|
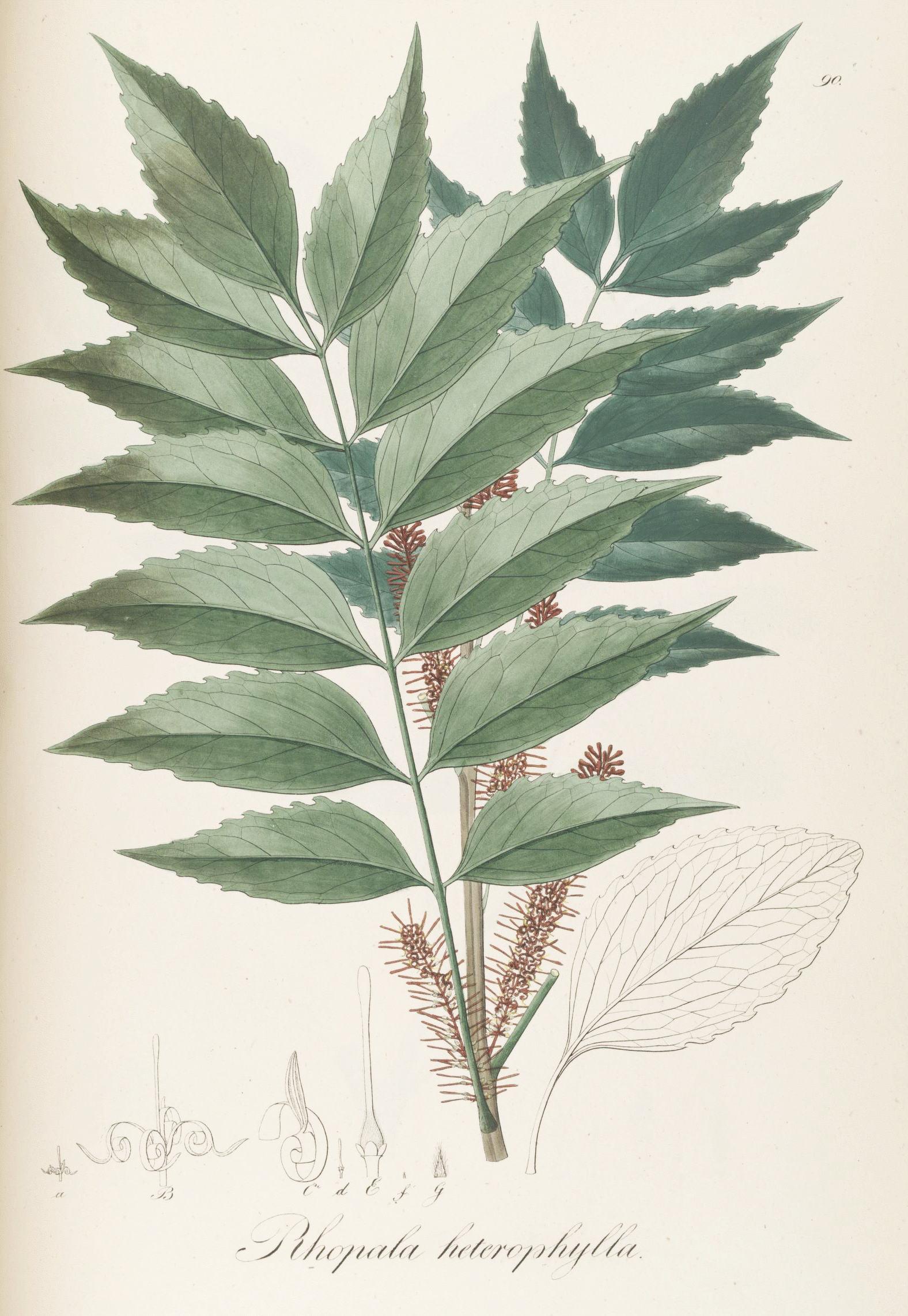
Hollandaea
''Hollandaea'' is a small genus of plants in the family Proteaceae containing four species of Australian rainforest trees. All four species are endemic to restricted areas of the Wet Tropics of northeast Queensland. Naming and classification European science formally described this genus in 1887, authored by German–Australian government botanist Ferdinand von Mueller, who named it in honour of Sir Henry Holland, Secretary of State for the Colonies from 1888 to 1892. Lawrie Johnson and Barbara G. Briggs noted the unusual fruits and placed genus in its own subtribe Hollandaeinae within the tribe Helicieae in the subfamily Grevilleoideae in their 1975 monograph " On the Proteaceae: the evolution and classification of a southern family". Molecular genetic analysis shows ''Hollandaea'' correlates most closely with the genus ''Helicia'' and the two are classified in the subtribe Heliciinae within the tribe Roupaleae. Species *'' Hollandaea diabolica'' *'' Hollandaea porphyrocarp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollandaea Diabolica
''Hollandaea diabolica'' is a species of Australian rainforest tree, constituting part of the plant family Proteaceae. It is endemic to restricted areas of the rainforests of the Wet Tropics region of northeastern Queensland. ''Hollandaea diabolica'' was recognised by botanical science only as recently as the 1990s and formally scientifically described in 2012 by botanists Andrew Ford and Peter Weston. Around the early 1990s the trees were recognised only in a restricted area in the mountains west and north west of Mossman, Queensland. Another population of ''H. diabolica'' affinity was subsequently found south of Mount Bellenden Ker but collections were only of sterile material and not yet fertile and fruiting material. They may grow naturally only in the restricted mountains areas reported, further field work will clarify this. For the restricted, disjunct and small known populations of these trees, the authorities of their 2012 species naming, Andrew Ford and Peter Weston, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollandaea Porphyrocarpa
''Hollandaea porphyrocarpa'' is a species of small Australian rainforest tree in the plant family Proteaceae. It is endemic to restricted areas of the rainforests of the Wet Tropics region of northeastern Queensland. ''Hollandaea porphyrocarpa'' was recognised by botanical science only as recently as the 1990s and formally scientifically described in 2012 by botanists Andrew Ford and Peter Weston. Around the early 1990s the trees were recognised only in a restricted area in the mountains west and north west of Mossman, Queensland. They may grow naturally only in the restricted mountains areas reported, further field work will clarify this. The authorities of this species 2012 naming, Andrew Ford and Peter Weston, recommend for the very restricted and small known population of these trees, the conservation status of vulnerable according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollandaea Sayeriana
''Hollandaea sayeriana'', sometimes named Sayer's silky oak, is a small species of Australian rainforest trees in the plant family Proteaceae. They are endemic to restricted areas of the rainforests of the Wet Tropics region of northeastern Queensland, in the region of Mounts Bellenden Ker, Bartle Frere and the eastern Atherton Tableland. They grow as understory trees beneath the canopy of lowlands to tablelands rainforests, up to about altitude. this species has the official, current, Qld government conservation status of "near threatened" species. In 1886–87, German-Australian government botanist Ferdinand von Mueller Baron Sir Ferdinand Jacob Heinrich von Mueller, (german: Müller; 30 June 1825 – 10 October 1896) was a German-Australian physician, geographer, and most notably, a botanist. He was appointed government botanist for the then colony of Vict ... formally scientifically described this species, named after his associate, botanical collector William A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollandaea Riparia
''Hollandaea riparia'', sometimes named roaring Meg hollandaea, is a species of Australian rainforest tree, in the plant family Proteaceae. They are endemic to restricted areas of the rainforests of the Wet Tropics region of northeastern Queensland. They were named for growing naturally only in riparian and gallery forest as rheophytes (river streamside plants). Botanists have found them only in a restricted natural range in the Daintree Rainforest region. this species has the official, current, Qld government conservation status of "vulnerable" species. Australian botanist Bernie Hyland Bernard Hyland (Bernard Patrick Matthew Hyland, born 1937), known as Bernie Hyland, is an Australian botanist. He has contributed significantly to the understanding of Australian plants, in particular numerous species of his home and workplace ... formally scientifically named and described this species in 1995 in the ''Flora of Australia'' (series). References Proteaceae Flora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicia
''Helicia'' is a genus of 110 species of trees and shrubs, constituting part of the plant family Proteaceae. They grow naturally in rainforests throughout tropical South and Southeast Asia, including India, Sri Lanka, Indochina, Peninsular Malaysia to New Guinea and as far south as New South Wales. Conservation At global, national and regional government scales, many ''Helicia'' species have been threatened with extinction, as officially recognised by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and by continental, national and local governments. Sixteen species have official IUCN global conservation statuses of either "critically endangered", "endangered", "vulnerable" or "near threatened" (in terms of global extinction). Naming and classification In 1790, notable pioneer botanist João de Loureiro described this genus as ''Helicia'' in his publication ''Flora Cochinchinensis''. The type species for the genus was ''Helicia cochinchinensis'', the type specimen of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grevilleoideae
The Grevilleoideae are a subfamily of the plant family Proteaceae. Mainly restricted to the Southern Hemisphere, it contains around 46 genera and about 950 species. Genera include ''Banksia'', ''Grevillea'', and ''Macadamia''. Description The Grevilleoideae grow as trees, shrubs, or subshrubs. They are highly variable, making a simple, diagnostic identification key for the subfamily essentially impossible to provide. One common and fairly diagnostic characteristic is the occurrence of flowers in pairs that share a common bract. However, a few Grevilleoideae taxa do not have this property, having solitary flowers or inflorescences of unpaired flowers. In most taxa, the flowers occur in densely packed heads or spikes, and the fruit is a follicle. Distribution and habitat Grevilleoideae are mainly a Southern Hemisphere family. The main centre of diversity is Australia, with around 700 of 950 species occurring there, and South America also contains taxa. However, the Grevilleoidea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Proteales. Well-known genera include ''Protea'', ''Banksia'', ''Embothrium'', ''Grevillea'', ''Hakea'' and ''Macadamia''. Species such as the New South Wales waratah (''Telopea speciosissima''), king protea (''Protea cynaroides''), and various species of ''Banksia'', ''soman'', and ''Leucadendron'' are popular cut flowers. The nuts of ''Macadamia integrifolia'' are widely grown commercially and consumed, as are those of Gevuina avellana on a smaller scale. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentrations of diversity. Etymology The name Proteaceae was adapted by Robert Brown from the name Proteae coined in 1789 for the family by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, based on the genus ''Protea'', which in 1767 Carl Linnaeus derived from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Plant Name Index
The Australian Plant Name Index (APNI) is an online database of all published names of Australian vascular plants. It covers all names, whether current names, synonyms or invalid names. It includes bibliographic and typification details, information from the Australian Plant Census including distribution by state, links to other resources such as specimen collection maps and plant photographs, and the facility for notes and comments on other aspects. History Originally the brainchild of Nancy Tyson Burbidge, it began as a four-volume printed work consisting of 3,055 pages, and containing over 60,000 plant names. Compiled by Arthur Chapman, it was part of the Australian Biological Resources Study (ABRS). In 1991 it was made available as an online database, and handed over to the Australian National Botanic Gardens. Two years later, responsibility for its maintenance was given to the newly formed Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research. Scope Recognised by Australian herbaria as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mossman, Queensland
Mossman is a rural town and locality in the Shire of Douglas, Queensland, Australia. It is the administrative centre for the Douglas Shire Council In the , the locality of Mossman had a population of 1,937 people. Geography Mossman in Far North Queensland on the Mossman River. Mossman is located on the Captain Cook Highway north of the regional city of Cairns, and east of the Mount Carbine Tableland. The Mossman River flows through the locality from west ( Finlayvale / Mossman Gorge) to east ( Newell / Bonnie Doon). Mossman Gorge, a popular attraction within Daintree National Park and the broader Wet Tropics of Queensland World Heritage area is located west of town. Sugar cane farming is an important aspect of the local economy, with Mossman Central Mill, the only sugar mill in the district (), processing the cane before sending it to Cairns for shipping domestically and internationally. There is a network of cane tramways through Mossman and nearby sugarcane growing ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daintree Rainforest
The Daintree Rainforest is a region on the northeast coast of Queensland, Australia, north of Mossman, Queensland, Mossman and Cairns. At around , the Daintree is a part of the largest continuous area of tropical rainforest on the Australia (continent), Australian continent. The Daintree Rainforest is a part of the Wet Tropics of Queensland Rainforest, that spans across the Cairns Region. The Wet Tropics Rainforest (that the Daintree is a part of) is the oldest continually surviving tropical rainforest in the world. Along the coastline north of the Daintree River, tropical forest grows right down to the edge of the sea. In 2009 as part of the Q150 celebrations, the Daintree Rainforest was announced as one of the Q150 Icons of Queensland for its role as a "natural attraction". History and description About Daintree Rainforest The Daintree Rainforest was once a vast forest that covered the entire Australian continent. It is a rare survival of 120 million years of climate change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheophyte
A rheophyte is a plant that lives in fast moving water currents in an environment where few other organisms can survive. Rheophytes tend to be found in currents that move at rates of one to two meters per second and that are up to 1 to 2 m deep. The amount of force produced by these currents, and the damaging debris they can carry, makes this environment inhospitable to most plants. Rheophytes are able to live in such environments because their leaves are streamlined so as put up little resistance to the flow of water. The leaves tend to be quite narrow and flexible as well. Simply being an aquatic plant with narrow leaves is not a sufficient condition for being a rheophyte. In order to prevent being uprooted by the rushing currents, rheophytes have an extremely strong wide spreading root systems. Rheophytes comprise two main groups - obligate rheophytes (or 'true' rheophytes) and facultative rheophytes. Apart from being adapted for fast currents, the survival of obligate rheophyte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallery Forest
A gallery forest is one formed as a corridor along rivers or wetlands, projecting into landscapes that are otherwise only sparsely treed such as savannas, grasslands, or deserts. The gallery forest maintains a more temperate microclimate above the river. Defined as long and narrow forest vegetation associated with rivers, gallery forests are structurally and floristically heterogeneous. The habitats of these forests differ from the surrounding landscapes because they are, for example, more nutrient-rich or moister and/or there is less chance of fires. The forests are sometimes only a few meters wide, because they depend on the water they lie along. Ecology characteristics The riparian zones in which they grow offer greater protection from fire which would kill tree seedlings. In addition, the alluvial soils of the gallery habitat are often of higher fertility and have better drainage than the soils of the surrounding landscape with a more reliable water supply at depth. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |