company also designs and manufactures a range of light aircraft engines. Types past and present include microlights (Ultralight or ULM), including the ''Calypso'', two-seat trainers and recreational aircraft (J120/J160/ J170/J230) and four-seat aircraft (J400/J430/J450). The aircraft are built largely of composite materials and are conventional high-wing monoplanes with typically tricycle undercarriage. Taildragger versions were produced in the early days of Jabiru. The wings could be removed for ease of storage or transportation. Use of modern composite techniques has resulted in a strong yet light structure. The aircraft are designed around the pilot and passengers, being spacious and comfortable for touring, yet with a small footprint and frontal profile. Controls include a centrally mounted control column, brake an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
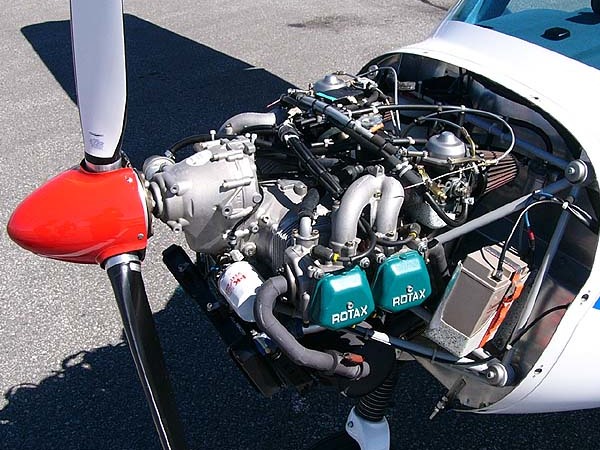
Rotax
Rotax is the brand name for a range of internal combustion engines developed and manufactured by the Austrian company BRP-Rotax GmbH & Co KG (until 2016 BRP-Powertrain GmbH & Co. KG), in turn owned by the Canadian Bombardier Recreational Products. Rotax four-stroke and advanced two-stroke engines are used in a wide variety of small land, sea and airborne vehicles. Bombardier Recreational Products (BRP) use them in their own range of such vehicles. In the light aircraft class, in 1998 Rotax outsold all other aero engine manufacturers combined.Gunston, W.; "''World Encyclopaedia of Aero Engines''", 4th Edition, Patrick Stephens Ltd, 1998, Page 170. History The company was founded in 1920 in Dresden, Germany, as ROTAX-WERK AG. In 1930, it was taken over by Fichtel & Sachs and transferred its operations to Schweinfurt, Germany. Operations were moved to Wels, Austria, in 1943 and finally to Gunskirchen, Austria, in 1947. In 1959, the majority of Rotax shares were taken over b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teledyne Continental Motors
Continental Aerospace Technologies is an aircraft engine manufacturer located at the Brookley Aeroplex in Mobile, Alabama, United States. It was originally spun off from automobile engine manufacturer Continental Motors Company in 1929 and owned by Teledyne Technologies from 1969 until December 2010. The company is now part of Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), which is a Government of the People's Republic of China state-owned aerospace company headquartered in Beijing. Although Continental is most well known for its engines for light aircraft, it was also contracted to produce the air-cooled V-12 AV-1790-5B gasoline engine for the U.S. Army's M47 Patton tank and the diesel AVDS-1790-2A and its derivatives for the M48, M60 Patton, and Merkava main battle tanks. The company also produced engines for various independent manufacturers of automobiles, tractors, and stationary equipment (pumps, generators, and machinery drives) from the 1920s to the 1960s. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycoming Engines
Lycoming Engines is a major American manufacturer of aircraft engines. With a factory in Williamsport, Pennsylvania, Lycoming produces a line of horizontally opposed, air-cooled, four, six and eight-cylinder engines including the only FAA-certified aerobatic and helicopter piston engines on the market. The company has built more than 325,000 piston aircraft engines and powers more than half the world's general aviation fleet, both rotary and fixed wing. Lycoming is an operating division of Avco Corporation, itself a subsidiary of Textron. History Sewing machines, bicycles and fashion Lycoming dates its founding to 1845 by " Madame Ellen Curtis Demorest". However, the early history of the company (especially prior to 1860) is unclear; biographer Ishbel Ross notes that the marriage of Ellen Louise Curtis to William Jennings Demorest took place in 1858, somewhat later than the purported date of establishment of the company. A few years later in New York, between c. 1860 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |