|
History Of Greenland
The history of Greenland is a history of life under extreme Arctic conditions: currently, an ice sheet covers about eighty percent of the island, restricting human activity largely to the coasts. The first humans are thought to have arrived in Greenland around 2500 BCE. Their descendants most likely died out and were replaced and succeeded by several other human groups migrating from continental North America since then. There has been no evidence discovered that Greenland was known to Norsemen until the 9th century CE, when Norse Icelandic explorers settled on its southwestern coast. The ancestors of the Greenlandic Inuit who live there today appear to have migrated there later, around the year 1200, across the Nares Strait from northern Canada. While the Inuit survived in the icy world of the Little Ice Age, the early Norse settlements along the southwestern coast disappeared, leaving the Inuit as the only inhabitants of the island for several centuries. During this time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saqqaq Culture
The Saqqaq culture was a Paleo-Eskimo culture in southern Greenland. It was named after the settlement of Saqqaq, the site of many archaeological finds. The Saqqaq were the longest-residing residents of Greenland in all of history. Timeframe The earliest known archaeological culture in southern Greenland, the Saqqaq existed from around 2500 BCE until about 800 BCE.Saqqaq culture profile — from the Greenland Research Centre at the National Museum of Denmark. This culture coexisted with the Independence I culture of nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
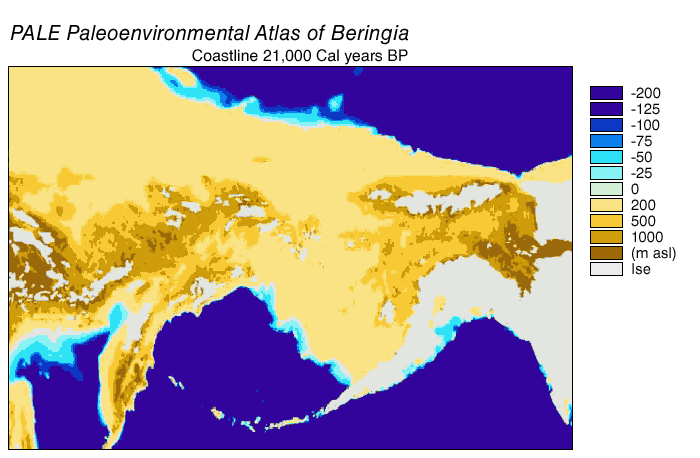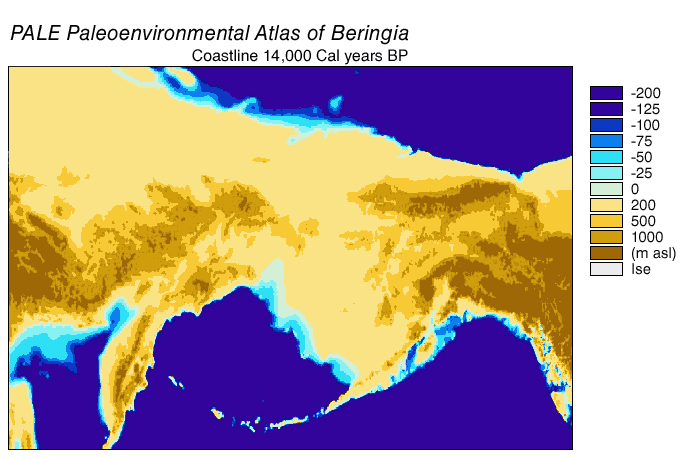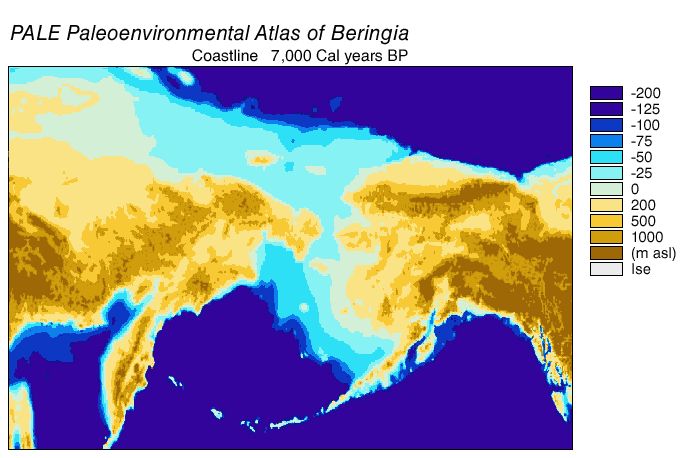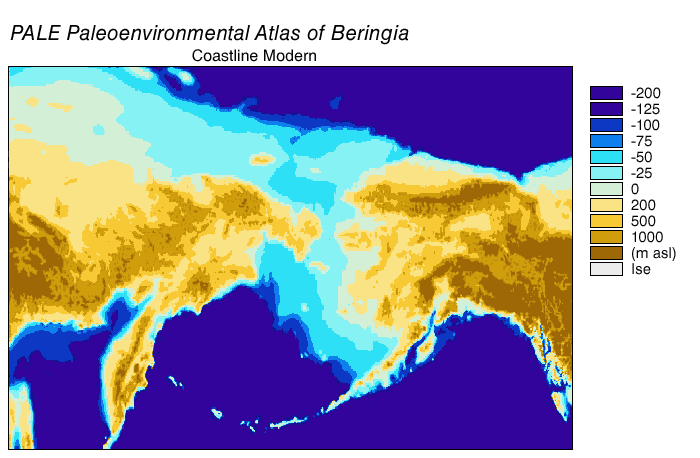
Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Peninsula, Chukchi and Kamchatka peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and Yukon in Canada. The area includes land lying on the North American Plate and Siberian land east of the Chersky Range. At various times, it formed a land bridge referred to as the Bering land bridge, that was up to wide at its greatest extent and which covered an area as large as British Columbia and Alberta together, totaling about , allowing biological dispersal to occur between Asia and North America. Today, the only land that is visible from the central part of the Bering land bridge are the Diomede Islands, the Pribilof Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paleo-Inuit
The Paleo-Eskimo meaning ''"old Eskimos"'', also known as, pre-Thule or pre-Inuit, were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka (e.g., Chertov Ovrag) in present-day Russia across North America to Greenland before the arrival of the modern Inuit (formerly called Eskimo) and related cultures. The first known Paleo-Eskimo cultures developed by 3900 to 3600 BCE, but were gradually displaced in most of the region, with the last one, the Dorset culture, disappearing around 1500 CE. Paleo-Eskimo groups included the Pre-Dorset; the Saqqaq culture of Greenland (2500–800 BCE); the Independence I and Independence II cultures of northeastern Canada and Greenland (c. 2400–1800 BCE and c. 800–1 BCE); the Groswater of Labrador, Nunavik, and Newfoundland and the Dorset culture (500 BCE – 1400 CE), which spread across Arctic North America. The Dorset was the last major "Paleo-Eskimo" culture in the Arctic before the migration east from present-day Alaska of the Thule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arctic Cultures 900-1500 (no Caption)
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway (Nordland, Troms, Finnmark, Svalbard and Jan Mayen), northernmost Sweden (Västerbotten, Norrbotten and Lapland (Sweden), Lappland), northern Finland (North Ostrobothnia, Kainuu and Lapland (Finland), Lappi), Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), the United States (Alaska), Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), and northern Iceland (Grímsey and Kolbeinsey), along with the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas. Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying cryosphere, snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost under the tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organisation created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisbon Treaty. aiming to foster economic integration among its member states. It was subsequently renamed the European Community (EC) upon becoming integrated into the Three pillars of the European Union, first pillar of the newly formed European Union (EU) in 1993. In the popular language, the singular ''European Community'' was sometimes inaccurately used in the wider sense of the plural ''European Communities'', in spite of the latter designation covering all the three constituent entities of the first pillar. The EEC was also known as the European Common Market (ECM) in the English-speaking countries, and sometimes referred to as the European Community even before it was officially renamed as such in 1993. In 2009, the EC formally ceased to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Home Rule
Home rule is the government of a colony, dependent country, or region by its own citizens. It is thus the power of a part (administrative division) of a state or an external dependent country to exercise such of the state's powers of governance within its own administrative area that have been decentralized to it by the central government. Home rule may govern in an autonomous administrative division; in contrast, though, there is no sovereignty separate from that of the parent state, and thus no separate chief military command nor separate foreign policy and diplomacy. In the British Isles, it traditionally referred to self-government, devolution or independence of the countries of the United Kingdom—initially Ireland, and later Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. In the United States and other countries organised as federations of states, the term usually refers to the process and mechanisms of self-government as exercised by municipalities, counties, or other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland in the north Atlantic Ocean.* * * Metropolitan Denmark, also called "continental Denmark" or "Denmark proper", consists of the northern Jutland peninsula and an archipelago of 406 islands. It is the southernmost of the Scandinavian countries, lying southwest of Sweden, south of Norway, and north of Germany, with which it shares a short border. Denmark proper is situated between the North Sea to the west and the Baltic Sea to the east.The island of Bornholm is offset to the east of the rest of the country, in the Baltic Sea. The Kingdom of Denmark, including the Faroe Islands and Greenland, has roughly List of islands of Denmark, 1,400 islands greater than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |