|
History Of Chinese
In historical linguistics, the history of the Chinese language includes the various changes over time of the Chinese language in its various incarnations. Earliest known origins of the Chinese language date back 6,000 years. Modern day characters had not been introduced until centuries later, leaving many components of Chinese language quite obscure and unknown. Sino-Tibetan ancestry Chinese is part of the Sino-Tibetan language family, a group of languages that all descend from Proto-Sino-Tibetan. The relationship between Chinese and other Sino-Tibetan languages is an area of active research and controversy, as is the attempt to reconstruct Proto-Sino-Tibetan. The main difficulty in both of these efforts is that, while there is very good documentation that allows for the reconstruction of the ancient sounds of Chinese, there is no written documentation of the point where Chinese split from the rest of the Sino-Tibetan languages. This is actually a common problem in historical l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Linguistics
Historical linguistics, also termed diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of language change over time. Principal concerns of historical linguistics include: # to describe and account for observed changes in particular languages # to reconstruct the pre-history of languages and to determine their relatedness, grouping them into language families ( comparative linguistics) # to develop general theories about how and why language changes # to describe the history of speech communities # to study the history of words, i.e. etymology Historical linguistics is founded on the Uniformitarian Principle, which is defined by linguist Donald Ringe as: History and development Western modern historical linguistics dates from the late-18th century. It grew out of the earlier discipline of philology, the study of ancient texts and documents dating back to antiquity. At first, historical linguistics served as the cornerstone of comparative linguistics, primarily as a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and laying the foundations for the much longer lasting Tang dynasty. Founded by Emperor Wen of Sui, the Sui dynasty capital was Chang'an (which was renamed Daxing, modern Xi'an, Shaanxi) from 581–605 and later Luoyang (605–18). Emperors Wen and his successor Yang undertook various centralized reforms, most notably the equal-field system, intended to reduce economic inequality and improve agricultural productivity; the institution of the Five Departments and Six Board (五省六曹 or 五省六部) system, which is a predecessor of Three Departments and Six Ministries system; and the standardization and re-unification of the coinage. They also spread and encouraged Buddhism throughout the empire. By the middle of the dynasty, the newly unifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standardized form of Mandarin Chinese that was first developed during the Republican Era (1912‒1949). It is designated as the official language of mainland China and a major language in the United Nations, Singapore, and Taiwan. It is largely based on the Beijing dialect. Standard Chinese is a pluricentric language with local standards in mainland China, Taiwan and Singapore that mainly differ in their lexicon. Hong Kong written Chinese, used for formal written communication in Hong Kong and Macau, is a form of Standard Chinese that is read aloud with the Cantonese reading of characters. Like other Sinitic languages, Standard Chinese is a tonal language with topic-prominent organization and subject–verb–object (SVO) word order. Compared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varieties Of Chinese
Chinese, also known as Sinitic, is a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family consisting of hundreds of local varieties, many of which are not mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the more mountainous southeast of mainland China. The varieties are typically classified into several groups: Mandarin, Wu, Min, Xiang, Gan, Hakka and Yue, though some varieties remain unclassified. These groups are neither clades nor individual languages defined by mutual intelligibility, but reflect common phonological developments from Middle Chinese. Chinese varieties differ most in their phonology, and to a lesser extent in vocabulary and syntax. Southern varieties tend to have fewer initial consonants than northern and central varieties, but more often preserve the Middle Chinese final consonants. All have phonemic tones, with northern varieties tending to have fewer distinctions than southern ones. Many have tone sandhi, with the most complex patterns in the coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthoepy
Orthoepy is the study of pronunciation of a particular language, within a specific oral tradition. The term is from the Greek ὀρθοέπεια, from ὀρθός ''orthos'' ("correct") and ἔπος ''epos'' ("speech"). The antonym is '' cacoepy'' "bad or wrong pronunciation". The pronunciation of the word ''orthoepy'' itself varies widely; the OED recognizes the variants , , , and for British English, as well as for American English. The pronunciation is sometimes clarified with a diaeresis: ''orthoëpy'', such as in the title of Edward Barrett Warman's ''Warman's Practical Orthoëpy and Critique'', published in 1888 and found in Google Books. Warman states on page 5: "Words possess three special characteristics: They have their Eye-life - Orthography; Ear-life - Orthoëpy; Soul-life - Significance." As with Warman's book, the purpose of this article is "to deal exclusively with the ear-life, or orthoëpy. Overview In English grammar, orthoepy is the study of correct pronunc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers to the language or dialect of one's ethnic group rather than one's first language. The first language of a child is part of that child's personal, social and cultural identity. Another impact of the first language is that it brings about the reflection and learning of successful social patterns of acting and speaking. Research suggests that while a non-native speaker may develop fluency in a targeted language after about two years of immersion, it can take between five and seven years for that child to be on the same working level as their native speaking counterparts. On 17 November 1999, UNESCO designated 21 February as International Mother Language Day. Definitions One of the more widely accepted definitions of native spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, autonomous regions of Guangxi, and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet as well as Southeast Asian countries: Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the northwest and low elevations in the southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys by as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west. In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the ancient states of Ba and Shu. Their conquest by Qin strengthened it and paved the way for Qin Shi Huang's unification of China under the Qin dynasty. During the Three Kingdoms era, Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
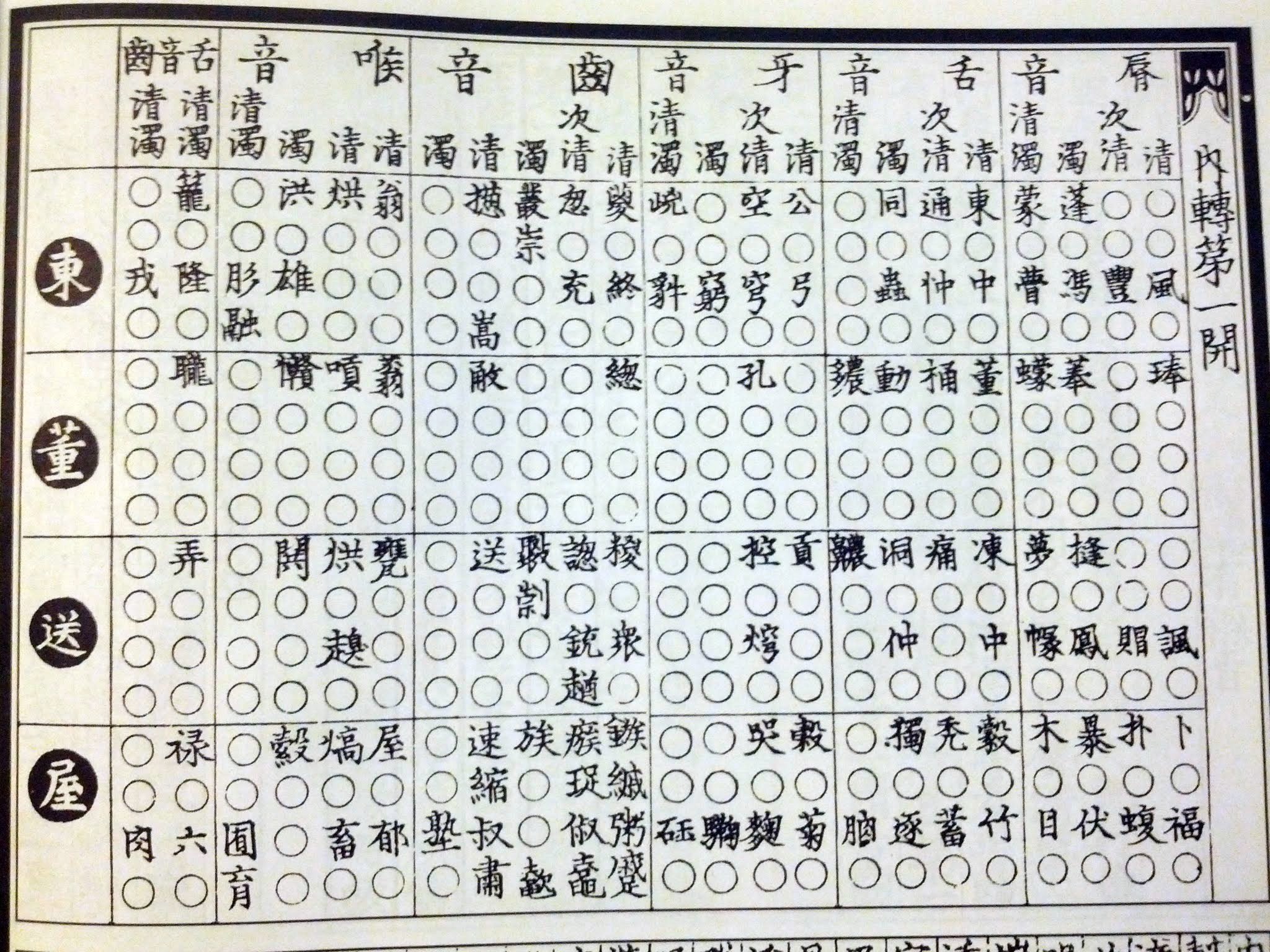
Yunjing
The ''Yunjing'' () is one of the two oldest existing examples of a Chinese rhyme table – a series of charts which arrange Chinese characters in large tables according to their tone and syllable structures to indicate their proper pronunciations. Current versions of the ''Yunjing'' date to AD 1161 and 1203 editions published by Zhang Linzhi (張麟之). The original author(s) and date of composition of the ''Yunjing'' are unknown. Some of its elements, such as certain choices in its ordering, reflect features particular to the Tang dynasty, but no conclusive proof of an actual date of composition has yet been found. The ''Yunjing'' contains 43 tables (), each of which tabulates combinations of a particular final rhyme (listed in rows) with various initials (listed in columns), in up to four tones, to show in a grid pattern all possible syllables. Empty circles on the grid denote that the author(s) were unaware of any word with that particular pronunciation. By locating a char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rime Table
A rime table or rhyme table () is a Chinese phonological model, tabulating the syllables of the series of rime dictionaries beginning with the ''Qieyun'' (601) by their onsets, rhyme groups, tones and other properties. The method gave a significantly more precise and systematic account of the sounds of those dictionaries than the previously used analysis, but many of its details remain obscure. The phonological system that is implicit in the rime dictionaries and analysed in the rime tables is known as Middle Chinese, and is the traditional starting point for efforts to recover the sounds of early forms of Chinese. Some authors distinguish the two layers as Early and Late Middle Chinese respectively. The earliest rime tables are associated with Chinese Buddhist monks, who are believed to have been inspired by the Sanskrit syllable charts in the Siddham script they used to study the language. The oldest extant rime tables are the 12th-century ''Yunjing'' ("mirror of rhymes") an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangyun
The ''Guangyun'' (''Kuang-yun''; ) is a Chinese rime dictionary that was compiled from 1007 to 1008 under the patronage of Emperor Zhenzong of Song. Its full name was ''Dà Sòng chóngxiū guǎngyùn'' (, literally "Great Song revised and expanded rhymes"). Chen Pengnian (, 961–1017) and Qiu Yong () were the chief editors. The dictionary is a revision and expansion of the influential '' Qieyun'' rime dictionary of 601, and was itself later revised as the ''Jiyun''. ''Pingshui Yun'' system, the standard for poetry rhyming after the Song Dynasty, is also based on ''Guangyun''. Until the discovery of an almost complete early 8th century edition of the ''Qieyun'' in 1947, the ''Guangyun'' was the most accurate available account of the ''Qieyun'' phonology, and was heavily used in early work on the reconstruction of Middle Chinese. It is still used as a major source. The ''Guangyun'' has a similar hierarchical organization to the ''Qieyun'': * The dictionary is split into four ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rime Dictionary
A rime dictionary, rhyme dictionary, or rime book () is an ancient type of Chinese dictionary that collates Chinese character, characters by tone (linguistics), tone and rhyme, instead of by radical (Chinese character), radical. The most important rime dictionary tradition began with the ''Qieyun'' (601), which codified correct pronunciations for reading the classics and writing poetry by combining the reading traditions of north and south China. This work became very popular during the Tang dynasty, and went through a series of revisions and expansions, of which the most famous is the ''Guangyun'' (1007–1008). These dictionaries specify the pronunciations of characters using the ''fanqie, fǎnqiè'' method, giving a pair of characters indicating the syllable onset, onset and remainder of the syllable respectively. The later rime tables gave a significantly more precise and systematic account of the sounds of these dictionaries by tabulating syllables by their onsets, rhyme g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |